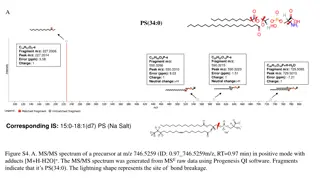
Ion Suppression in Mass Spectrometry Challenges and Solutions
Ion suppression is a critical issue in mass spectrometry that can significantly affect the accuracy and reliability of analytical results. This phenomenon occurs when the presence of co-eluting substances interferes with the detection of target ions,
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Ion Suppression in Mass Spectrometry: Challenges and Solutions Ion suppression is a ubiquitous phenomenon in mass spectrometry, affecting the accurate quantification of analytes within complex matrices. Understanding the mechanisms, impact, and mitigation strategies is crucial for reliable analytical results. www.iroatech.com
Causes of Ion Suppression Matrix Effects Adduct Formation 1 2 Co-eluting compounds can compete for ionization, leading to suppressed signal intensities of the target analyte. Analyte molecules can form adducts with matrix components, resulting in a decrease in the abundance of the parent ion. Charge Competition Surface Adsorption 3 4 Multiple analytes in the sample can compete for the same charge, reducing the ionization efficiency of individual components. Analyte molecules can adsorb onto the surface of the analytical system, leading to a reduction in the amount of analyte available for ionization.
Impact of Ion Suppression on Analytical Accuracy Underestimation of analyte concentration Loss of sensitivity Poor reproducibility of results False negatives in quantitative analysis
Sample Preparation Techniques to Mitigate Ion Suppression Extraction Dilution Clean-up Techniques like liquid-liquid extraction or solid-phase extraction aim to remove interfering compounds from the sample matrix. Diluting the sample can reduce the concentration of matrix components, minimizing their impact on analyte ionization. Techniques such as precipitation or filtration can remove particulate matter or other contaminants from the sample.
Chromatographic Strategies for Ion Suppression Reduction Gradient Elution Utilizing a gradient elution profile in liquid chromatography can separate analytes from interfering matrix components. Column Selection Choosing a suitable chromatographic column with high selectivity and resolution can minimize co-elution of interfering compounds. Mobile Phase Optimization Optimizing the composition and pH of the mobile phase can improve analyte separation and reduce ion suppression.
Advances in Mass Spectrometry Instrumentation to Address Ion Suppression High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRMS) Tandem Mass Spectrometry (MS/MS) HRMS instruments provide improved mass accuracy and resolution, enabling the identification and quantification of analytes even in the presence of complex matrices. MS/MS techniques offer enhanced selectivity by fragmenting ions and detecting characteristic fragment ions, reducing interference from matrix components. Electrospray Ionization (ESI) Optimization Optimizing ESI parameters, such as the capillary voltage and source temperature, can improve analyte ionization and minimize ion suppression.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives Ion suppression remains a significant challenge in mass spectrometry, but advancements in sample preparation, chromatography, and instrumentation provide a toolbox for mitigating its impact. Future research focuses on developing innovative approaches for addressing ion suppression in complex matrices, ensuring accurate and reliable analytical results.
Get In Touch 734-265- 0884 info@iroatech.co m www.iroatech.co m