Understanding Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease
Dementia and Alzheimer's disease are neurocognitive disorders that impact a person's memory, cognitive functions, and social abilities. Alzheimer's is the most common form of dementia and is characterized by the presence of plaques and tangles in the brain. Symptoms of dementia include cognitive changes, memory loss, difficulty communicating, personality changes, and more. The progression of dementia is typically classified into three stages: early/mild, middle/moderate, and late/advanced. Assessments and interventions are available to help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
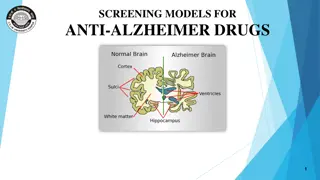
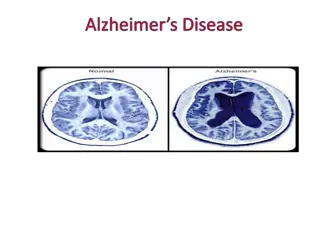
Dementia vs. Alzheimer disease? Dementia describes a group of symptoms which affects a person s thinking, judgment, and social abilities Alzheimer disease Most Common form of dementia Plaques and tangles in their brain causing damage to healthy neurons and the fibers connecting them
Symptoms of Dementia Cognitive changes Memory loss Difficulty communicating or findings words Personality changes Depression Anxiety Agitation Hallucinations
Dementia in the 3 Stage Model: Stage 1 Early/Mild dementia Sometimes this phased is missed because it is often associated with old age. This person may begin to: Lost interest in hobbies and activities, have difficulty handling money, more forgetful of recent events, more irritable
Dementia in the 3 Stage Model: Stage 2 Middle/moderate dementia Problems start becoming more noticeable This person may begin to Confused regarding time and place, become lost in familiar places, forgetful of more recent events, behave inappropriately (wearing winter clothes during a hot day), see or hear things that re not there
Dementia in the 3 Stage Model: Stage 3 Late/Advanced/End stage: The person is severely disabled and needs total care This person may: Unable to remember events that happened a few minutes before, lose their ability to understand or use speech, needs help with eating, washing, bathing, uncontrolled movements, bedridden.
Assessments ACL (6 levels) Assessment of Motor and Process Skills (AMPS) Rivermead perceptual assessment Rivermead behavioral memory test
Interventions Environmental change Create a safe environment Prevent falls, avoid scatter rugs, extension cords, or any clutter Create a calm environment Remove clutter or stressors, no background distraction Monitor personal comfort Make sure room temp. is comfortable, also monitor skin irritation (pressure sores) Provide security object Favorite blanket, book, or anything comfortable that they are familiar with Provide opportunities for exercise Wandering is sometimes caused by the need to move
Question 1 A patient with Alzheimer's disease is being cared for at home by the spouse and requires minimal supervision with ADL. The patient is cooperative but wanders around the house repeatedly asking, "What should I do?" The best OT intervention for this problem is to: A.)Assist the spouse in developing a routine of home activities for the patient. B.)Instruct the patient in the use of a diary to help with memory deficits. C.)Provide the patient with a structured craft activity. D.)Develop a short-term behavioral reinforcement program.
Question 2 A patient who has Alzheimer s disease is aware of his own and other s movements and completes simple gross motor actions when asked. When instructing caregivers about dressing activities, the OTR should explain that the patient can be expected to: A.)be unable to assist in any way B.)self-dress independently when provided with setup C.)assist the caregiver by moving body parts when asked D.)self-dress at bedtime
Question 3 A patient with Alzheimer s disease becomes restless and agitated and begins to swear during an OT group activity. The OTR should first: A.)remove the patient from the group and provide reality orientation B.)assess environmental stimuli and ensure group safety C.)assess the group s response to the patient s behavior D.)ignore the patient s behavior and continue the session
Question 4 A patient who has Alzheimer's disease has attained maximum benefit from OT services and will be discharged. The case manager suggests that discharge be delayed by 2 weeks because third- party reimbursement will cover another 14 days of treatment. In this situation, the OTR's next action would be to: A.) discuss the issue with the patient's family B.)reevaluate the patient and set new goals C.)concur with the case manager's suggestion D.)discharge the patient from therapy
Question 5 An OTR in a home health agency is developing an education and support group for family members caring for relatives who have Alzheimer's disease. In order to conduct a needs assessment to establish the relevance of the group, the OTR would: A.) complete a literature search to identify the typical issues addressed in caregiver support groups B.)interview family members of newly diagnosed clients through referral by local physicians C.)conduct focus groups of nurses and therapists in the home health agency to identify caregivers' needs D.)conduct a survey of caregivers in the local community to identify their chief concerns
Question 6 An OTR is providing consultative services to a long-term care facility that is renovating the Alzheimer's care unit. The environmental adaptations that would best support the functional needs of this population are? A.) putting locks on all doors to prevent residents from wandering into other residents' rooms B.)placing maps of the area on walls throughout the hallways so that residents can re-orient themselves if they get lost C.)minimizing personal belongings to reduce clutter and the probability of losing valuable items D.)providing self-contained, safe indoor and outdoor spaces where residents can walk independently without risk
Question 7 While assessing a patient's bathing skills in the hospital shower room, the OTR notices that the grab bar has come loose from the wall. The OTR should first: A.) alert the patient to the hazard and avoid use of the grab bar B.)request that the bathroom be closed until the grab bar is repaired C.)notify other OT staff of the hazard D.)move to another location to complete the activity
Question 8 When providing caregiver training to the spouse of an individual diagnosed with early stage dementia, the OT will MOST likely need to instruct the caregiver in strategies to compensate for what deficits? A. Short-term memory. B. Fine and gross motor skills. C. Social skills. D. Dressing skills.
Question 9 An OT is working with an elderly patient with mild to moderate severity of Alzheimer disease who was admitted to the hospital after accidentally setting a kitchen fire. What is the MOST appropriate information to provide caregivers with after discharge regarding cooking? A. Recommend outpatient OT services to teach kitchen safety. B. Seek volunteer companion services for home supervision. C. Identify transportation services to bring the person to a community meal site. D. Refer to home-delivered meal services.
Question 10 During the cleanup portion of a cooking activity, an elderly woman with a diagnosis of depression and dementia begins to dry the plates and utensils she has already dried. What should the OT do NEXT? A. Tell the client that the same dishes and utensils are being redried. B. Put the dried dishes away and begin to hand her wet dishes. C. Suggest the client stop the activity because it seems too difficult. D. Ask the client to describe what she is doing.
Question 11 The OT is meeting with the family of an elderly individual who has just been diagnosed with early-stage dementia. The client has had three car accidents within the past 3 months and the family does not feel that continued driving would be safe. They report difficulties with repeatedly getting lost, parallel parking, and driving more slowly than is reasonably safe. Which of the following areas would be MOST important to assess when determining this individual s ability to drive safely? A. Cognition. B. Problem-solving. C. Interpersonal skills. D. Orientation.
Question 12 An OT working for an assisted living corporation needs to design programs to engage residents with dementia who wander and pace the halls throughout the day. What is the BEST type of movement-oriented programming to employ to engage these residents? A. Reminiscing about previous jobs. B. Walking as part of a walking club. C. Singing oldies in a group. D. Participating in a craft activity requiring concentration.
Question 13 An OT practitioner is planning a program to address the needs of persons with Alzheimer s disease, and their families, as part of a hospital outreach program. What area of intervention would be MOST beneficial to maintaining safety and supporting function at home for people in the moderate to severe stages of Alzheimer s disease? A. Strength and endurance activities. B. Cognitive rehabilitation techniques. C. Environmental modification. D. Assertiveness skills.
Question 14 The OT has been asked to identify strategies to reduce agitation in residents of an SNF with mid- to late-stage Alzheimer s disease. What are the MOST appropriate environmental modifications? A. Provide rocking chairs, music, dimmed light, and reduced clutter. B. Train caregivers in use of validation and reinforcement. C. Install monitoring devices such as door alarms, pressure gates, and video monitors. D. Institute mealtime positioning and adaptive feeding strategies.