Basics of Biology: Introduction, Branches, and Importance
Biology, the study of living organisms, encompasses various branches such as botany, zoology, morphology, and genetics. Understanding biology is crucial for solving environmental issues, conserving natural resources, and pursuing careers in diverse fields like medicine and agriculture. Living organisms exhibit characteristics such as cellular organization, metabolism, and adaptation to their environment, making biology a fascinating and essential field of study.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter Objectives By the end of the chapter, the student should be able to: Define Biology. Describe the branches of Biology. Explain the importance of biology in our daily life. Outline the characteristics of living things.
What is Biology? Biology is a word that is derived from two Greek words bios and logos. Bios mean life while logos mean knowledge. Biology is the branch of science that deals with the study of living things. The aim of biology is to explain the living world in terms of scientific principles. Living things interact with non-living things in their physical environment
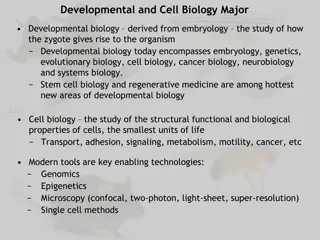
Branches of Biology Biology is a large body of knowledge that is divided into two main branches namely: Botany and Zoology, Botany is the study of plants while zoology is the study of animals. These branches of biology are still wide and complex. Therefore, at more advanced and specialised levels.
Branches of Biology There are smaller branches of biology that exist. Examples are: Morphology: the study of form and shape Anatomy: the study of internal structure Cytology: the study of cells Histology: the study of tissue. Embryology: the study of development Physiology: the study of functions Taxonomy: the study of classification, identification and naming of living organisms. Ecology: the study of living things in their surrounding Genetics: the study of inheritance and variation. Parasitology: the study of parasites. Entomology: the study of insects Pathology: the study of diseases
Importance of Biology In studying biology, one acquires very useful knowledge that can be used in many ways. Some of these are listed below: 1) In solving environmental problems such as shortage of food, poor health services, pollution, misuse of environmental resources 2) Conservation of natural resources: The knowledge of biology has made us aware of that deforestation; 3) Entry into careers: such as medicine, agriculture, public health, veterinary practice, animal husbandry, horticulture and dentistry. 4) To study ourselves better: in biology we learn what our body and other living organisms are made up of and how their bodies are work.
Characteristics of Living Things The following are the major characteristics of living things: 1. Cellular organization: Living organisms are made up of small units called cells. 2. Nutrition is a process by which living things acquire and utilise nutrients. 3. Metabolism: Is a chemical change taking place inside living body. 4. Respiration is the energy producing process that occurs in all cells of living things. 5. Excretion is the process by which waste or harmful materials, resulting from chemical reactions within cells of living things, are eliminated. 6. Growth and Development: Growth is an irreversible increase in size and mass. On the other hand, development refers to the irreversible change in the complexity of the structure of living things. 7. Reproduction is the process by which living things give rise to new individuals of the same kind.
Review Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Define Biology. Differentiate the two branches of biology. What is the main aim of biology? Differentiate Anatomy and physiology. Why do we study biology? Living organisms are made up of small units called what? What is the difference between growth and development? 7.