Understanding Sound Waves and Human Hearing
Sound waves are longitudinal waves where particles move in the same direction. The human body hears sounds through vibrations reaching the cochlea, which produces electrical signals for the brain to interpret. Properties of sound waves include traveling through various mediums at different speeds. Frequency determines pitch, while amplitude affects volume. Echoes can help measure distances based on the speed of sound.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
LO: Explain the characteristics of a sound wave How does the human body hear sounds? Discuss with someone else, and be ready to share your thoughts
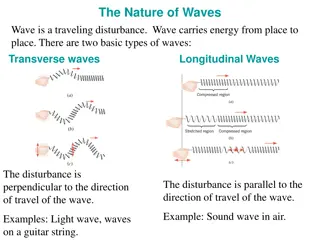
Sound waves are longitudinal waves Longitudinal wave: A wave in which the particles move in the same direction as the wave
Sound waves and hearing Sound waves cause the eardrum to vibrate These vibrations reach the cochlea The cochlea produces electrical signals which are sent to the brain The brain interprets these signals as sound BBC Image reproduced with kind permission of the BBC
Properties of sound waves Vibrations can travel through materials in any state Speed depends on the medium In air, sound travels at roughly 340m/s In fresh water, sound travels at roughly 1481m/s In general, the more particles to vibrate, the faster sound can travel Sound cannot travel in a vacuum, since there are no particles
Properties of sound waves The frequency is the number of waves each second High frequency = high pitch Low frequency = low pitch For each wave, describe the pitch and the volume. 10 minutes The amplitude is the height of a sound wave from its peak to its trough High amplitude = loud Low amplitude = quiet Use the words frequency and amplitude in your answers.
Sound and Echoes Sound waves can be reflected off surfaces. Some surfaces are better at reflecting sound than others. Where are you more likely to find an echo? How would you describe the surfaces in the places you tend to find echoes?
Sound and Echoes Because we know the speed of sound, we can use echoes to work out how far away something is. In the time taken between making a noise and hearing the echo, sound has travelled to an object and back again. Distance = speed x time So we multiply the speed of sound by the time taken to travel to the cliff and back. This gives the distance to the cliff and back. Divide this by two for the distance to the cliff Distance Time Speed
Sound and Echoes Distance = speed x time Speed = distance / time Time = distance / speed Use this to answer the questions on echoes 10 minutes Distance Time Speed
Further information For more information on U-boat war visit uboatproject.wales or peoplescollection.wales/users/29486