Exploring Human Origins: Evolution and Phylogenetic Trees
Delve into the fascinating realm of human origins through an examination of humans and African apes, evidence for evolution, and the construction of phylogenetic trees. Understand the relationships between species, common ancestors, and key evolutionary developments that have shaped the course of human evolution. Explore topics such as primates, cranial capacity, body proportions, and the significance of Australopithecus in our evolutionary history.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ASSET TUTORING REVISION 2020 HUMAN ORIGINS 1: Humans and African Apes, Evidence for Evolution, Phylogenetic trees For each section please read the exam guidelines first before going on to the content. Learn all the content in this presentation
Humans as primates along with many African apes Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Order Primates Genus Homo Species sapiens
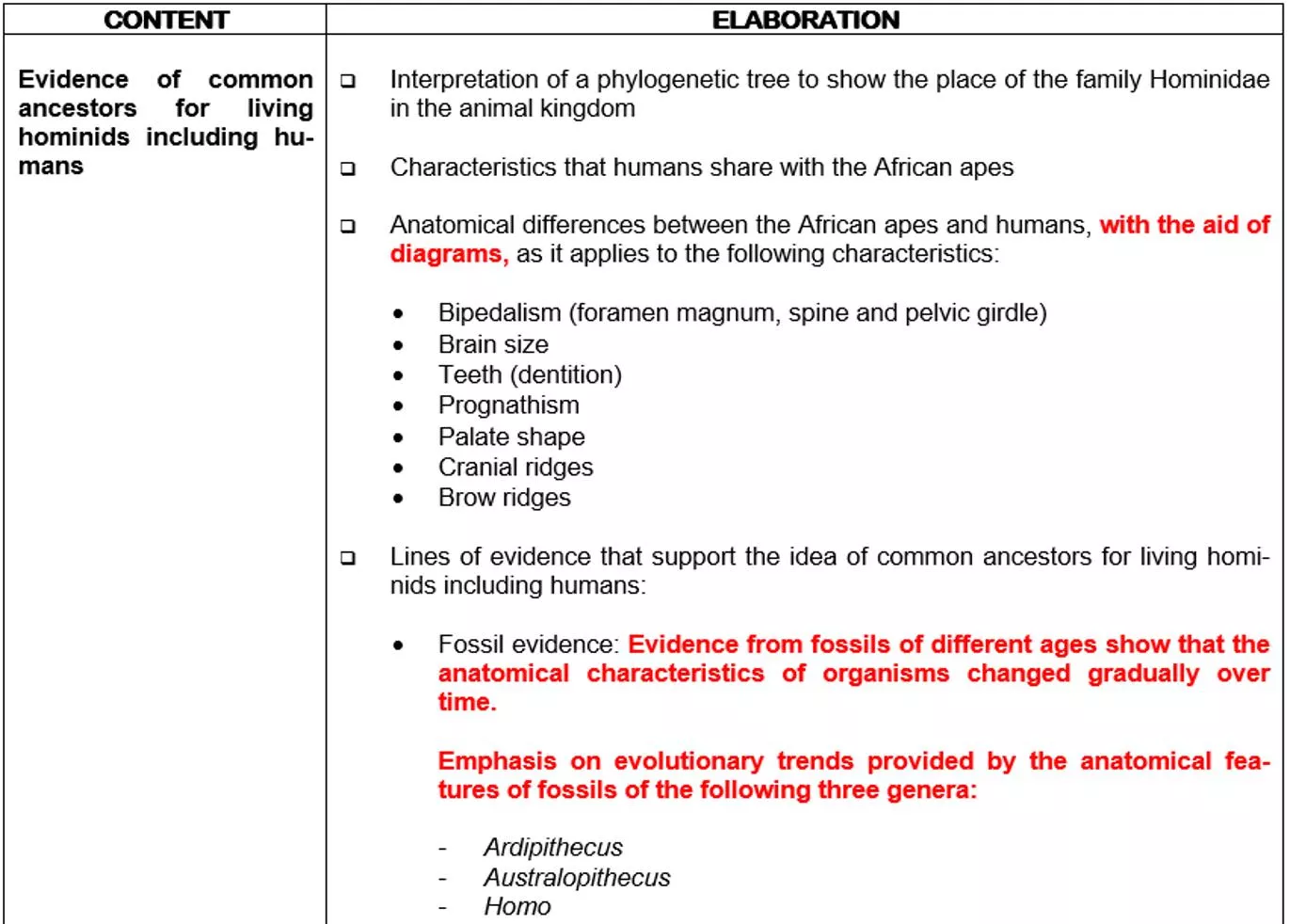
Phylogenetic trees a reminder Show relationships between genera or species Must show a geological timeline. Must show when different groups branched off from other groups in terms of geological time. Evidence that is used to make a phylogenetic tree is usually fossil evidence ie fossils that have been dated. Usually the oldest organisms or ancestors are at the bottom of the tree
Evidence of common ancestors for living hominids including humans Interpretation of a phylogenetic tree to show the place of the family Hominidae in the animal kingdom
What is a phylogenetic tree? What does every phylogenetic tree show? Look at the phylogenetic tree that shows the place of the family Hominidae in the animal kingdom and answer the following questions: 1. Who is the most closely related organism to humans? Give evidence from the phylogenetic tree. (2) 2. When did the gorilla s branch off from the humans and chimpanzees common ancestor? (2) 3. Using evidence from the phylogenetic tree, can anyone say that humans are descended from chimpanzees? (3)
Humans, Hominins and African Apes: A big change in body proportions: from the long arms and short legs of apes to the short arms and long legs of humans Mixed treeand ground Tree-dweller Ground Ground Ground
?What about AUSTRALOPITHECUS?
The Dental Arcade Looking at the palate, or roof of the mouth and the teeth (dentition) ANGULAR INTERMEDIATE cheek teeth parallel curved, not angular 2-1-2-3 PARABOLIC curved 2-1-2-3 2-1-2-3 Incisors Gap (diastema) between incisors and canine Intermediate No diastema Canine does not project Canine does not project Canine (projects beyond level of other teeth) Cheek teeth (premolars and molars)
Comparison of hands Chimpanzee Human A. sediba
Characteristics that humans and African apes share They have a large brain They have eyes in front of their head They have freely rotating arms They have long upper arms with rotation around the elbow joints They have bare fingertips or nails instead of claws They have opposable thumbs
Anatomical differences between African apes and humans as it applies to the following characteristics Characteristic African apes Anatomical differences between the African apes and humans, with the aid of diagrams, as it applies to the following characteristics: Humans forward position under the centre of the skull More curved S shaped spine Bipedalism foramen magnum in a backward position less curved C shaped spine Bipedalism spine Bipedalism pelvic girdle Long narrow pelvis Small brain present/smaller cranial capacity Short wide pelvis larger brain present/larger cranial capacity Brain size (cranial capacity) large canines present, gap present between canines and incisors large jaw, more prognathous Teeth (dentition) small canines, no gaps between the teeth smaller jaws, not prognathous Prognathism long and rectangular, sometimes described as a U shape cranial ridge visible above cranium Well developed/protrudes out of skull Small and curved, sometimes described as a C shape Palate shape Cranial ridges No cranial ridge Brow ridges Not well developed
Lines of evidence that support the idea of common ancestors for living hominids including humans Fossil evidence: Evidence from fossils of different ages show that the anatomical characteristics of organisms changed gradually over time. Genetic evidence: Mitochondrial DNA tracking MtDNA back through female ancestors Cultural evidence: Tool-making. Looking at more recent aspects of humans as social animals eg tools and grave goods
Fossil evidence see slides on our hominid ancestors
Cultural Evidence Stone age tools used as weapons, jewelry and in agriculture as well as rock paintings are evidence for evolution. Oldest tools found in Africa 20 000-year-old burial from Italy (Homo sapiens). This teenage boy was buried with grave-goods (ivory necklace and bone ornaments), indicating a burial ritual

 undefined
undefined