Visible Light Waves in Medicine and Physics
Visible light waves play a crucial role in medicine and physics, where they are the only electromagnetic waves that humans can see. These waves create the colors of the rainbow with varying wavelengths, allowing us to perceive different colors and forms of light. Understanding the properties of visible light waves as electromagnetic radiation helps in applications such as medical analysis, photon behavior, and refraction through different mediums.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Tishk International University Faculty of Science Medical Analyzer Department Medical Physics Application of Visible Light Wave in Medicine Practical Session (2) First Grade- 2020-2021 Instructor: Assist. Prof. Dr. Ronak T. Ali Assistant: M. Adam
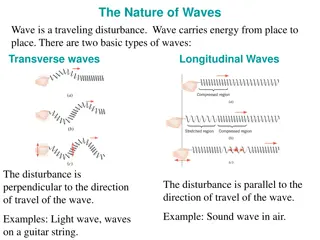
When an electric field changes, so does the magnetic field. The changing magnetic field causes the electric field to change. When one field vibrates so does the other. RESULT-An electromagnetic wave.
Definition Visible light waves are the onlyelectromagnetic waves we can see. We see these waves as the colors of the rainbow. Each color has a different wavelength. Red has the longest wavelength and violet has the shortest wavelength. When all the waves are seen together, they makewhite light.
Waves or Particles? Electromagnetic radiation has properties of waves but also can be thought of as a stream of particles. Example: Light Light as a wave: Light behaves as a transverse wave which we can filter using polarized lenses. Light as particles (photons): When directed at a substance light can knock electrons off of a substance (Photoelectric effect)
humans can see the waves with = 390- 750 nm and f = 400- 790 THz ( 1 THz = 1012Hz). visible light wave has a wavelenght ( ) is 400- 720 nm, while Frequency (f) of visible light wave is 400- 789 THz. *1 THz=1012Hz
When light enters a new medium it bends (refracts). Each wavelength bends a different amount allowing white light to separate into it s various colors ROYGBIV.
How to happen? When white lightshines through a prism, the white light is broken apart into the colors of the visible light spectrum. Water vapor in the atmospherecan also break apart wavelengths creating a rainbow. Each color in a rainbow corresponds to a different wavelength ofelectromagnetic spectrum.
Color Wavelength Color violet blue cyan green yellow orange red Frequency 668 789 THz 631 668 THz 606 630 THz 526 606 THz 508 526 THz 484 508 THz 400 484 THz Wavelength 380 450 nm 450 475 nm 476 495 nm 495 570 nm 570 590 nm 590 620 nm 620 750 nm
Figure Sir Isaac Newton was the first to test the visible light from the sun that through on a prism and produces a bearn of light that can divided into several colors such as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and purple.
Even though man is now very efficient at making artificiallight, the sun is still the major source of light in the world. The sun is both beneficial andhazardous to our health. Light has some interesting properties, many of which are used in medicine: - 1. The speed of light changes when it goes from material into another. The ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to its speed in a given material is called theindex of refraction. If a light beam meets a new material at an angle other than perpendicular, it bends, or is refracted. This property permits light to be focused and is the reason we can read and see objects clearly.
2. Light behaves both as a wave and as a particle. As produces interference and diffraction, which are of minor importance in medicine. As a particle it can be absorbed by a single molecule. When a light photon is absorbed its energy is used in various ways. It can cause a chemical change in the molecule that in turn can cause an electrical change. This is basically what happens when a light photon is absorbed in one of the sensitive cells of the retina (the light-sensitive part of the eye). The chemical change in a particular point of the retina triggers an electrical signal to the brain to inform it that a light photon has been absorbed at that point. a wave it
3. Light is reflected to some extent from all surfaces. There are two types of reflection. Diffuse reflection occurs when rough surfaces scatter the light in many directions. Specular reflection is more useful type of reflection; it is obtained from very smooth shiny surfaces such as mirrors where the light is reflected at the angle at which it strikes the surface. Mirrors are used in many medical instruments. an angle that is equal to
Applications of visible light in medicine 1- An obvious use of visible light in medicine is to permit the physician to obtain visual information about the patient regarding, for example, the color of his skin and the presence of abnormal structures in or on his body. this one is done with mirrors. The curved surface focuses the light at the region of interest. More sophisticated instruments, such as the ophthalmoscope for looking into the eyes and the otoscope for looking into the ears, use basically the same principle.
2- A number of instruments, called endoscopes, are used for viewing internal body cavities. Special purpose endoscopes are often given names indicating their purpose. For example, cystoscopes are used to examine the bladder, proctoscopes are used for examining the rectum, and bronchoscopes are used for examining the air passages into the lungs.
The development of fiberoptic techniques permitted the construction of flexible endoscopes. Flexible endoscopes can be used to obtain information from regions of the body that cannot be examined with rigid endoscopes, such as the small intestine and much of the large intestine. Flexible have an opening or channel that permits the physician to take samples of the tissues (biopsies) for later microscopic examination. endoscopes usually
3- Transillumination is used clinically in the detection of hydrocephalus (water-head) in infants. Since the skull of young infants is not fully calcified, light is able to penetrate to the inside of the skull; if there is an excess of relatively clear cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the skull, - light is scattered to different parts of the skull producing patterns characteristic of hydrocephalus. - The special transilluminating device uses a 150W projection bulb as the light source. - The device has a two-position trigger switch. The infant is taken into a dark room for the study; after a few minutes of dark adaptation the physician pulls the trigger to its first position, which turns on a red light that permits him to find the patient. The physician then points the barrel at the part of the head to be studied and pulls the trigger to the second position, which turns off the red light and turns on the intense white light used for the study. Infrared absorbing glass in the beam removes almost all of the IR radiation so that the light striking the infant is primarily visible light.
4- Transillumination is also used to detect pneumothorax (collapsed lung) in infants. The bright light penetrates the thin front chest wall and reflects off the back chest wall pneumothorax. to indicate the degree of The physician can then insert a needle attached to a syringe into the area of collapse to remove the air between the lung and chest wall, causing the lung to reinflate. The sinuses, the gums, the breasts, and the testes have also been studied with transillumination.
5- Visible light has an important therapeutic use. Since light is a form of energy and is selectively absorbed in certain molecules, it should not be surprising that it can cause important physiological effects. Many premature infants have jaundice, a condition in which an excess of bilirubin is excreted by the liver into the blood. Relatively recently (1958) it was discovered that most premature infants recover from jaundice if their bodies are exposed to visible light (phototherapy).
SampleProblem~ 1. What iscolour that has the shortest wavelenght? a. Red b. Violet c. Green d. Yellow 2. How long wavelength of violet colour? a. 620-750nm b. 590-620nm c. 380-450nm d. 450-475nm
Link of Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bHD8zYImKqA https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2Qz5Oof52Cs https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tSkAk7pSpbs