Qualitative Tests of Proteins & Amino Acids: Overview and Analysis
In this lab, you will delve into the qualitative tests for proteins and amino acids, understanding their structures, classifications, and importance in food and human nutrition. The tests include solubility tests and identification tests for both amino acids and proteins, revealing their presence and characteristics. Explore the classifications of amino acids based on their sources and polarity, shedding light on essential and non-essential amino acids. Enhance your knowledge of protein analysis through various chemical tests like Ninhydrin, Xanthoproteic, Lead Sulfite, and Millon's tests.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
LAB 4 : QUALITATIVE TESTS OF PROTEINS & AMINO ACIDS DR. SHAIMAA MUNTHER
Objectives: General information about amino acids. Qualitative tests of amino acids. Tests for proteins
Introduction Food are divided into three classes : 1-Carbohydrate Source of energy. 2- Lipid Principal of energy reserve. 3- Proteins Energy and biomolecules for growth and cellular maintance.
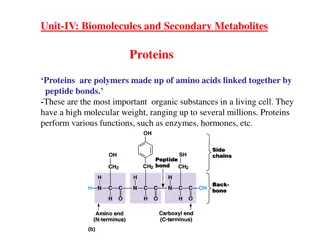
Amino acid structure (Building blocks of proteins which linked to peptide bond ) Each amino acid consists of : 1. Central carbon atoms 2. An amino group 3. Carboxyl group 4. Side chain (All amino acids found in proteins have this basic structure, differing only in the structure of the R-group or the side chain.)
Classification of amino acids according source Essential amino acids: Humans incapable of forming requisite and must be Required in diet. Non essential amino acids: Not required in diet.
Classification of amino acids according to their (polarity) in water 1- Non-polar (Hydrophobic amino acid) : are amino acid that contain C,H in their side chain (hate water, normally buried inside the protein core) 2- Uncharged polar. 3-polar amino acids: amino acid that contain in their side chain O,N and they can dissolve in water ( like dissolve like ) hydrophilic (love water),tend to found on surface A-Basic polar (positively charged). B- Acidic polar (negatively charged). Note: Polar amino acids are more soluble in water than non-polar.
Amino acids & Protein Analysis A. Solubility test. B. Identification tests for amino acids : There number of test to detect the presence of amino acid ,These are largely depend on the nature of amino acids side chain usually. Example of these tests are : Ninhydrin test: for -L amino acids 1. Xanthoproteic test: for Aromatic amino acids 2. Lead sulfite test: detection of amino acids containing sulfhydryl group (- SH) 3. Millon's test: for amino acids containing hydroxy phenyl group 4. C. Identification tests for proteins : The presence of proteins in a solution is often detected by general tests, such as biuret or specific tests that depend on the presence of a specific proteins.
Solubility Tests Objective: To investigate the solubility of selected amino acid in various solutions -Principle: Polar amino acids are soluble in polar solvent, and vice versa. The solubilities of amino acids in water are highly variable.
The solubility of amino acids and proteins is largely dependent on the solution pH. The structural changes in an amino acid or protein that take place at different pH values alter the relative solubility of the molecule. In acidic solutions, both amino and carboxylic groups are protonated. In basic solutions, both groups are deprotonated. Amino acids are essentially soluble in water. Their solubility in water, dilute alkali and dilute acid vary from one compound to the other depending on the structure of their side chains.