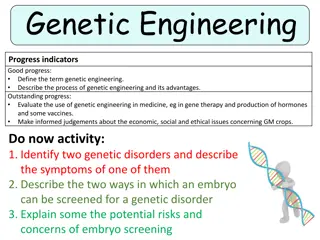
Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism in Genetic Disorders
Explore the intricate pathways of purine and pyrimidine catabolism, salvage, and degradation. Uncover the causes and symptoms of genetic disorders like Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome and Gout. Discover the importance of ribonucleotides conversion to deoxyribonucleotides in DNA synthesis. Dive into the mechanisms behind pyrimidine catabolism and the conversion of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides essential for cellular functions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PURINE AND PYRIMIDINE CATABOLISM
PURINE SALVAGE PATHWAY From normal turnover of cellular nucleic acids Obtained from the diet Reutilization of adenine, hypoxanthine, and guanine Two enzymes: 1. Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase 2. Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
Hypoxanthine Xanthine dehydrogenase Xanthine Allopurinol http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8c/Allopurinol_V.1.svg/150px-Allopurinol_V.1.svg.png
GOUT structure of organic compound: 7,9-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6,8(3H)-trione http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/fc/Case_30-bottom.jpg/120px-Case_30-bottom.jpg
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome Build up of hypoxanthine and guanine Degradation of hypoxanthine and guanine results in increased uric acid Absence of Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Excess uric acid in urine often results in orange crystals in the diaper of affected children Severe mental retardation Self-mutilation Involuntary movements Gout
LESCH-NYHAN SYNDROME File:XlinkRecessive.jpg
RIBONUCLEOTIDES TO DEOXYRIBONUCLEOTIDES Very Important!
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/thumb/6/6e/Rnr.jpg/400px-Rnr.jpghttp://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/thumb/6/6e/Rnr.jpg/400px-Rnr.jpg
DNA Base Pairing Guanine-Cytosine Adenine-Thymine
CHARGAFFS RULE %A = %T and %G = %C In DNA, 1:1 ratio between purines and pyrimidines Organism %A %G %C %T A/T G/C %GC %AT X174 24.0 23.3 21.5 31.2 0.77 1.08 44.8 55.2 Maize 26.8 22.8 23.2 27.2 0.99 0.98 46.1 54.0 Octopus 33.2 17.6 17.6 31.6 1.05 1.00 35.2 64.8 Chicken 28.0 22.0 21.6 28.4 0.99 1.02 43.7 56.4 Rat 28.6 21.4 20.5 28.4 1.01 1.00 42.9 57.0 Human 29.3 20.7 20.0 30.0 0.98 1.04 40.7 59.3 Grasshopper 29.3 20.5 20.7 29.3 1.00 0.99 41.2 58.6 Sea Urchin 32.8 17.7 17.3 32.1 1.02 1.02 35.0 64.9 Wheat 27.3 22.7 22.8 27.1 1.01 1.00 45.5 54.4 Yeast 31.3 18.7 17.1 32.9 0.95 1.09 35.8 64.4 E. Coli 24.7 26.0 25.7 23.6 1.05 1.01 51.7 48.3
SUMMARY Purines: Uric acid Reutilization of adenine, hypoxanthine and guanine End product: Urate (a.k.a.: Uric Acid ) Altered metabolism: Gout Pyrimidines: Citric acid intermediates Acetyl-CoA derived from Cytosine and Uracil degradation; Propionyl-CoA (Succinoyl-CoA) from Thymine degradation Ammonia and CO2 Ring undergoes complete degradation