Understanding the Prisoner's Dilemma and Game Theory
Delve into the intricacies of the Prisoner's Dilemma, a classic example of game theory, where rational individuals may fail to cooperate even when it's in their best interest. Explore Nash Equilibrium, real-world applications, and strategies to solve such dilemmas through external forces, negotiation, and legal responses.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Law, Economics and the Prisoners Dilemma Tim Mason
Red v Blue Game Group A Red Red Blue Blue Group B Red Blue Red Blue Score A +3 -6 +6 +3 Score B +3 +6 -6 +3
Game Theory Analyzing the decisionmaking process when there are more than one decision-makers where each agent s payoff possibly depends on the actions taken by the other agents.
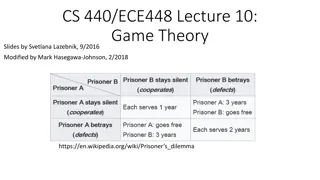
The Prisoners Dilemma Two members of a criminal gang are arrested and imprisoned. Each prisoner is in solitary confinement with no means of communicating with the other. The prosecutors lack sufficient evidence to convict the pair on the principal charge. Simultaneously, the prosecutors offer each prisoner a bargain. Each prisoner is given the opportunity either to: betray the other by testifying that the other committed the crime, or to cooperate with the other by remaining silent.
What are we seeing? Why might 2 completely rational individuals fail to cooperate even when it is in their best interests to do so?
Nash Equilibrium Nash equilibrium: a stable state of a system involving the interaction of different participants, in which no participant can gain by a unilateral change of strategy if the strategies of the others remain unchanged.
The Prisoners Dilemma as a model for real world problems What kinds of real world situations might the model be used to describe? Situations in which two entities could gain important benefits from cooperating or suffer from the failure to do so, but find it merely difficult or expensive, not necessarily impossible, to coordinate their activities to achieve cooperation. Arms buildup CO2 emissions and global warming Airport baggage carousels Drug use in sport Tragedy of the Commons (overfishing, overfarming)
What responses are there to solve the dilemma? Introduce an external force to provide sanctions Introduce Negotiation and cooperation, or reduce barriers to communication and negotiation. Legal Responses: Contract Law (private parties) International treaties (States) Property Rights
How does the law respond to problems such as this? CONTRACT LAW Expectation damages forward looking. Where would you have been if the agreement had been carried out? TORT LAW (private wrongdoing) Backwards looking. Restorative Justice: putting you back in the position you were in before the wrong was committed. CRIMINAL LAW Retribution (punishment), deterrence, rehabilitation PROPERTY LAW Assigning property rights to private parties. Allowing negotiation from that point.
Difference between Red v Blue game and Prisoner s Dilemma?
Arm Exercise Negotiation