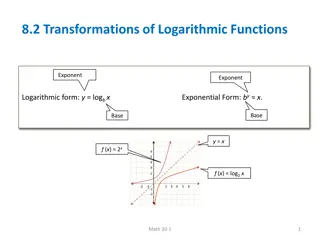
Understanding Forms of Energy and Energy Transformations
Exploring the different forms of energy and how they can be transformed according to the Law of Conservation of Energy. The relationship between potential and kinetic energy is explained with clear examples, highlighting how energy can be stored or in motion. Potential energy is described in objects ready to return to their original state.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Forms of Energy Add these notes to your graphic organizer. Refer to textbook chapter 9, section 1 for additional information
What do we need to know? S8P2. Students will be familiar with the forms and transformations of energy. a. Explain energy transformation in terms of the Law of Conservation of Energy.
The law of conservation of energy states that: Energy is never destroyed Energy is never created Energy may be transformed or converted from one form to another Energy is constantly changing forms
What ELSE do we need to know? b. Explain the relationship between potential and kinetic energy. http://www.animationplayhouse.com/dancing_giraffees.gif How about a little music?
http://www.animationplayhouse.com/dancing_giraffees.gif http://t2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcQJwbgxstvCrGaLAxqyO_kL2YshpWsI1znpU-hD1zf-8BQqNEPo kinetic energy potential energy
potential energy kinetic energy http://www.animationplayhouse.com/dancing_giraffees.gif
kinetic energy http://www.animationplayhouse.com/dancing_giraffees.gif potential energy
Kinetic energy Potential energy
Kinetic Energy Energy of motion Depends on speed mass More speed = more KE More mass = more KE
Potential EnergyStored energy Energy of position, shape, or condition More weight = more PE More height = more PE girl on a swing pendulum
Potential energy is found in objects that want to bounce back into their natural shape when they are stretched, squished, or turned. sling shot
c. Compare and contrast the different forms of energy (heat, light, electricity, mechanical motion, sound) and their characteristics. Forms of Energy include:
Mechanical (Motion) Energytotal of potential and kinetic energy energy caused by objects that are moving
Greatest potential energy at top (slowest/stopped) Greatest kinetic energy at the bottom while going the fastest
Watch the juggler Michael Davis at Ford's Theater This theater is in Washington, D.C. President Abraham Lincoln was assassinated while watching a show from one of the upper balcony seats in this very same theater. President Ronald Reagan and his wife are enjoying this show. http://www.youtube.com/embed/n6mbW-jMtrY?feature=player_detailpage
Thermal energy (heat)the total motion of the atoms and molecules within a substance ex. Atoms move faster in hot water than ice Hot water-faster Ice-slower
Gravitational potential energyenergy stored because of where it is placed (higher = more PE) (Depends on weight and height)
Chemical energy energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules (released during chemical changes) http://myzerowaste.com/wp-content/uploads/2009/12/batteries.jpg
Sound energyenergy caused by an objects vibrations (It travels in waves but cannot move through empty space.)
Radiant energy (light)produced by the vibrations of electrically charged particles that travel in waves. Can travel through a vacuum (empty space) ex. Sunlight, X-rays, lamps, see p.636 http://mrmackenzie.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2010/11/Hand.jpg http://api.ning.com/files/15fqs3JP5yL9n2FbooDsBT1OjHY8FTTPxrUcOhmLDqKbejq6ysDXsGjC-8Ph45p2JAr9INTRBvmkAo6eke8WJ3UFeWoUt640/sun.gif http://dubeysantiques.files.wordpress.com/2011/11/lighting_lamps_japanese_satsuma_pair.jpg
Nuclear energystored energy that comes from the nucleus of an atom. Released when atoms are split apart (fission) or joined together (fusion) ex. nuclear power plants
Now youve got them all. Study them tonight!
Resource websites: http://www.eia.doe.gov/kids/energy.cfm?page=about_forms_of_energy-basics http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ks2bitesize/science/physical_processes/