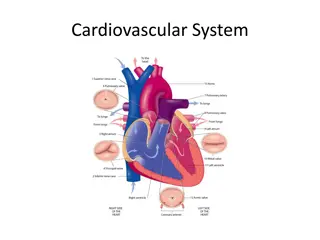
Understanding the Control of Heart Beat
The heart controls its own beat through the cardiac cycle initiated by the Sinoatrial node (SA node). This myogenic system allows the heart to contract and relax without the need for external impulses. The cardiac muscle responds to electrical waves, leading to synchronized contractions of the atria and ventricles. Any erratic contractions, like in fibrillation, can be corrected with electric shock treatment to restart the SA node rhythm.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Heart Control of the Heart Beat
The Heart Beat The heart is made up of cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle is myogenic, which means it naturally contracts and relaxes. Therefore, it receives no impulse from a nerve to make it contract.
The Heart Beat The cardiac cycle is initiated by a small patch of muscle called the Sinoatrial node (SAN) or pacemaker. This node sets the rhythm for all the other cardiac muscle. Pacemaker cells have an inbuilt rhythm that is faster than the other cells in the heart.
The Heart Beat The SA node sends out an excitation wave of electrical activity over the atrial walls. The cardiac muscle responds to this wave by contracting at the same speed as the SAN. This results in both atria contracting simultaneously.
The Heart Beat There is a delay between atrial contraction and ventricular contraction. Fibres between the two chambers that do not conduct the excitation phase cause this delay. Therefore, the wave is conducted through a patch of fibres in the septum known as the atrio-ventricular node or AVN.
The Heart Beat After about a delay of 0.1 seconds the AV node passes the wave onto another set of conducting fibres that run down the centre of the septum between the ventricles called the Purkyne fibres.
The Heart Beat The wave is then transmitted (very rapidly) down to the bottom of the septum, where it spreads through the ventricles walls in an upward direction. This movement causes the muscle to contract and the ventricles squeeze the blood out of the heart.
The Heart Beat Fibrillation is the result of the contractions of the atria and ventricles becoming erratic and out of sync. Using electric shock treatment to restart the SA node can rectify the problem.
This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.