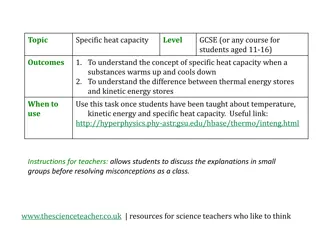
Understanding Temperature, Energy, and Heat Transfer
Explore the concepts of temperature conversion, kinetic energy, total energy in gases, heat transfer mechanisms, and the impact of mass and specific heat capacity on temperature changes. Discover how energy affects phase changes and learn about boiling water dynamics.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The temperature in this classroom is about 73oF. What is that in Celsius? Kelvin? Celsius: 22.8oC Kelvin: 295.93 K
When measuring Temperature, what exactly are we measuring about the substance? Temperature is the measurement that relates to the average Kinetic Energy of a particle i.e. the motion of the particles. ?? =1 2? ?2=3 2???
Total Energy in a gas (Internal Energy) is the total Kinetic Energy of all the gas particles. ? = ?? = ??? =3 2???? =3 2??? =3 2??
3 types of Heat (Thermal Energy Exchange) Conduction heat transfer through physical contact of objects Relies on the vibrational motion of the molecules of the solid Convection The movement of hot and cold materials, mainly fluids, due to the differences in densities Responsible for Continental Drift, weather patterns Radiation Transfer of energy through light. How the energy from the sun reaches earth. Does not require a physical medium to travel through.
When Heat is added to removed from a material, its temperature changes. How much the temperature changes compared to how many Joules are added or removed depends on 2 factors: 1) Mass 2) Specific Heat Capacity ? = ?? ?
A 2 Liter bottle of water (1 kg/L) starts at room temperature (20oC) and gains energy through a heating coil that is producing 200 W (J/s) of power. How long does it take for the water to boil?
To change the state of matter of a material requires energy. How much energy is required depends upon the mass of the material and the Latent Heat. *Note the lack of Temperature here. When a material is going through a phase change, what happens to the temperature during that transition? ? = ??
Take that same 2 L bottle of water and now it is boiling with the 200 W power supply. How long does it take to completely boil away?