Analysis of Categorical Data at Marada Inn and Pelican Stores
The analysis includes rating frequencies and relative frequencies for quality ratings at Marada Inn, as well as customer transaction data at Pelican Stores during a promotion. Graphs and tables summarize qualitative variables for evaluation and managerial reporting.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
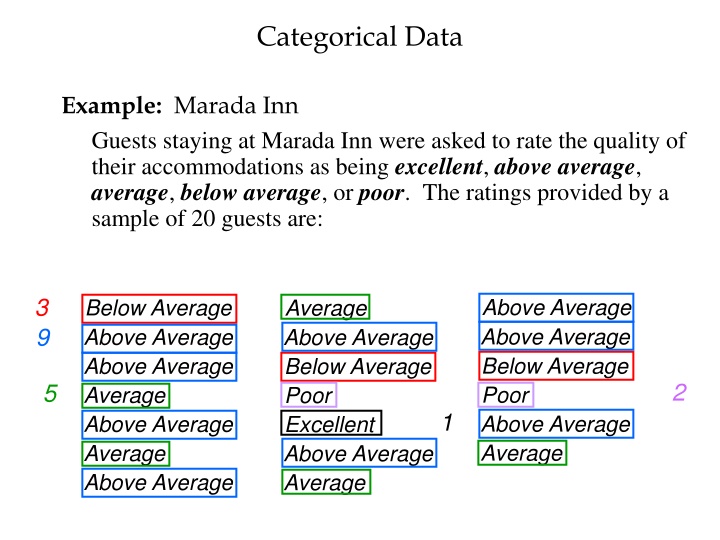
Categorical Data Example: Marada Inn Guests staying at Marada Inn were asked to rate the quality of their accommodations as being excellent, above average, average, below average, or poor. The ratings provided by a sample of 20 guests are: 3 9 Above Average Above Average Below Average Poor Above Average Average Below Average Above Average Above Average Average Above Average Average Above Average Average Above Average Below Average Poor Excellent Above Average Average 2 5 1
Categorical Data Example: Marada Inn Rating Frequency 2 3 5 9 Poor Below Average Average Above Average Excellent 1 Total 20
Categorical Data Example: Marada Inn Relative Frequency .10 .15 .25 .45 Percent Frequency Rating Frequency 10 Poor Below Average Average Above Average Excellent 2 3 5 9 15 25 45 5 100 1 .05 1.00 Total 20
Categorical Data Marada Inn Quality Ratings 10 9 8 7 Frequency 6 5 4 3 2 1 Rating Average Above Below Average Excellent Poor Average
Categorical Data Marada InnQuality Ratings Excellent 5% Poor 10% Below Average 15% Above Average 45% Average 25%
Pelican Stores Pelican Stores is chain of women s apparel stores. It recently ran a promotion in which discount coupons were set to customers of other National Clothing stores. Data collected for a sample of 100 in-store credit card transactions at Pelican Stores during one day while the promotion was running are shown in Table 2.18. Customers who made a purchase using a discount coupon are referred to as promotional customers and customers who made a purchase but did not use a discount coupon are referred to as regular customers. Because the promotional coupons were not set to regular Pelican Stores customers, management considers the sales made to people presenting the promotional coupons as sales it would not otherwise make. purchased 2 items, Customer 5 which cost her $54
Pelican Stores Pelican Stores is chain of women s apparel stores. It recently ran a promotion in which discount coupons were set to customers of other National Clothing stores. Data collected for a sample of 100 in-store credit card transactions at Pelican Stores during one day while the promotion was running are shown in Table 2.18. Customers who made a purchase using a discount coupon are referred to as promotional customers and customers who made a purchase but did not use a discount coupon are referred to as regular customers. Because the promotional coupons were not set to regular Pelican Stores customers, management considers the sales made to people presenting the promotional coupons as sales it would not otherwise make. Pelican s management would like to use this sample data to learn about its customer base and to evaluate the promotion involving discounts. Managerial Report 1.Using graphs and tables, summarize the qualitative variables. data_pelican.xls
Quantitative Data Example: Hudson Auto Repair The manager of Hudson Auto would like to have better understanding of the cost of parts used in the engine tune- ups performed in the shop. She examines 50 customer invoices for tune-ups. The costs of parts, rounded to the nearest dollar. 91 71 104 85 62 78 69 74 97 82 93 72 62 88 98 57 89 68 68 101 75 66 97 83 79 52 75 105 68 105 99 79 77 71 79 80 75 65 69 69 97 72 80 67 62 62 76 109 74 73
Quantitative Data Example: Hudson Auto Repair minimum 52 68 74 79 97 57 68 74 80 97 62 69 75 80 97 62 69 75 82 98 62 69 75 83 99 62 71 76 85 101 104 105 105 109 65 71 77 88 66 72 78 89 67 72 79 91 68 73 79 93 maximum
Quantitative Data Frequency Cost ($) 2 50-59 60-69 70-79 80-89 90-99 100-109 13 16 7 7 5 52 68 74 79 97 57 68 74 80 97 62 69 75 80 97 62 69 75 82 98 62 69 75 83 99 62 71 76 85 101 104 105 105 109 65 71 77 88 66 72 78 89 67 72 79 91 68 73 79 93
Quantitative Data Percent Freq Relative Freq Frequency 2 Cost ($) 2/50 .04 13/50 16/50 7/50 7/50 5/50 .10 4 50-59 60-69 70-79 80-89 90-99 100-109 26 32 14 14 .26 .32 .14 .14 13 16 7 7 10 5 100 50 1.00
Quantitative Data Tune-up Parts Cost 18 16 14 12 Frequency 10 8 6 4 2 Parts Cost ($) 50 60 70 80 90 100 110
Quantitative Data Symmetric Moderately Skewed Left Highly Skewed Right
Quantitative Data Ogive for Hudson Auto Repair Parts Cost ($) Parts Cumulative Frequency 2 15 31 38 45 50 Frequency Cost ($) 2 50-59 60-69 70-79 80-89 90-99 100-109 < 60 < 70 < 80 < 90 < 100 < 110 13 16 7 7 5 50
Quantitative Data Ogive for Hudson Auto Repair Cumulative Relative Frequency .04 .30 .62 .76 .90 Cumulative Percent Frequency Cumulative Frequency 2 15 31 38 45 50 Cost ($) < 60 < 70 < 80 < 90 < 100 < 110 4 30 62 76 90 100 1.00
Quantitative Data Example: Hudson Auto Repair ($110, 100%) Tune-up Parts Cost 100 Cumulative Percent Frequency ($100, 90%) 80 60 ($90, 76%) ($50, 0%) 40 ($80, 62%) ($70, 30%) 20 Parts Cost ($) 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 ($60, 4%)
Pelican Stores -- continued Pelican Stores is chain of women s apparel stores. It recently ran a promotion in which discount coupons were set to customers of other National Clothing stores. Data collected for a sample of 100 in-store credit card transactions at Pelican Stores during one day while the promotion was running are shown in Table 2.18. Customers who made a purchase using a discount coupon are referred to as promotional customers and customers who made a purchase but did not use a discount coupon are referred to as regular customers. Because the promotional coupons were not set to regular Pelican Stores customers, management considers the sales made to people presenting the promotional coupons as sales it would not otherwise make. Pelican s management would like to use this sample data to learn about its customer base and to evaluate the promotion involving discounts. Managerial Report 1.Using graphs and tables, summarize the qualitative variables. 2.Using graphs and tables, summarize the quantitative variables. data_pelican.xls
Summarizing Two variables Home Style Price Range Total Colonial Log Split A-Frame < $99,000 > $99,000 18 6 19 12 12 14 16 3 55 45 100 Total 30 20 35 15 Example: Finger Lakes Homes.xls qualitative variable Quantitative variable
Summarizing Two variables Home Style Price Range Total Colonial Log Split A-Frame < $99,000 > $99,000 18 6 19 12 12 14 16 3 55 45 100 Total 30 20 35 15 Example: Finger Lakes Homes.xls
Summarizing Two variables Home Style Price Range Total Colonial Log Split A-Frame < $99,000 > $99,000 18 6 19 12 12 14 16 3 55 45 100 Total 30 20 35 15 Price Range Home Style Total Colonial Log Split A-Frame 1.0000 1.0000 0.3273 0.2667 0.1091 0.3455 0.2182 0.3111 0.3556 0.0667 < $99,000 > $99,000
Summarizing Two variables Home Style Price Range Colonial Log Split A-Frame < $99,000 > $99,000 18 6 19 12 12 14 16 3 Total 30 20 35 15 Price Range Home Style Colonial Log Split A-Frame 0.6000 0.4000 0.30 0.70 0.5429 0.4571 0.8000 0.2000 < $99,000 > $99,000 Total 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000
Summarizing Two variables The crosstabulation for the aggregated UC-Berkley data is Admitted 3738 1494 5232 Denied 4704 2827 7531 Total 8442 4321 12763 Male Female Total Male acceptance rate is higher when data is aggregated. Dividing all of the frequencies above by the number of observations yields what the joint probability table below Admitted 0.2929 0.1171 0.4099 Denied 0.3686 0.2215 0.5901 Total 0.6614 0.3386 1.0000 Male Female Total
Summarizing Two variables Female Male Admitted 89 17 106 Denied 19 8 27 Total 108 25 133 Admitted 512 313 825 Denied 313 207 520 Total 825 520 1345 A B A B Total Total Compute the row percentages to show the Simpson s Paradox Female Male Admitted 0.8241 0.6800 Denied 0.1759 0.3200 Total 1.0000 1.0000 Admitted 0.6206 0.6019 Denied 0.3794 0.3981 Total 1.0000 1.0000 A B A B data_simpson.xls
Summarizing Two variables A Negative Relationship y QBigMacs 21 2 x PBigMacs 5.00 0.50
Summarizing Two variables No Apparent Relationship y QNoseHairTrimmers xPBigMacs
Summarizing Two variables Example: Panthers Football Team The Panthers football team is interested in investigating the relationship, if any, between interceptions made and points scored. x = Number of Interceptions y = Number of Points Scored 1 3 2 1 3 14 24 18 17 30
Summarizing Two variables y 35 Number of Points Scored 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 x 1 0 2 3 4 Number of Interceptions
Pelican Stores -- continued Pelican Stores is chain of women s apparel stores. It recently ran a promotion in which discount coupons were set to customers of other National Clothing stores. Data collected for a sample of 100 in-store credit card transactions at Pelican Stores during one day while the promotion was running are shown in Table 2.18. Customers who made a purchase using a discount coupon are referred to as promotional customers and customers who made a purchase but did not use a discount coupon are referred to as regular customers. Because the promotional coupons were not set to regular Pelican Stores customers, management considers the sales made to people presenting the promotional coupons as sales it would not otherwise make. Pelican s management would like to use this sample data to learn about its customer base and to evaluate the promotion involving discounts. Managerial Report 1.Using graphs and tables, summarize the qualitative variables. 2.Using graphs and tables, summarize the quantitative variables. 3.Using pivot tables and scatter plots, summarize the variables. data_pelican.xls