Understanding Animal Tissues: Epithelial, Muscle, Nerve, and Connective Tissues
Explore the four general categories of animal tissue - epithelial, muscle, nerve, and connective tissues. Learn about the traits, classification, examples, and functions of each type of tissue. From the tightly packed cells of epithelial tissue to the excitable nature of muscle tissue, delve into the fascinating world of animal tissues.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
I. Generalizations A. Definition B. Four general categories of animal tissue 1. epithelial 2. muscle 3. nerve 4. connective
II. Epithelial tissue A. General Traits or characteristics 1. found on a body surface either internal or external 2. tightly packed cells 3. free border or free surface 4. rest on a basement membrane 5. nonvascular
B. Naming or classifying epithelial tissue 1. First Name a. Simple b. Stratified c. Pseudostratified 2. Second name a. Cuboidal b. Squamous c. Columnar
C. Examples of naming 1. simple cuboidal 2. stratified squamous 3. pseudostratified 4. stratified cuboidal
D. Specific examples 1. stratified squamous a. Location b. function
Examples continued 2. transitional a. Location b. Function
Examples continued 3. simple cuboidal a. Location b. function
III. Muscle tissue A. General traits 1. excitable tissue 2. can shorten
B. Types of muscle tissue 1. skeletal muscle a. multinucleate b. voluntary c. striated
2. Smooth muscle a. Involuntary b. Visceral c. structure
3. Cardiac muscle-mixture of two a. One nucleus/cell b. Autorythmic c. Striated d. Intercalated disc http://t0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcTZWokQrZ1xjxs0DLtiU5qzRGl8vgUsDUHY6fpqWvpROiXpwHK32JedkkI8
IV. Nervous tissue A. General Traits 1. Irritable 2. Conductive
B. Two cell types 1. neurons a. Cell body b. Axon c. Dendrite 2. Glia cells (caretakers)
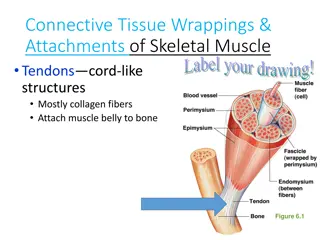
V. Connective Tissues A. Common traits 1. possess fibers 2. widely scattered cells 3. ground tissue (matrix) 4. analogy
VI. Membranes A. Cutaneous B. Mucous 1. contain glands 2. open to outside C. Serous 1. occur in paired sheets 2. don t open to outside 3. no glandular tissue