Understanding Mendel's Genetic Vocabulary
Explore essential genetic terms such as Trait, Gene, Allele, Genotype, Phenotype, Dominant Allele, Recessive Allele, Heterozygous, and Homozygous in the context of Mendel's groundbreaking work on inheritance patterns. Understanding these terms is crucial for comprehending how genetic traits are passed down through generations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
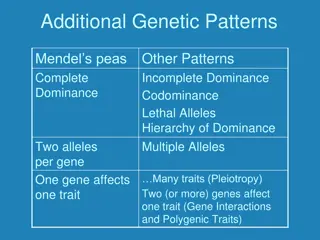
Vocab for understanding Mendel
1. Trait: Specific characteristic (seed color, plant height) Generally controlled by 2 alleles of a gene
2. Gene: Factors that determine traits (Sections of DNA)
3. Allele Different forms of a gene
4. Genotype: Combination of alleles inherited from parents
Phenotype: Physical appearance of the genotype (adjective) Ex/ purple petals, white petals, freckles, blonde hair, brown hair, dimples 5.
Genotypes and Phenotypes can be found by determining the alleles that were passed down from the parents
6. Dominant Allele: Produces a dominant phenotype in individuals who have at least one copy of the dominant allele Represented by a capital letter P = purple petal color
7. Recessive Allele For a recessive allele to produce a recessive phenotype, the individual must have TWO copies of the recessive allele Represented by a lowercase letter p = white petal color
Heterozygous: Organisms that have two DIFFERENT alleles for the same trait (hybrid) The presence of the dominant allele will produce the dominant phenotype 8.
9. Homozygous: Organisms that have two IDENTICAL alleles for a particular trait (purebred) The phenotype will be determined by whether they have two dominant alleles or two recessive alleles
10. Following traits through generations: P : Parent generation F1: 1st filial (1st set of offspring from parents) F2: 2nd filial (offspring of second generation)
11. Punnett Square: Grid that shows probable outcome of a genetic cross (fertilization)