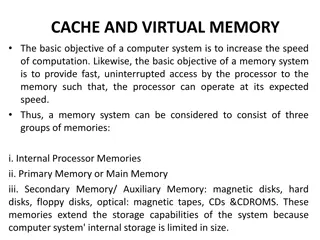
Understanding Semantic Effects in Verbal Short-term Memory
Investigating the impact of semantic knowledge and similarity on verbal short-term memory, this study delves into how imageability of words influences recall. Key findings highlight the influence of semantic relatedness and the imageability effect on memory retention, shedding light on the mechanisms underlying verbal information processing.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Semantic Effects In Verbal Short-term Memory: Where Do They Come From? Kowialiewski Benjamin Majerus Steve
Introduction Verbal short-term memory: temporary storage of verbal information Recall
Introduction Semantic knowledge has a dramatic influence on vSTM span. A A A B B B Related A B C D E F Unrelated
Introduction Semantic similarity effect A A A B B B Ex: leaf tree branch arm leg hand A B C D E F Ex: lake hand road flute mask dress
Introduction A A A B B B High imageability words A B C D E F Low imageability words
Introduction Imageability effect A A A B B B Ex: pork waffel leg pencil ball cage A B C D E F Ex: stress wave tax glory gender smart
Introduction Martin, Saffran, & Dell (1996) Cowan (2001) Oberauer (2002) Majerus (2013) Long-term memory Focus of attention
Introduction Martin, Saffran, & Dell (1996) Cowan (2001) Oberauer (2002) Majerus (2013)
Introduction Martin, Saffran, & Dell (1996) Cowan (2001) Oberauer (2002) Majerus (2013)
Introduction Martin, Saffran, & Dell (1996) Cowan (2001) Oberauer (2002) Majerus (2013)
Dell (1986) Martin, Saffran & Dell (1996) Introduction RAT DOG CAT MAT LOG FOG
Dell (1986) Martin, Saffran & Dell (1996) Introduction: the semantic similarity effect RAT DOG CAT MAT LOG FOG
Dell (1986) Martin, Saffran & Dell (1996) Introduction: the semantic similarity effect RAT DOG CAT MAT LOG FOG
Dell (1986) Martin, Saffran & Dell (1996) Introduction: the semantic similarity effect RAT DOG CAT MAT LOG FOG
Dell (1986) Martin, Saffran & Dell (1996) Introduction: the semantic similarity effect RAT DOG CAT MAT LOG FOG Decay!
Introduction Interactive activations should continue to occur when the focus of attention is taken away from linguistic representations.
Dell (1986) Martin, Saffran & Dell (1996) Introduction: the semantic similarity effect RAT DOG CAT MAT LOG FOG
Method: Experiment 1 Ex: leaf tree branch arm leg hand Ex: lake hand road flute mask dress
Method: Experiment 1 Ex: leaf tree branch arm leg hand Ex: lake hand road flute mask dress
Method: Experiment 1 Recall Recall Interference Recall Recall Interference Recall Interference Recall
Method: Experiment 1 5 seconds Interference 45 45 42 39
Method: Experiment 1 RAT DOG CAT MAT LOG FOG
Method: Experiment 1 RAT DOG CAT MAT LOG FOG
Results: Experiment 1 1.0 1.0 N o interference Interference 0.9 0.9 0.8 0.8 0.7 0.7 P ro p o rtio n R e ca lle d P ro p o rtio n R e ca lle d 0.6 0.6 0.5 0.5 0.4 0.4 0.3 0.3 Related 0.2 0.2 Unrelated 0.1 0.1 0.0 0.0 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 S e ria l P o sitio n S e ria l P o sitio n Interference x Semantic: BF10 = 4688 N = 30
Method: Experiment 2a Imageability effect A A A B B B Ex: pork waffel leg pencil ball cage A B C D E F Ex: stress wave tax glory gender smart
Method: Experiment 2a RAT DOG CAT MAT LOG FOG
Results: Experiment 2a 1.0 1.0 N o interference Interference 0.9 0.9 High imageability 0.8 0.8 Low imageability 0.7 0.7 P ro p o rtio n R e ca lle d P ro p o rtio n R e ca lle d 0.6 0.6 0.5 0.5 0.4 0.4 0.3 0.3 0.2 0.2 0.1 0.1 0.0 0.0 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 S e ria l P o sitio n S e ria l P o sitio n Interference x Imageability: BF01 = 1.93 N = 30
Method: Experiment 2b Recall Recall Interference Recall Recall Interference Recall Interference Recall
Method: Experiment 2b Recall Recall Recall Recall Interference Recall Interference Recall Interference
Results: Experiment 2b 1.0 1.0 N o interference Interference 0.9 0.9 High imageability 0.8 0.8 Low imageability 0.7 0.7 P ro p o rtio n R e ca lle d P ro p o rtio n R e ca lle d 0.6 0.6 0.5 0.5 0.4 0.4 0.3 0.3 0.2 0.2 0.1 0.1 0.0 0.0 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 S e ria l P o sitio n S e ria l P o sitio n Interference x Imageability: BF01 = 3.98 N = 30
Discussion The semantic similarity effect was stronger under interference. This was not observed as regards the imageability effect.
Discussion RAT DOG CAT MAT LOG FOG
Discussion CAT LOG
Discussion CAT
Discussion CAT
Discussion CAT
Discussion Imageability effect Normal pace Slow pace Campoy, Castell , Provencio, Hitch, & Baddeley (2015)
Discussion Kowialiewski & Majerus (2018), JML
Conclusion Interactive activation can occur automatically, when attention is driven away from vSTM content. This is not the case as regards high imageability words, whose semantic features require deeper activation within the linguistic system.
Discussion Evans, Lambon Ralph, & Woollams (2012)
Dell (1986) Martin, Saffran & Dell (1996) Introduction DOG CAT MAT LOG FOG RAT M C D A O G T
Discussion CAT
Discussion CAT