Government Structures and Mechanisms for Intersectoral Collaboration
Explore the role of government in Health in All Policies (HiAP) and whole-of-government approaches, including the varying implementation of HiAP in different contexts. Learn about common structures such as Cabinet committees, Parliamentary committees, Interdepartmental committees, and more, used for intersectoral action. Understand how these mechanisms influence agenda setting, policy formulation, and implementation stages to promote effective collaboration across sectors.
- Government structures
- Intersectoral collaboration
- HiAP
- Whole-of-government approaches
- Policy implementation
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
STRUCTURES AND MECHANISMS FOR INTERSECTORAL COLLABORATION 5 MODULE 5 PART 2 The role of government in HiAP/ Whole-of-government approaches
LEARNING OBJECTIVES 5 List and appraise different government structures and mechanisms for intersectoral action 1
HiAP IMPLEMENTATION VARIES IN DIFFERENT CONTEXTS 5 HiAP has been implemented differently in different contexts reflecting local social and political cultures as well as government structures. Nevertheless, it is possible to make some generalizations about the structures and mechanisms commonly used for intersectoral action.
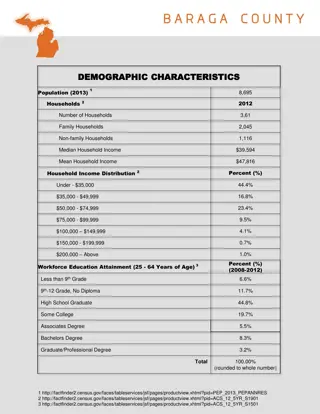
STRUCTURES AND MECHANISMS COMMONLY USED FOR INTERSECTORAL ACTION 5 Some of the most common government structures and mechanisms for intersectoral action include: 1 Cabinet committees and secretariats; 2 Parliamentary committees; Interdepartmental committees and units; 3 Mega-ministries and merges; 4 Joint budgeting; 5 Intersectoral policy-making procedures; and 6 Non-government stakeholder engagement. 7
CABINET COMMITTEES AND SECRETARIATS 5 1 REVIEW AGENDA SETTING Cabinet committees: promotes engagement process with ministers. Report Identify problem Evaluate Research Monitor Set agenda Cabinet secretariats: coordination role; facilitates timely and collective decision- making. IMPLEMENTATION FORMULATION Have the most notable influence on the agenda setting and policy formation stages of the policy cycle Enforce policy Develop options and strategies Implement policy Negotiate Formulate policy
5 PARLIAMENTARY COMMITTEES 2 REVIEW AGENDA SETTING Report Identify problem Evaluate Research Parliamentary committees: can enhance the potential influence of findings and support the longevity of an issue. Monitor Set agenda IMPLEMENTATION FORMULATION Can have influence on the agenda setting and policy review stages of the policy cycle. Enforce policy Develop options and strategies Implement policy Negotiate Formulate policy
INTERDEPARTMENTAL COMMITTEES AND UNITS 5 3 REVIEW AGENDA SETTING Report Identify problem Evaluate Research Interdepartmental committees and units: promote orientation around a shared priority. They are usually made up of civil servants and operate at the bureaucratic level. Monitor Set agenda IMPLEMENTATION FORMULATION Can influence the entire policy cycle. Enforce policy Develop options and strategies Implement policy Negotiate Formulate policy
5 MEGA-MINISTRIES AND MERGES 4 REVIEW AGENDA SETTING Identify problem Report Research Evaluate Mega-ministries and merges: aim to bring different areas of government closer together and thereby improve collaboration and policy-making. Set agenda Monitor IMPLEMENTATION FORMULATION Costs of reorganizations tend to be high and the benefits are contested. Enforce policy Develop options and strategies Implement policy Negotiate Formulate policy
5 JOINT BUDGETING 5 REVIEW AGENDA SETTING Report Identify problem Evaluate Research Monitor Set agenda Joint budgeting: promotes integrated budgets, and supports the alignment of resources for common goals. IMPLEMENTATION FORMULATION Mainly influences the implementation stage of the policy cycle. Develop options and strategies Enforce policy Negotiate Implement policy Formulate policy
INTERSECTORAL POLICY-MAKING PROCEDURES 5 6 REVIEW AGENDA SETTING Report Identify problem Evaluate Research Intersectoral policy- making procedures: multiple measures that promote intersectoral collaboration; e.g. impact assessments, policy proposals. Monitor Set agenda IMPLEMENTATION FORMULATION Mainly influences the policy formation stage of the policy cycle. Enforce policy Develop options and strategies Implement policy Negotiate Formulate policy
NON-GOVERNMENT STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT 5 7 REVIEW AGENDA SETTING Non-government stakeholder engagement: government engagement with non- government stakeholders is crucial for joined-up work and the HiAP approach. Report Identify problem Evaluate Research Monitor Set agenda IMPLEMENTATION FORMULATION Most common during the agenda setting, policy formation and policy implementation stages. Enforce policy Develop options and strategies Implement policy Negotiate Formulate policy
End of Module 5 Part 2 Please continue to Module 6