Understanding Complements in Grammar
A comprehensive guide to understanding complements in grammar, covering direct objects, indirect objects, subject complements, and object complements. Discover how complements complete the meaning of verbs and identify essential elements in a sentence. Explore the different types of complements and their roles in sentence structure.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
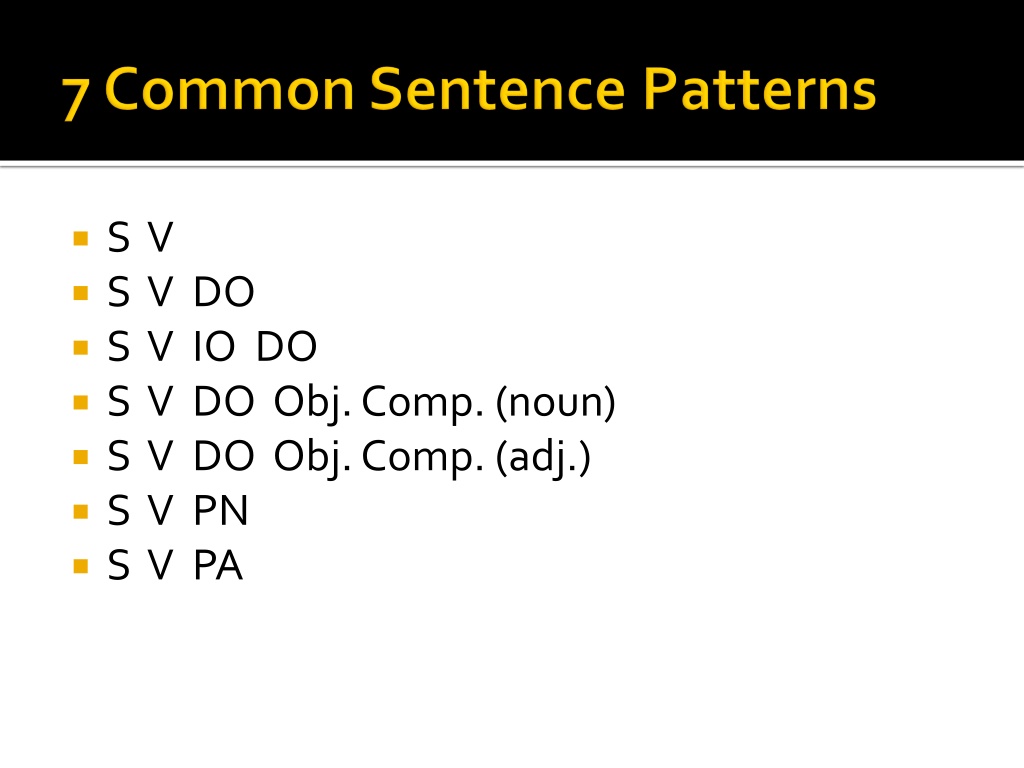
S V S V DO S V IO DO S V DO Obj. Comp. (noun) S V DO Obj. Comp. (adj.) S V PN S V PA
A word or group of words that completes the meaning of the verb There are four kinds of complements Indirect objects Direct Objects Object complements Subject Complements
The word complement is only applied to pronouns, nouns, and predicate adjectives. Adverbs and adverb phrases are not complements.
DO answers the question what? or whom? After an action verb IO answers the question to whom? Or to what? or for what? after an action verb Find your action verb(s) first
A sentence must have a DO to have an IO IOs will always appear between the verb and DO
Word or word group that completes the meaning of the ACTION VERB by identifying or modifying the DIRECT OBJECT 1. Look for ACTION VERB first 2. Find the DIRECT OBJECT 3. Look for the Objective Complement
Engineers find plans essential. (adjective) Nations often make their bridges symbols. (noun) Only found in sentences with a DO and these verbs (below) or a similar verb with the general meaning of make or consider appoint, choose, elect, prove, call, consider, name, vote
Completes the meaning of a LINKING VERB and identifies or modifies the SUBJECT Predicate nominative-noun or pronoun following a linking verb & refers to the same person or thing as the subject of the verb Predicate adjective-an adjective that follows a linking verb & modifies the subject of the verb
To determine whether a verb is being used as a linking verb or action verb, use am, are, or is, for the verb. If the sentence makes sense, then the original verbs is a linking verb. The kids looked sad. The dog looked at me.
Subject Complements 1. Look for the LINKING VERB 2. Find the SUBJECT of the linking verb 3. Look for the COMPLEMENT Is it a noun or adjective? (use dictionary) Nouns are predicate nominatives Adjectives are predicate adjectives
What questions does the direct object always answer about the verb? 1. What questions does the indirect object always answer about the verb? 2. What does the object complement modify? 3. What kind of verb can have a DO? 4. What kind of verb can have a subject complement? 5. What must you have before you can have a IO? 6.
It is the form a noun or pronoun takes to indicate its use in a sentence There are 3 cases: Nominative Objective Possessive
The form of a noun is the same for nominative and objective case Whether the noun is the subject or an object, it stays the same For possessive, it usually adds an apostrophe and an s
Nominative When it is the subject The cowran to the boy. Objective When it is an object The boy hit the cow.
A personal pronoun refers to the person speaking First person Second person Third person
Most have 3 forms, but the one it takes depends on its use in the sentence. They indicate gender, number and person
1. The change in form of pronouns to show their relationship to other words in the sentence is called case. he his him All 3 pronouns can be used to refer to the same person. Their difference in form is due to their difference in _____________. 2. A. I recognized him. B. He recognized me. The pronoun I in sentence a and the pronoun me in sentence b means mean the same person. Are the pronouns I and me in the same case? _______ 3. A pronoun is in the nominative case when it fits before an action verb as its subject- he laughed; she fell; we won; they lost. Underline the nominative pronoun: They blamed us. 4. ________ invited Rosa. Underline 3 pronouns that are in the nominative case because they could serve as the subject in the sentence above. I him she we them her 5. A pronoun is in the objective case when it fits after an action verb as its direct object- pushed me; stopped him; asked her; beat us; called them. Underline the objective pronoun: They blamed us.
1. Use the nominative case of a pronoun when it is used as the subject of a verb. Underline the correct pronoun: You and (I, me) can study together. 2. Use the objective case of a pronoun when it is used as the object of a verb or a preposition. Underline the correct pronouns: Several friends save (them, they) for (me, I). 3. You would never say, Him pushed the car or Me pushed the car ; so don t make the same mistake by saying, Him and me pushed the car. Underline the correct pronouns: (He, Him) and (I, me) counted the votes. 4. When you use pronouns in pairs or when couple a pronoun with a noun, use the same case that you would use if the pronouns were used singly. These flowers are from Pete. These flowers are from me. Underline the correct pronoun: These flowers are from Pete and (I, me). 5. The Smiths will call for you. We will call for you. Underline the correct pronoun: The Smiths or (us, we) will call for you.
Correct the following sentences if they need to be corrected. 1. Me will go to the mall tomorrow. 2. Crystal and me are giving a party. 3. Her got a new hairstyle. 4. Randall and him both got new sneakers.