Understanding Classical Mechanics and Fields in Physics
Explore the concepts of radiation, matter, fields, Hamiltonian, and more in classical mechanics with a focus on velocity-dependent potentials and conservative systems. Dive into the detailed discussions on gauge theory, Coulomb gauge, magnetic fields, and Hamiltonian operators within the framework of physics.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
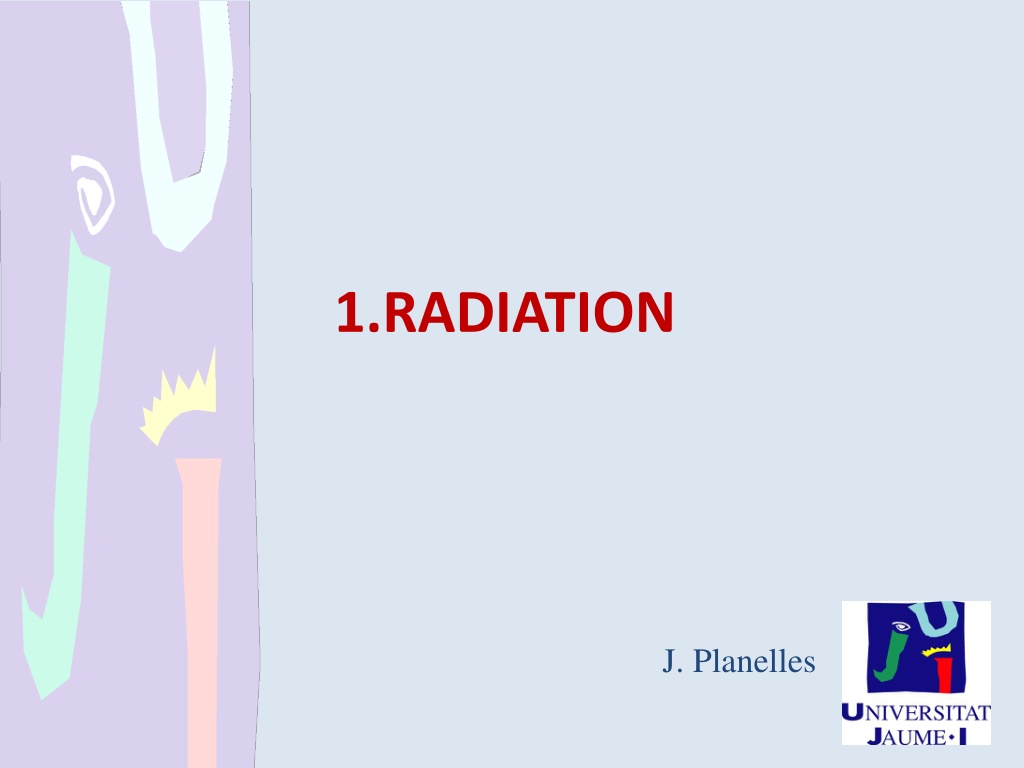
1.RADIATION J. Planelles
2.Matter and Field J. Planelles
Classical Mechanics: an overview Newton s Law Conservative systems Lagrange equation
Velocity-dependent potentials Time-independent field No magnetic monopoles
Velocity-dependent potentials: cont. kinematic momentum: canonical momentum: Hamiltonian:
Conservative systems: V(x,y,z) & L = T - V canonical momentum: kinematic momentum: Hamiltonian:
Gauge ; We may select : Coulomb Gauge :
Magnetic field: summary No magnetic monopoles: vector potential velocity-dependent potential: No conservative field: Lagrangian: kinematic momentum Canonical momentum: Hamiltonian: Coulomb gauge: Hamiltonian operator:
3. Electron-photon interaction (selection rules and resonanace) J. Planelles
Hamiltonian of a charge in an electromagnetic field Set of charges {qi}:
Time-dependent perturbation theory (cont.) Transition probability: Taylor expansion:
Time-dependent perturbation theory (cont.) resonance: resonance: selection rule:
Time-dependent perturbation theory (cont.) First (and larger) perturbation term: (with q = - e, m of electron) Integral involved: Single photon transition Spontaneous emission
Time-dependent perturbation theory (cont.) After some algebra:
Time-dependent perturbation theory (cont.) Second (smaller) perturbation term: (q = - e, m of electron) terms : two-photon transitions two-photon transitions: weak ( use LASER). e.g. Raman