Understanding the Role of Multifidus Muscle in Spinal Health
Exploring the multifaceted role of the multifidus muscle in lumbar spine stability and control through histochemical studies and clinical comparisons. Insights into muscle changes with spinal conditions and the importance of maintaining its integrity for overall spinal health are discussed.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ProTec Spine and Sports Medicine Laney Nelson DC, DABCSP
Disclaimer.. I do not receive any moneys from the sale of the ProTec Device I have a contract that is based on funding an orphanage of my choice. That Being said: Let discuss the Elephant in the Room What should I purchase the ProTec Device 1. Protect clinical outcomes 2. Protect your health 3. Protect your market
Athletic Position / Prayer Positioning 1. Hip Flexion to 45 degrees 2. Bend knees over t4oes 3. Contract Lats 4. Contract Core 5. Engage in Recreational Activity
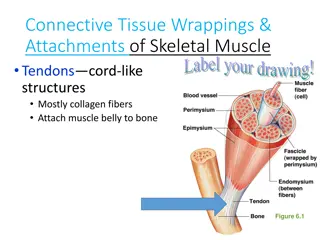
Fast Twitch- Middle Layer stability 4 layers to Multifidus Deep layer is primary fast twitch fibers Last layer to be rehabilitated
J Manual &Manipulative Therapy 2009 V16,#4 84- 91 A Morphological Comparison of the Human Lumbar Multifidus by chemical Dissection 4 distinct layers of the lumbar multifidus separated by fascial cleavage planes Conclusion: The study supports the belief that the multifidus has a significant role in control and stabilization of the lumbar spine in multiple planes of actions . Sector stabilty
Histochemistry & Morphology of the multifidus Muscle in IVD Spine 2000 25:17,2191-219 Assessed diseased and normal sides Both type I and type II smaller on diseased side when compared to normal side Type II weakened on diseased side Conclusion When SLR is positive both Type I and Type II were smaller than normal side
Histochemical Changes in Multifidus Muscle with HNP Spine 2001;26:622-626 L5 pathology Affected side Both type I and type II both decreased 6.4% decrease for type I 9.8% decrease for type II Non Affected side L4 no changes noted.
J. Spine Volume 18, #5 1993 Multifidus Pre surgical muscle biopsy compared with 5 year later biopsy Type II atrophy at 5 years did not change Type I fibers abnormal Surgical intervention failed to correct Type II correlated well with positive or negative surgical outcome Good outcome more Type II More Importantly: They are reversible and can be diminished by adequate therapy.
J of Back & Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation 19 (2006) Changes of Muscular fiber types in Erector Spinae & Multifidus in the unstable lumbar spine Deep bundles of multifidus act as a fast dynanmic brakes in the segment in which the static stabilizers failed. Type IIX react when normal ROM is exceeded to prevent abnormal shift and thus stabilize the spinal segment.
Proving the subluxation complex: Improved Activation of Lumbar Multifidus following Spine Manipulation Journal of Orthopedic & Sports Physical Therapy 2007; Vol 37, #10 Measured the multifidus at L4-5, L5-S1 at rest Manipulated the re measured 3.5% increase without manipulation exercise only 17.2% post manipulation 20.6% 24 hours post manipulation
European Journal of Spine (1998) 7:376-380 Facet Joint Remolding in generative Spondylolisthesis: an investigation of joint orientation and tropism Axial rotation creates a wrap around situation for the contralateral joint capsule Promotes degenerative fibrocartilage metaplasia Metaplasia leads to bone spur at lateral margins (wrap around affect)
Identifying Pain Generators Pain generator Spondylosis ligament Facets SI Disc Muscle / ligament Injection Program SI, Pars, Transforaminal Selective Nerve Root Flexion and Extension study Study MRI muscle fat for deactivation
Frequency and Clinical Predictors of Adverse Reactions to Chiropractic Frequency and Clinical Predictors of Adverse Reactions to Chiropractic Care in the UCLA Neck Pain Study Care in the UCLA Neck Pain Study Spine Volume 30, Number 13, pp1477-1484 2005 30.4% of participants receiving cervical manipulation developed adverse symptoms Conclusion: Our results suggest that adverse reaction to chiropractic care for neck pain are common and that despite what imprecise estimation, adverse reactions appear more likely to follow cervical spine manipulation than mobilization. Result: We have developed more and more soft tissue therapies, and instrument assisted adjusting. Our profession is moving away from manipulation while PT are moving more toward it. Rather than creating an opportunity to make it more effective
Teaching Overhand Throwing Step 1: On Guard Grip Step 2: Step back and Pivot Step 3: Balance and Hold 90/90 Step 4: T- position Throw the front site Step 5: Big Chest Chest to the Target Step 6: Release / Contract backside
Step 1: Grip and Preparation 4 seam 2 seam Cross Seam Spinners Athletic position prior to movement Head and eyes straight Shoulder back
Step 2: Step Back & Pivot Step 1: Left foot step back at 15 degree off rubber Step 2: While front foot pivots from pedicular to partallel to rubber Step 3: As the hands come up the right foot will pivot to complete parallel.
Step 3: Balance and Hold Key is front side is quiet Quad contracts lower leg is quiet 1. Train with ankle weights with reps to get to desired pitch count Back is Straight Head is not ducked Shoulders not rolled Key and practice is to a balanced point
Step 4: T position Front site T position for young kids and beginners Get on top of the fast ball Front gun site on the target Elbow lead if older more experienced thrower Go from shoulder lead to 90 back shoulder then to 90/90
Step 5: Big Chest From T position Thumb comes up and elbow down fast creating the plate position Use rubber banding attached to fence to train muscle memory From Elbow Lead Position: Elbow down to side of chest hard - hand comes up to plate position Pulling elbow down will accelerate the chest to the forward position Creating a lag time for the throwing hand to come to a 90/90 position Elbow hitting chest will create a sound
Step 6: Release Pump Handel With chest acceleration throwing hand begins follow through Throwing hand goes on to be outside of set let Once release is complete then hands go to defensive positon Set leg is 15-30 degrees from perpendicular to home plate Contract buttock and push off aggressively on push off leg Push off leg becomes the pump handle Train kids by assuming release position and having coach lift back left after push off
Home & Office Rehabilitation 5 Commercial exercise Use a 55 cm ball Every 30 minutes TV show has at least 5 breaks for doing sets Daily Fast Twitch Exercise Prayer one and two footed Banding up down / in out Supine Core single leg, Tow and three points of contact Apply fast twitch principles
Thank you.. Feel free to contact me at drlaneynelson@gmail.com 801-232-3511