Renal Physiology and Functions
This content covers the aims of studying renal physiology, functions of the kidney, basic renal processes, renal secretion, urine formation, and types of renal failure. It delves into topics such as water balance, electrolyte balance, urine production, and the components of the urinary system. The images provided help visualize the concepts discussed throughout the content.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Renal Physiology M.sc. Duaa falah pharmacology and toxicology
Aim of Study 1) Know function of the kidney 2) Know the anatomy of urinary system 3) Define the urinary and basic renal process 4) Know types of renal failure
Functions of The kidney 1) Water balance 2) Electrolyte balance 3) Plasma volume 4) Acid-base balance 5) Osmolarity balance 6) Excretion 7) Hormone secretion
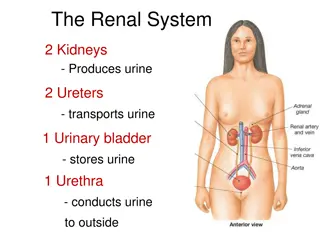
THE URINARY SYSTEM 1) Kidneys 2) Blood supply: Renal arteries and veins 3) Ureter 4) Urinary bladder 5) Urethra
Urine Urine is a waste by product formed from excess water and metabolic waste molecules during the process of renal system filtration. The primary function of the renal system is to regulate blood volume and plasma osmolarity, and waste removal via urine is essentially a convenient way that the body performs many functions using one process. Urine formation occurs during three processes:
Basic Renal Process 1) Glomerular Filtration: Filtering of blood into tubule forming the primitive urine. 2) Tubular Reabsorption: Absorption of substances needed by body from tubule to blood. 3) Tubular Secretion: Secretion of substances to be eliminated from the body into the tubule from the blood.
Renal secretion The substances that are secreted into the tubular fluid for removal from the body include: 1) Potassium ions (K+) 2) Hydrogen ions (H+) 3) Ammonium ions (NH4+) 4) Creatinine 5) Urea 6) Some hormones 7) Some drugs (e.g., penicillin)
Renal Failure Acute: Sudden onset, rapid reduction in urine output - usually reversible Chronic: Progressive, not reversible Up to 75% function can be lost before it is noticeable.