Transcriptomic Changes in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of International Space Station Crew Members
The study analyzed transcriptomic changes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of International Space Station crew members. Blood samples were collected before and after spaceflight, and differentially expressed genes were identified using RNA-seq analysis. Several genes, including CDKN1A (p21) and NF-κB-related genes, showed changes in expression levels. Upstream regulators analysis indicated activation of NF-κB genes, suggesting potential adaptation during the space mission.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
TRANSCRIPTOMIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD MONONUCLEAR CELLS OF INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION CREWMEMBERS Maria Moreno-Villanueva1,2, Stephanie Krieger3, Ye Zhang4, Brian Crucian1, Honglu Wu1 1NASA Johnson Space Center, Houston, Texas, 2University of Konstanz, Konstanz, Germany, 3KBR, Houston, Texas, 4NASA Kennedy Space Center, Cape Canaveral, Florida COSPAR, Athens, July, 2022
Blood collection schedule (Functional Immune) Blood collection schedule (Functional Immune) Blood drawn in flight was transported to JSC at ambient temperature. For crewmembers, the R0 samples were drawn immediately after returning to JSC, or in the case of international astronauts, after returning to DLR . Blood samples drawn from crewmembers and from ground matching subjects at JSC were aged. Data from 8 crewmembers are discussed here.
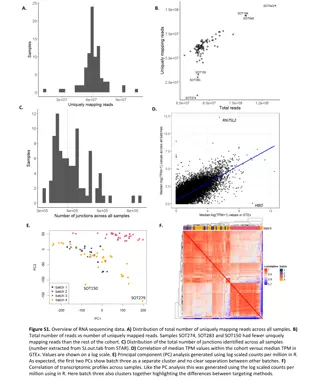
Number of differentially expressed genes Number of significantly expressed genes 1500 1000 500 0 L180 L45 MF LF R0 R30 R90 -500 -1000 -1500 Upregulated Downregulated RNA was isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). Transcriptomics analysis was performed using RNA-seq. Differentially expressed genes were determined by performing contrast analysis, using all time points of the ground control subjects combined as a control. The fold change threshold is 1.5 and the FDR < 0.05.
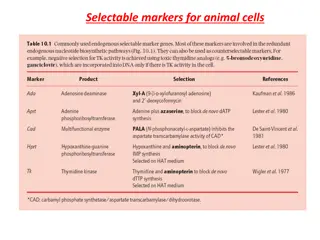
Selected differentially expressed genes Selected differentially expressed genes CDKN1A (p21) was downregulated in space. Several NF B and NF B inhibitor genes were upregulated in space.
Upstream regulators (Ingenuity Pathway Analysis, IPA) Upstream Regulators 30 20 10 0 L180 L45 MF LF R0 R30 R90 -10 -20 -30 Upregulated Downregulated Upstream regulators were determined using z>2.0 and p<0.05 as thresholds. No significant upstream regulators were identified for other pre- and post-flight time points.
Upstream regulators (Continued) Upstream regulators (Continued) Most of the regulation relationships were activation at R0. NF B genes (NFKB1, REL and RELA) were identified as upstream regulators. Does the data indicate adaptation at LF?
Pathway Analysis (IPA) Pathway Analysis (IPA) Among the canonical pathways are cardiac hypertrophy, osteoarthritis and neuroinflammation (Z>2, p<0.05). These pathways are activated more at LF.
NF B B in space in space Chronic activation of Chronic activation of NF Chronic activation of NF B may be related to chronic inflammation and other causes. Chronic activation of NF B in space can be associated with several health risks (Zhang et al. Transcriptomics, NF- B Pathway, and Their Potential Spaceflight- Related Health Consequences. Int J Mol Sci 2017).
Alterations of Immune Related Genes Alterations of Immune Related Genes Gene expression change Proteins in plasma were measured in Functional Immune project. A comparison between plasma cytokines and gene expression in PBMC will be made on crewmembers from the same study. A preliminary comparison shows similarities between sample types was found for some of the cytokines such as IL-1B and GM-CSF.
Potential implications of the transcriptomics data Senescence Senescence Several senescence related genes such as CDKN1A (p21), p53 and TGF were downregulated in space. Can senescence provide an explanation for telomere lengthening in space? Association with other risks Association with other risks Immune dysfunction Osteoarthritis Neuroinflammation Cardiac hypertrophy microRNA data is being analyzed microRNA data is being analyzed
CONCLUSIONS Results of the preliminary analysis indicate that most of the gene expression changes occurred at MF, LF and R+0, with most of these expression levels returning to baseline by R+30. A number of cell cycle related genes such as p21 and VEGF were downregulated in space. Our data suggests chronic activation of the NF B pathway during flight. There appears to be an adaptation to the space environment at LF time point. Network analysis of the RNA data suggests a spaceflight effect on pathways not only in the immune system, but also on others involving neuroinflammation and oxidative stress.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT NASA JSC George Makedonas University of Wisconsin Mark Berres Sandra Splinter BonDurant Uniformed Services University Brian C. Schaefer This work is supported by the NASA Human Research Program.




![[PDF⚡READ❤ONLINE] The International Space Station: Building for the Future (Spri](/thumb/21686/pdf-read-online-the-international-space-station-building-for-the-future-spri.jpg)