Understanding Polarizations in Optics
Explore the concepts of S and P polarizations in optics, delve into Fresnel Equations for perpendicular and parallel electric fields, understand boundary conditions for electric and magnetic fields at interfaces, and learn about reflection and transmission coefficients for perpendicularly and parallel polarized light.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
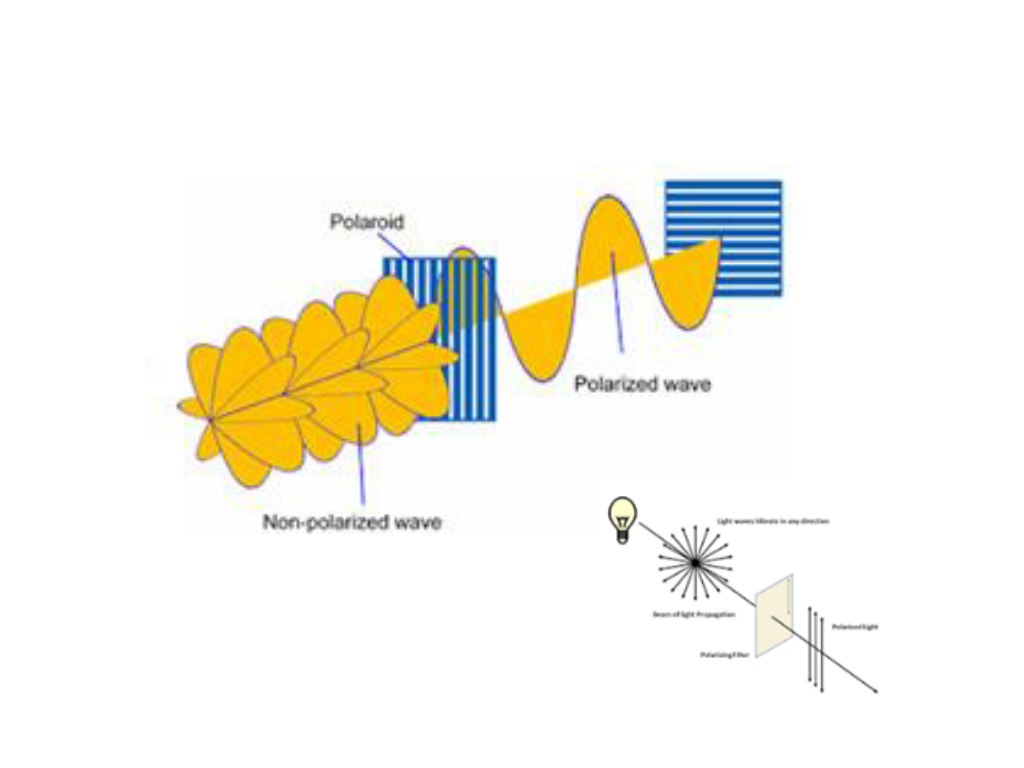
Definitions: S and P polarizations The amount of reflected (and transmitted) light is different for the two different incident polarizations.
Fresnel EquationsPerpendicular E field Augustin Fresnel was the first to do this calculation (1820 s). We treat the case of s-polarization first:
Boundary Condition for the Electric Field at an Interface: s polarization
Boundary Condition for the Magnetic Field at an Interface: s polarization -Hi(y=0) Cos i +Hr(y=0) Cos r = -Ht Cos t
Reflection and Transmission for Perpendicularly Polarized Light E0i+E0r=E0t -H0i Cos i +H0r Cos r = -H0t Cos t i = r , H=nE/ co
Reflection & Transmission Coefficients for Perpendicularly Polarized Light These equations are called the Fresnel Equations for perpendicularly polarized (s-polarized) light.
Fresnel EquationsParallel electric field Now, the case of P polarization:
Reflection & Transmission Coefficients for Parallel Polarized Light H0i -H0r=H0t E0i Cos i -E0r Cos r = E0t Cos t These equations are called the Fresnel Equations for parallel polarized (p-polarized) light.
Reflection Coefficients for an Air-to-Glass Interface
Reflection Coefficients for a Glass-to-Air Interface
