Understanding Nutrition and the Human Digestive System
This quiz tests your knowledge on nutrition in the human body and the digestive system. It covers topics such as omnivores, absorption processes, enzymes, and the functions of various organs like the pancreas and intestines. Explore these concepts to enhance your understanding of how food is processed and utilized by the human body.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
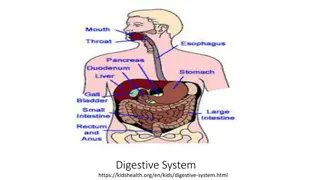
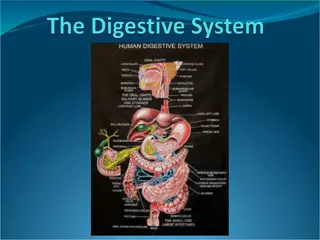
3.3.3 Nutrition in the Human 3.3.4 Human Digestive System 1 Follow-Me iQuiz
Q. What is meant by the term omnivore? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is meant by absorption? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is an autotrophic organism? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is meant by the term digestion? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is peristalsis? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Why is a low pH important in the stomach? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. The passage of the products of digestion from the intestine to the blood is called ... Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is a carnivore? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Why is fibre important? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name an enzyme that is involved in the digestion of fat. Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. State a role of beneficial bacteria in the alimentary canal. Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. State two ways in which the villi are adapted for the absorption of soluble foods. Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is a protease enzyme? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is a herbivore? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is a heterotrophic organism? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What are the final products of the digestion of a protein? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name a carbohydrate-digesting enzyme in the human alimentary canal Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is the role of bile in fat digestion? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Where in the alimentary canal does this amylase act? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Describe two functions of bile in relation to digestion. Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Where is lipase produced? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What are the products of fat digestion? Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. State the product(s) of amylase digestion. Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name a structure in the human digestive system, other than teeth, which is involved in mechanical digestion. Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Mouth and Small intestine Absorption Emulsification Amino acids Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH; Makes alkaline Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Amino acids Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Muscular contractions to move food Muscular contractions to move food Amylase Fatty acids and glycerol Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that eats both animals and plants Kills germs; Optimal pH for enzymes Pancreas Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on animals only Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Thin-walled; Lacteal Prevent constipation; Prevent bowel cancer; For peristalsis Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Animal that feeds on plants only Production of vitamins; Inhibition of pathogens Lipase Tongue; Oesophagus; Stomach; Small intestine Breaking down food Makes its own food Tongue; Oesophagus; Breaking down food Makes its own food Uses food already made by other organisms Stomach; Small intestine Breaks down protein Maltose Uses food already made by other organisms Breaks down protein Maltose
CONGRATULATIONS You re Brilliant
Incorrect Please CLICK on THIS BOX to Try Again Please CLICK on THIS BOX to Try Again