Maximizing Your Research Impact: Understanding the Research Life Cycle
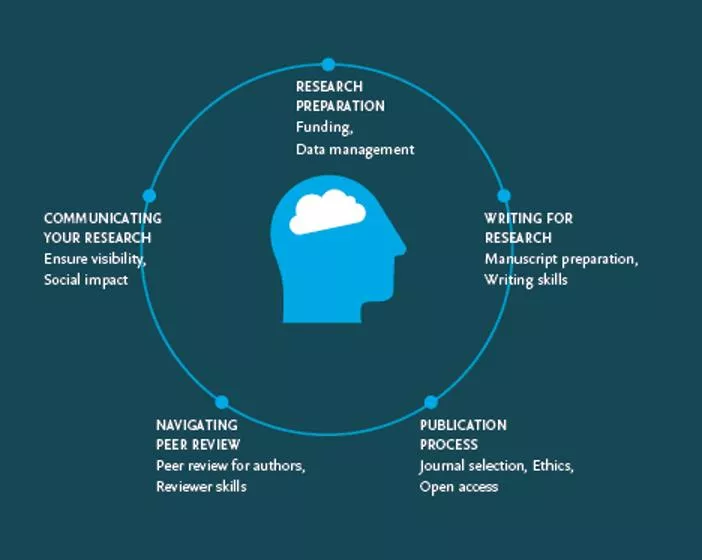
Research life cycle plays a crucial role in enhancing publication opportunities by guiding researchers through key stages such as research preparation, data management, collaboration, and writing for research. It emphasizes the importance of being well-prepared, managing data efficiently, fostering collaborations, and honing writing skills to increase chances of publication in high-impact journals.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Understanding the research life cycle And how it can help boost your chances in getting published Ana Morzinger / Yingzhi Wang May 11th2022
Why is the research life cycle important? As a researcher your end goal is to make an impact with your work. Being aware of each step of the research life cycle will help with this because: You will understand how each step is interconnected and be prepared for what is coming next You will have awareness on how to successfully complete each step You can design your own personalized research path | 2
First stage: Research Preparation In this stage it is important to know how to apply for grants and receive funding, manage your data and form successful academic collaborations 1. Funding Successful applications: Read carefully the guidance notes Ask advice from your peers, colleagues, collaborators, mentors. If necessarily organize an informal peer review Prepare well for interviews do mock interviews Write the application with reviewers in mind Learn more about this with Funding Hacks for Researchers or Successful Research Grants Getting it Right | 3
First stage: Research Preparation 2. Data Management Creating a research data management has a role to play beyond funding. As well as saving researchers time and effort when running experiments, it benefits the wider scientific community, as well-organized data can be used by other researchers in their work. Increase your chances of getting cited by publishing your data in a journal like Data in Brief. Learn more about this with Creating a good research data management plan and How Researchers Benefit From Citing Data 3. Research Collaboration It is widely accepted that collaboration in research across disciplines, between young and more senior researchers and with practitioners is critical to the career of novice researchers. The increasingly interdisciplinary, complex and costly characteristics of modern science encourage scientists to get involved in collaborative research. Learn more about this with The key to successful academic collaborations and Making academic-industry collaborations work | 4
Second stage: Writing for research In this stage it is important to develop your writing skills to boost your chances of being accepted in a high impact journal 1. Preparing your manuscript for publication If you already have a journal in mind that you wish to publish in at this stage you can already check the journals Guide for Authors to make sure your manuscript is structured correctly. While writing your manuscript you should have: An understanding of the general structure of the research article: Title, Abstract, Keywords, Introduction, Methods, Results & Discussion, Conclusion, Acknowledgements, References, Supporting Materials Specific keywords that are used as labels for the manuscript and for indexation Author should be ordered in the correct way. Learn more about Authorship and Ethics in this webinar A short title that will grab the readers attention An interesting, understandable and specific abstract. Authors tend to write the abstract last so they can ensure they capture all essential information. A clear abstract will strongly influence whether your work is considered or not Learn more with Structuring your Article Correctly , How to Prepare your Manuscript and How to Write an Abstract and Improve your Article | 5
Second stage: Writing for research 2. Start thinking about your proposal If you have written a review article, it is important also to think about writing a proposal since a journal will usually ask authors to first send a proposal that introduces the review article. Common elements of proposals are: A concise description of the intended article An explanation of why it s a good fit with the journal A list of key research articles on the topic, Potentially include a summary of the intended audience or the authors own expertise in the topic. Learn how to write a proposal with this webinar How to prepare a proposal for a review article Learn more with Structuring your Article Correctly , How to Prepare your Manuscript and How to Write an Abstract and Improve your Article | 6
Third stage: Publication Process 1. Behind the scenes: learn how articles get published You have now finished your manuscript it s time to get published! During this period, we recommend investing the time to understand how an article gets published. The back scene involving editors, journal managers, Publishers and every essential step to get your article published. This webinar deep dives into the Publishing Journal Cycle 2. Using AI to match your abstract to a journal An important way to understand if a journal matches your manuscript is by analysing the journals aims & scopes, published articles and editorial board. To save time and energy you could also use a tool powered by artificial intelligence that can help you match your manuscript to relevant journals. A free to use tool such as JournalFinder 3. Using the right metrics to evaluate a journal Make sure you are using the right metrics to evaluate a journal. This webinar deep dives into what the right metrics can be. Learning how to spot a reliable or predatory journal is also important and is tackled in this webinar | 7
Fourth stage: Peer Review This can be a gut wrenching time your manuscript was accepted for peer review and now you are awaiting the feedback. To ease that feeling, it s important to understand the process of peer review: Many journals have an editorial team with an editor-in- chief and a number of scientific editors who are assigned responsibility for the peer review of individual papers. These journals often hold discussions before accepting a paper. Watch our webinar on How to Respond to Reviewers Comments and How Do Editors Look At Your Paper? Want to make an impact, contribute to the research community and expand your network? Become a reviewer with our certified peer review course | 8
Fifth stage: Communicating your research Communicating your research focuses on getting your work more exposure while making an impact: 1. Lay summaries: Journal articles are written with researchers in mind, so the content isn t always easy to follow for people outside academia. That is where lay summaries, play a helpful role. Lay summaries make your research accessible and understandable to the world. Learn how to write a lay summary here 2. Conferences: Conferences and research are somewhat inseparable. Chances are you ll be heading to a conference at some point in your career which gives you the perfect opportunity to present your research. Make sure you have the conference skills to do this effectively and watch this webinar 3. Social Media: Researchers can use it to profile their work, exchange ideas and results, and to meet like-minded peers. The benefits of using social media are abundant, but it s important to know how to leverage the power of each platform type. Learn how to build on your online presence with this webinar Deep dive more into how you can increase your visibility and effectively communicate your work by watching How to promote yourself and your research as an Early Career Researcher | 9
Key Takeaways Before starting to write make sure you already have your authorships in order Increase your chances of getting cited by carefully managing your data and sharing it to relevant journals like Data in Brief While preparing your manuscript and defining the keywords make sure they are repeated enough in your manuscript to increase the chances of visibility in a search engine While writing your research you can already think about journals to publish in. Make sure you check the journals Guide for Authors to ensure your manuscript is ordered correctly | 10
Thank you. Ana Morzinger a.morzinger@elsevier.com
Formulating research questions P: Patient or population being studied I: Intervention (by the researchers) or exposure (of the patient) C: Comparison with standard practice or with unexposed patients O: Outcome or results that we want to obtain once we have designed our study T: Time required to evaluate the results and frame the question Example: Is prophylaxis with oral antibiotics in oncological colon surgery effective in reducing surgical site infection? | 12




 undefined
undefined