Understanding Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) and Its Impact
Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a rare autoimmune disease where the immune system wrongly attacks platelets, leading to low platelet count. It can affect individuals of all ages, with symptoms appearing post-virus, vaccination, or certain medications. ITP can result in fatigue, bruising, and bleeding, affecting quality of life. The I-WISh study delves into the real-world impact of ITP, surveying patients and physicians on symptoms, emotions, treatment perceptions, and overall quality of life.
Uploaded on Apr 05, 2024 | 3 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Contents 1. What is immune thrombocytopenia (ITP)? 2. I-WISh background 3. Results: Diagnosis pathway 4. Results: Symptomology 5. Results: The ITP Life Quality Index (ILQI) and emotional burden 6. Results: Impact of ITP on work, finances and support 7. Results: Treatment goals 8. Results: Perceptions on the patient and physician relationship 9. Summary
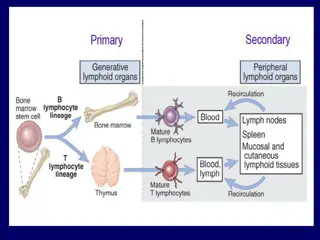
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a rare autoimmune disease characterised by low platelets In ITP, the immune system mistakes the platelets as being foreign and destroys them:1,2 For most people the cause is unknown, but symptoms can show following a virus, vaccination or certain medications1 ITP can affect both children and adults differently, and is more common in women than men3 ITP can result in debilitating fatigue and have a substantial impact on quality of life (QoL), requiring ongoing medical management4,5 ITP can cause excessive bruising or bleeding due to reduced number of platelets in the blood3,4 1. Guy s and St Thomas NHS. Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). Available at: https://www.guysandstthomas.nhs.uk/resources/patient-information/haematology/Immune-thrombocytopenia-web-friendly.pdf. Accessed: August 2020. 2. Grimaldi-Bensouda L, et al. Haematologica 2016;101:1039 1045. 3. Oxford University Hospitals NHS. Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) information for patients. Available at: https://www.ouh.nhs.uk/patient-guide/leaflets/files/12388Pitp.pdf. Accessed: August 2020. 4. National Organization for Rare Disorders 2019. Immune Thrombocytopenia. Available at: https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/immune-thrombocytopenia/. Accessed: August 2020. 5. Michel M. European Journal of Haematology. 2009;82:3 7.
ITP Patient demographic ITP can affect both children and adults differently and is more common in women than men1 2/3 of adult ~200,000 ITP patients are likely to develop a chronic form of the disease2 people affected by ITP worldwide1 Mean age of adults at diagnosis: 50 years with incidence increasing with age2 Incidence of ITP in adults: 2.8 3.9 per 100,000 people2 1. National Organization for Rare Disorders 2019. Immune Thrombocytopenia. Available at: https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/immune-thrombocytopenia/. Accessed: August 2020. 2. Grimaldi-Bensouda L, et al. Haematologica 2016;101:1039 1045.
I-WISh: A real-world survey on the impact of ITP on patients 2 The ITP World Impact Survey (I-WISh) is a collaborative investigation among global ITP experts, patient organisations and Novartis that analysed the real-world impact of ITP on patients : 1 Patient and physician perceptions of symptoms and treatment Impact of ITP in terms of symptom, emotional and economic burden Perceptions of symptoms Impact on patients Need for early intervention objectives quality of life (QoL) Impact on QoL 3 Level of symptom awareness, functionality and the need for early treatment intervention management of the condition 5 Perceptions of treatment options Impact of ITP on patients QoL development of an ITP Life Quality Index? opinions on treatment 4 Degree of disconnect between the patients and physicians perceptions of treatment options
I-WISh: Around 1,500 patients and 470 physicians participated from 13 countries Patients and physicians completed a survey either online or by pen and paper Respondents were recruited via various channels: Physicians were recruited via: Local fieldwork agencies Patients were recruited via: Patient organisations Treating physicians *Patients recruited via physicians and patient organisations **Physicians recruited via local fieldwork agencies PAGs icon from Noun Project, by Gregor Cresnar; physician icon from Noun Project by Martin Lebreton FR
Over 1 in 5 patients experienced a delay in receiving their ITP diagnosis Patient estimates of diagnosis timelines were greater than physicians, with patients reporting: nearly 4 months for a formal ITP diagnosis following initial presentation 4 63% of these patients experienced a high level of anxiety during delay to diagnosis stated a desire for more support 73% Patients wanted further support from: 50% 60% Their physician Patient organisations Calendar icon from Noun Project by AlePio; PAGs icon from Noun Project, by Gregor Cresnar; physician icon from Noun Project by Martin Lebreton FR
In 86% of cases, patients were diagnosed by a haematologist Physician-perceived factors leading to delay in diagnosis: 58% 68% 53% 55% 52% of patients initially presented to their general practitioner / family doctor Exclusion of other causes of thrombocytopenia Misdiagnosis Diagnostic examination Time to refer to specialist For most patients, regardless of their perceived symptom load, physicians stated they would conduct: Of the physicians that believed patients were misdiagnosed prior to their formal ITP diagnosis, 67% reported drug- induced thrombocytopenia to be the main condition a physical examination peripheral blood smear complete blood count
Patients identified fatigue as a key symptom in terms of frequency and severity More patients than physicians reported fatigue as a key symptom: Patient-reported symptoms (currently experienced) Physician-reported symptoms (overall most common) Fatigue 50% Petechiae 82% 60% Anxiety surrounding stable platelet count 32% Purpura 74% 50% 40% Petechiae* 31% Bleeding from the gums 69% Bruising occurring for no known reason 30% 30% Epistaxis 69% 50% 20% 31% 10% 0% *Petechiae: tiny purple, red or brown spots on the skin Purpura: purple bruising on the skin Epistaxis; nosebleeds Patient Physicians
Patient-reported severity generally decreased for signs & symptoms from diagnosis to survey completion Though patient-reported severity generally decreased over time for the majority of signs & symptoms, fatigue, anxiety around platelet count, depression and heavy menstrual bleeding continued to be rated as severe symptoms Fatigue was a key symptom reported at both diagnosis and survey completion, suggesting that it remains a key unmet need regardless of duration of disease Symptom severity Symptoms At diagnosis At survey completion 73% 65% Fatigue 60% 74% Thrombosis Severity score for thrombosis increased by survey completion 68% 64% Depression Anxiety around platelet count 77% 64%
I-WISh: The ITP Quality of Life (QoL) and emotional burden
Patients reported a significant impact of ITP on their quality of life and emotional wellbeing Most patients felt that ITP had a negative impact on their energy levels, capacity to exercise, work, concentrate and undertake daily tasks at least 50% of the time 1 in 2 patients (49%) indicated that ITP had a high impact on their emotional wellbeing 85% 77% 63% Energy levels Normal capacity to exercise of patients stated a high level of concern about their condition worsening Patients with a high symptom burden reported greater emotional impact, with 80% worrying about worsening ITP 75% 73% Ability to carry out daily tasks Concentrate on everyday tasks
Physicians were not always aligned with patients on symptoms with highest QoL impact Top 3 symptoms patients would most like resolved physicians think have highest impact on QoL Heavy menstrual bleeding 75% Blood in urine/stool 81% 66% Profuse bleeding during surgery Thrombosis 74% 79% Fatigue 73% Heavy menstrual bleeding 78% The proportion of patients reporting at least some impact of ITP increased as symptom burden increased 98% of patients with the greatest symptom burden reported that ITP impacted on their energy levels of physicians agreed that ITP-related fatigue can reduce a patient s QoL
Physicians were aligned with patient-reported emotional impact of ITP Physician-perceived factors driving an emotional impact in ITP 90% 80% of physicians would like to start using a patient-reported quality of life (QoL) tool for ITP 70% 69% 60% 50% 82% 40% 74% 73% 67% 30% of physicians do/would use a QoL assessment tool at least every 6 months for their patients 20% 84% 10% 0% Anxiety about platelet count Fear around the disease Frustrations with disease Stress
I-WISh: Impact of ITP on work and support
Over one-third of patients indicated that their ITP impacts their work productivity Of the patients surveyed: 60% 52% 49% 29% were currently working (full- or part-time) reported needing some level of caregiver assistance with main caregiver being a spouse either reduced, or seriously considered reducing working hours had seriously considered terminating their job as a result of their disease Despite ITP s impact on productivity, two thirds (63%) of patients work more than 30 hours each week
Physicians and patients differ on primary treatment goals Most patients believed their current treatment approach was helping them achieve their treatment goal, this was observed regardless of the treatment patients were receiving 72% 64% of physicians consider reducing spontaneous bleeding the number one treatment goal of patients believe healthy blood counts is their top treatment priority The vast majority (88%) of physicians and patients indicate treatment goals are well discussed
I-WISh: Patient and physician relationships
Overall satisfaction between patients and physicians was high regarding communication, management and understanding of treatment goals 86% of patients consider their specialist doctor as their main healthcare professional 79% 88% 37% of patients report to be given information about their ITP, with leaflets the most popular form of physicians felt patients of patients were generally satisfied with the level of communication about their disease and treatment
ITP patients highlighted areas where more information or guidance could be provided Symptoms that may be experienced Treatment plan for therapy following discussions Explanation of potential drug side effects prior to treatment Information about new treatment options Explanations of the possible long-term complications prior to treatments/procedures
Summary: Symptom burden Patients: Most wanted to resolve heavy menstrual bleeding, thrombosis and fatigue Identified that the key symptom in terms of frequency and severity at both diagnosis and currently was fatigue -suggesting this remains an unmet need Felt that ITP negatively impacted their energy levels, capacity to exercise, work, concentrate and undertake daily tasks at least 50% of the time Physicians: 80% felt ITP symptoms had a high impact on patient s quality of life (QoL), whilst 59% agreed that ITP- related fatigue had a high impact on a patient s QoL 69% reported they would like to start using a patient-reported QoL tool for ITP Aligned with the patient-reported emotional impact of ITP
Summary: Diagnosis and impact Time for a formal diagnosis is an area for improvement, with patients on average reporting receiving one nearly 4 months from initial presentation 36% of patients indicated that ITP impacts their work productivity, with over 1/4 of patients having seriously considered terminating their job >50% patients reported needing some level of caregiver assistance Almost 50% of patients indicated that their ITP had a high impact on their emotional wellbeing, with 63% of patients stating a high level of concern about their condition worsening
Summary: Treatment goals and patient-physician relationship Physicians and patients differ on what their primary treatment goals are Physicians said reducing spontaneous bleeding is their top treatment goal (72%) Patients believe healthy blood counts to be their top priority (64%), as well as preventing episodes of worsening ITP (44%) and increasing energy levels (41%) Despite this, most patients believe their current treatment approach is helping them achieve their treatment goal Overall satisfaction between patients and physicians was highregarding communication, management and understand of treatment goals Areas for improvement: Patients understanding of potential drug side effects, and be made aware of new treatments Physicians understanding of how ITP is impacting their patients quality of life
THANK YOU 1. Cooper,N. et al. Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) World Impact Survey (I-WISh): Impact of ITP on health-related quality of life. American Journal of Hematology, 2020;96(2):199- 207. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.26036 2. Cooper,N. et al. Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) World Impact Survey (I-WISh): Patient and physician perceptions of diagnosis, signs and symptoms, and treatment. American Journal of Hematology, 2021;96(2):188-198. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.26045 3. Data on file Developed by Novartis for use by Patient Association Groups 7/21 126702