Robotics: The Ins and Outs of Machines
The components, types, and evolution of robots in this informative guide. With the expertise of MIT Museum, coordinators, and guest speakers, delve into the fascinating world of robotics.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
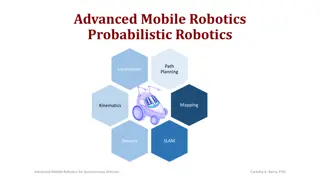
Robotics Theinsandoutsof machines Cadence, Katrina, and Adaora Creds: MIT Museum, our Coordinators, and guest speakers!
Components ofrobots The different elements that makes the robot work. 01 02 Introduction An introduction to what robotics is. Typesof robots Different types of robots there are in the world. 03 04 Evolution The advancements of robots throughout the ages.
01. Introduction
WhatIs Robotics? Robotics is the field of building and studying robots! (with both computer engineering and science involved.) Robots are a machine made from many components associated with hardware and software, (slide. 6.) A robot consists of a body, a brain, and a job, to perform many different types of task with efficiency. A robot s planning features, perception, and control, help it to perform in ways robots do!
02. Components
VS Hardware Software Any physical components of a robot or of a computer, such as a hard drive, mouse, keyboard, and etc. Internally directs and helps allow hardware to function using programming from the user - directing the computers overall efficiency. Fun Fact Fun Fact: Robots work mainly with the function, input and output! An example of this is if a person touches the robot (input), it is made to move away (output).
Hardware&software DeeperDive(ofRobotsandAI): Major components: Manipulators: A components similar to humans, (in the way we work.) Robots have manipulators which are joints and links, used to move. Controller: Usually a digital computer (consisting of both the hardware and software,) works like a brain, by assigning tasks for the robot to do, and how to accomplish them. End Effectors: Located on the other end of the manipulator (after being put on the base support.) These end effectors have control over the performance of the tasks created by the palms and fingers, like on a human body. Sensors: Sensors sense and measure the position, velocity, force, torque, proximity, temperature, and etc. of the robot itself, and the environment around it. Sensors are considered the most important, because without it combining forces with everything else, the robot would not know how to take notice and inform itself, to do its job. Locomotion Device: Just like humans have muscles to provide power to their joints and fingers, robots have motors to provide that power and movement (...locomotion) to them.
03. Evolution Fun Fact Fun Fact: 1921 was the first time we heard/used the term robot in the play R.U.R, by Karel apek. Which back then, literally meant force labor. Robot comes from the Czech word robota!
1. Unimate:1961 - Invented by George Devol - First industrial industrialrobot, which worked on a General Motors Assembly Line in 1961 - Was broadcasted on television to people all over the world in 1966 by NBC Studios in NYC
2.Shakey:1966- 1972 - Shakey was created in 1966 at the Stanford Research Institute - Shakey was the first general purpose purposerobot able to influence its own actions general - A 24 minute video of Shakey was released in 1969 and received a lot of media recognition such as the New York Times, National Geographic Magazine, and Life Magazine.
3.G.EWalkingTruck:1965 - Created in 1965 by the company GE (General Electric) - The walking truck was controlled by a human operator through hand and feet movements this allowed the robot to be able to walk using its 4 legs! - This robot weighed 3,000 pounds and could walk up to 5 mph
4.OSUHexapod:1977 - Developed at the Ohio State University in 1977 by Robert McGhee and his associates - First robot to have digital tethered control to move its legs - It functioned by active force sensing in its control systems - This robot was used for exploration purposes such as climbing up shallow stairs, walking on flat surfaces, and walking over obstacles
5.ODEX1Functionoid:1983 - Displayed in 1983 at the National Museum of American History - Built to demonstrate to the that you could coordinate and move objects with robots - It could manipulate its legs and structure due to the situation - It s leg height varied from 36 to 78 inches and width 25 to 105 inches
6.HondaP-Series:1993- 2000 - A series of prototype humanoid robots developed by Hondo from 1993 to 2000 - Honda engineers studied a human skeleton in order to make the robots walk and function in a humanlike manner - Multiple prototypes were developed but in 1997 P3 was introduced as the first completely independent humanoid walking robot
7.NASASojourner - Developed in 1997 by NASA to study the surface of Mars - The Sojourner was sent to mars in order to examine its surface - The Sojourner traveled in a spacecraft in order to actually get onto the planet - The robot stayed on Mars for 83 days although it was originally a 7 day mission - Took more than 550 pictures of Mars
04. TypesofRobots
Whyhave different types? robot's amazing adaptability and endurance level, they have a fantastic precision and accuracy level as well. Helping in many different fields, like data research, all the way to helping in your own backyard. With so many robots with so many different types of skills, robots and humans are adapting at an amazing speed! The main reason we have so many different types of robots is to help humans. Other than a
OverviewofTypesofRobots Exploration Medical/Healthcare Exploration robots can explore places that humans can not. Examples include, space and the ocean. Home/Entertainment Medical and healthcare robots assist hospital staff and the general public. Security/Patrol Home and entertainment robots provide domestic services to humans in beneficial ways. Security and patrol robots can be implemented to protect buildings or to remove dangerous objects.
OverviewofTypesofRobots Social Industrial Social robots can communicate with humans and be a companion, or provide both mental and physical assistance. Industrial robots are used for manufacturing by welding, assembling, and etc.
1 out of 2: 1 out of 2: A more in-depth view of Exploration robots Exploration robots are sent to places that are either too dangerous for human beings to explore or unable to. Exploration robots gather data from the environment they are put into and sends it back to us. For example the NASA rover Curiosity was sent to Mars to find out if Mars had the proper conditions for microbial life to survive. It studied rocks at the bottom of Gale crater, measured radiation levels, and took multiple photos of the planet. Curiosity on Mars taking a selfie. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
2 out of 2: 2 out of 2: A more in-depth view of IndustrialArms One of the most common robots out there, industrial arms work in many places and do many different things, in places you visit everyday. Robots can be repaired easily and have a way longer lifespan than humans. Due to this, industrial robots have been the most practical for industrial workplaces, as their very fast, reliable, and can multitask very well. Industrial Arms work/do arc and spot welding, material handling, machine tending, painting, packaging, assembly and etc. An Industrial Arm at work, welding. Creds: ANSI
Surprise: Picturesof ourRobots!
OurPhotos LegoMindstorms Silence-Bot When we visited the MIT Museum, we got to code our own robots to do something, using Microbits. (Adaora - in my group we made it move when it was silent, but stop when it heard a loud noise, (made to keep kids distracted but quiet, and help out busy parents. ) Rocinante Another MIT Robot made: (Katrina - Rocinante had a propeller made of popsicle sticks and a motor on the back so it could move through the ocean. Its googly eyes are cameras to send visual data back to us. Making the robot similar to a box fish provided camouflage so that the robot wouldn t scare other sea creatures away.) We built our own robots using small parts and motors, and used the Lego Mindstorm app to code them to dance and play music. (Adaora - In my group we made it play shake it off, which was the biggest challenge to code and upload it )
OurPhotos Aleph3000 Cadence- Aleph 3000 was a robot I designed to comfort the user by displaying a message on its chip that said I m so proud of you in big letters. It also danced around and played music once it was shaken or a button was pressed. This provided a sense of solace for the user.
Sources: Thank you for listening!!! Robots: 5 Important Components of Robots AT-AT Boy! GE's Walking Truck From The 1960s Mixed 'Star Wars' With Jules Verne | GE News Walking Truck: The Most Up-to-Date Encyclopedia, News, Review & Research The Czech Play That Gave Us the Word Robot | The MIT Press Reader 4: Hexapod of McGhee In 1977, McGhee and his group at Ohio State... Why Do We Send Robots To Space? | NASA Space Place NASA Science for Kids https://dailytitan.com/lifestyle/defunct-aging-robot-odex-1-awaits-fate-in-csuf-mechanical- engineering-lab/article_aed15cb7-b1b5-5ec9-a261-6ca3ec18708b.html https://www.wikiwand.com/en/Honda_P_series https://blog.ansi.org/2019/01/industrial-robots-safety-production-ria/#gref https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/robotics/robotic-arm.html https://www.automate.org/a3-content/joseph-engelberger-unimate https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shakey_the_robot https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/mars-sojourner/en/