Understanding Brain Roles and Sensory Preferences in Learning
World events are reshaping education towards e-learning, emphasizing the importance of quality in how information is processed for remote learning. The intricate workings of the brain, with its 100 billion brain cells and 500 trillion connections, play a significant role. Explore brain roles in information processing, sensory preferences, and organizing styles to enhance learning outcomes in the digital era.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
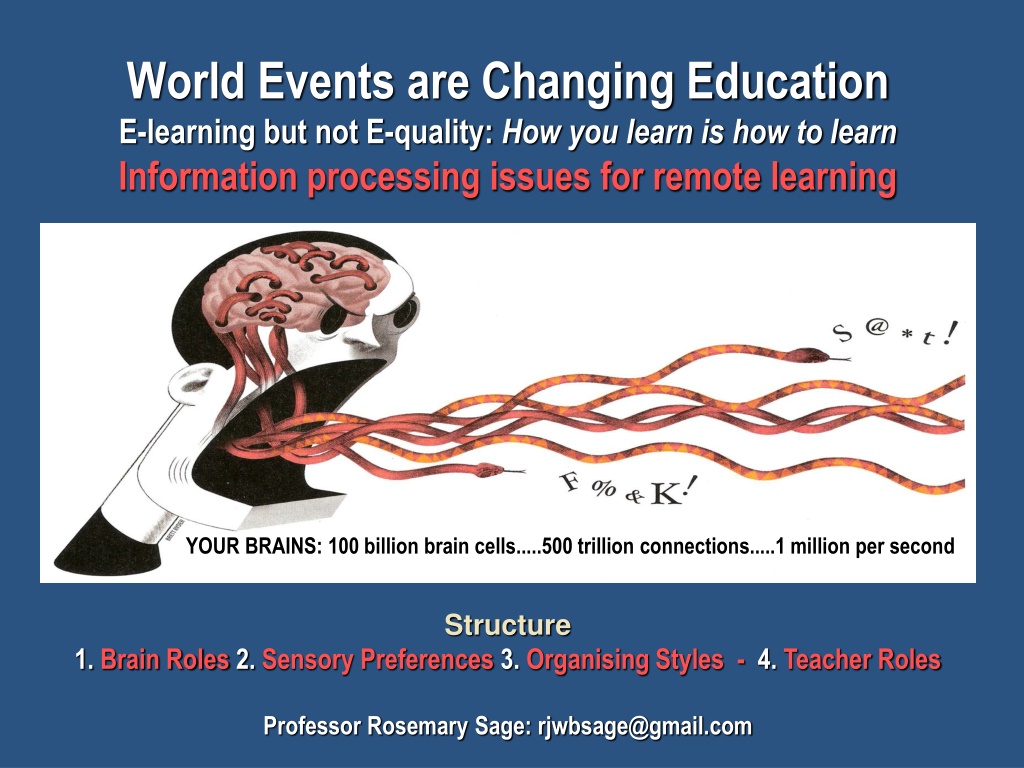
World Events are Changing Education E-learning but not E-quality: How you learn is how to learn Information processing issues for remote learning YOUR BRAINS: 100 billion brain cells.....500 trillion connections.....1 million per second Structure 1. Brain Roles 2. Sensory Preferences 3. Organising Styles - 4. Teacher Roles Professor Rosemary Sage: rjwbsage@gmail.com
1.Brain Roles in Information Processing The R seeingbrain processes images holistically - (4-7+ yr) The L saying/hearing brain processes words& parts (7+ yr) Holistic understanding Parts / facts analyses synthesises Education favours L brain learning (Sperry 1968). Students with problems have limited L or R brain growth. You cannot say what you see if the L & R brain do not connect.
Test out your 2 brains! Do they work together? See the word but Say the colour Most have R (visual) or L (verbal) brain dominance, reflected in their strengths Cross-laterals with no specific dominance take longer to process information.
2. Organising Styles R top down + L bottom up brain processing grasps information R works on outline, L on detail. How do work out the image? Miller s Puzzle (1986) We deliver information in a preferred R or L way (50% R & 50% L) Those opposite to us have more problems understanding our talk/text. Present information for both strategies. Allow visuals to be absorbed first before explaining, to help those with problems using both brain sides together.
3. 3. Sensory Preferences:Visual Processing What do you see?... .depends on which retina cells pick up the image & transmit it to the brain. Different cells pick up diverse colours, contrasts, back/foregrounds. Some deal with centralvision others peripheral. Images are interpreted differently by people. Teachers beware!
PROCESSING WORDS YOU HEAR Think of a white flower on a dark background ????????????? Words mean different things to us all We have a 3 min. attention span for speech Break up talk with tasks Give overview, topic structure & review Personal stories engage interest
PROCESSING MOVEMENT, TOUCH PROCESSING MOVEMENT, TOUCH AND POSITION IN SPACE AND POSITION IN SPACE How well can you read body language? 1. I can handle this easily 2. Let me think about this for a while 3. That will never work We all process haptic information differently
HOW DO YOU PROCESS, REPRESENT AND ORGANISE INFORMATION? We hear, we forget; We see, we remember; We do we understand - Chinese Proverb People preferences: SIGHT (29%) SIGHT (29%) VISUAL SOUND (34%) SOUND (34%) VERBAL Remember! We only give 20% full attention TOUCH, MOVEMENT TOUCH, MOVEMENT POSITION IN SPACE (37%) POSITION IN SPACE (37%) KINAESTHETIC / HAPTIC Note: use of senses depends on task. In sport kinaesthetic sense predominates Impact of message: 7% words, 38% voice, 55% gestures, movement, context Albert Mehrabian, 1969
How do we assemble information? Imagination, association, assumptions We must visualise to recall & understand (R brain) The placestrick: Take an imaginary walk in your house: Open the front door Walk into the hall Go to the kitchen Climb the stairs Enter the bathroom Wander to the bedroom! Now listen to the story!
Thinking: R brain creates possibilities L sequences steps to goal How can you pick the apples? R brain creative thinking Seek ladder Climb Tree Find stick to throw Blow apples Seek tallest person L brain critical thinking Select tallest Target apples Lift arms & pick Hand round Enjoy eating If apples are bigger than plums & plums bigger than currants apples are bigger than currants
Right brain fills in information/opinion gaps in talk/text Left brain sequences information logically Algy met the bear The bear met Algy It was bulgy The bulge was Algy What information is missing? In a UK city primary school - all entrants had thinking & language 2 + years below age. In senior school - 80% at 5-6 year level at age 12
MODEL TO ASSEMBLE INFORMATION & OPINION (Sage) 7 stages to the development of ideas (Sage) Clarity making ideas clear and interesting Record: generate ideas Recite: arrange ideas Refer: compare ideas Replay: sequence ideas in time Recount: Introduce, describe, discuss Report: Introduce, describe, discuss, reflect Relate: setting, characters, actions , results, reactions Content ideasrelevant for audience Conduct impression ideas make on others Convention rules governing the exchange of ideas 5 conversation moves must be in place for narrative thinking & structure 1. Follows conversation thread 2. Asks Questions 3. Answers Questions 4. Assembles &contributes ideas 5. Shows maintenance behaviour eye contact, smile, head nod
Japan develops R & L brain through formal talk activities & brain gym In this school pupils teach to develop narrative language & thinking. They give a lesson overview, structure &review with each member sharing their view of the content in the final part of the class.
4. Teacher Role in Developing Narrative Ideas 7 Levels (Sage) Development Tasks: Topic COPING WITH DISASTERS RECORD RECORD produce a range of ideas List items for survival. Decide 3 most urgent to provide. Make a poster Make a poster RECITE RECITE - arrange ideas but not necessarily in order What are your feelings & views about disasters? Arrange these on a poster Arrange these on a poster REFER REFER compare ideas- judge similarities/differences Compare 2 message systems, e.g. Morse Code & Heliograph Make a poster Make a poster REPLAY REPLAY - order ideas appropriately in time sequence How do you revive a drowning person with kiss of life ? Provide pictures Provide pictures & & written instructions written instructions RECOUNT RECOUNT explain ideas How? Why? Alice is trapped & injured on a roof & water rising. She needs carrying to safety. Draw images Draw images - - explain how how to do a to do a fireman s lift. fireman s lift. W explain it safe? Why hy is is it safe REPORT REPORT - introduce, describe & discuss ideas Report on a disaster for a news programme. Tell a story with pictures Tell a story with pictures - - review situation review situation RELATE RELATE produce ideas in a setting + events, actions, results, reactions Choose a disaster picture -many on the web. Tell story story - - setting, events, results setting, events, results & & reactions Tell reactions
Resting my R & L brain! Present for all information processing ways & narrative levels 75% children & adults - limited thinking & communication Give overview, structure & final review, with stories to aid understanding. Present visuals first- then explain. 3 min. is limit for speech attention - break with tasks. Only by sharing knowledge are you aware of understanding it. Give time for learners to say what they have learnt from a session. Articles to support: E-learning not E-quality; Does Technology Help or Hinder; Reign of Error, Reign of Terror