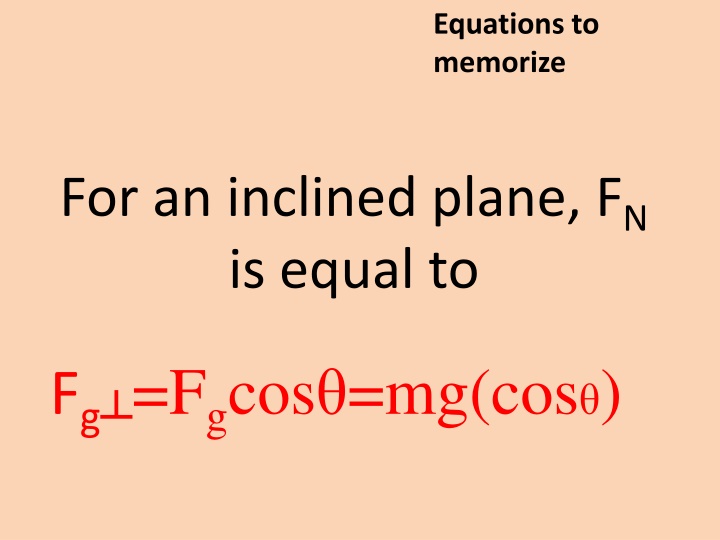Physics Equations to Memorize for Better Understanding
Learn essential physics equations for inclined planes, forces applied at angles, circle circumference, centripetal force, momentum change, resultant angles, slope calculations, and graph area formulas. Understand the relationships represented by different types of graphs to enhance your physics knowledge.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Equations to memorize For an inclined plane, FN is equal to Fg =Fgcos =mg(cos )
Equations to memorize For an inclined plane, FgII is equal to FgII=Fgsin =mg(sin )
Equations to memorize For a force applied at an angle, the horizontal (or force parallel to the surface) equals FAX=FAcos
Equations to memorize The equation for the circumference of a circle C=2 r
Equations to memorize Equation for centripetal force (combined version not on Ref Table) Fc=??2 ?
Equations to memorize Equation for change in momentum = impulse (long version of Newton s Second Law) Fnett=m v
Equations to memorize Angle of a resultant given horizontal and vertical components =tan-1(Ay/Ax)
Equations to memorize Equation for slope Slope = ( y/ x)
Equations to memorize Equation for area of a sloped (triangle) graph Area = 1/2bh or [(x-value)(y-value)]/2
Equations to memorize Equation for area of a straight line (rectangular) graph Area = bh or (x-value)(y-value)
Equations to memorize Equation for Fs when a mass is applied vertically Fs=Fg=mg (or kx=mg)
Name the type of relationship represented by the graph Inverse or inverse square
Name the type of relationship represented by the graph Direct
Name the type of relationship represented by the graph Direct Square
Vocabulary or concept A quantity in which both direction and magnitude are important Vector
Vocabulary or Concept Another word for mass Inertia
Vocabulary or Concept Mass x velocity = Momentum or impulse
Vocabulary or Concept The area where an object feels the force of another object with the same fundamental force carrier Field
Vocabulary or Concept The word for the size of a measurement Magnitude
Vocabulary or Concept When trying to solve for an unknown force using a force diagram, what 2 questions must you answer? What axis (x, y, or II)? Is it at equilibrium?
Vocabulary or Concept Term for the sum of two vector quantities Resultant
Vocabulary or Concept The term for an object that is not experiencing acceleration Constant velocity or equilibrium
Vocabulary or Concept The force causing an object to move in a circular path is always directed to The center of the circle
Vocabulary or Concept As an object moves further from the center of a planet, the mass of the object Remains the same (Fg changes)
Vocabulary or Concept For an object moving in a circle, at any point the velocity is directed Tangent to the circle
Vocabulary or Concept Centripetal acceleration is directed To the center of the circle
Vocabulary or Concept To determine the force of friction on an object that is remaining at rest you must use the coefficient of ____________ friction static
Vocabulary or Concept For an object in motion, the _____________ coefficient of friction must be used kinetic
Vocabulary or Concept The gravitational force is always attractive
Vocabulary or Concept The normal force is the force from a surface that always points Perpendicular to the surface
Vocabulary or Concept Net Force always agrees with acceleration
Vocabulary or Concept If acceleration is constant, Fnet will be Constant (uniform)
Vocabulary or Concept During a collision the momentum of the system before the event always equals Momentum after
Vocabulary or Concept For any given change in momentum an increase in time will cause Fnet to decrease
Vocabulary or Concept The rate in change of momentum is known as Fnet = ? ? ?= ? ?
STATE VARIABLE Normal Force FN
STATE VARIABLE Net force Fnet
STATE VARIABLE Spring constant k
STATE VARIABLE Coefficient of friction
STATE VARIABLE mass m
STATE VARIABLE Weight Fg
STATE VARIABLE Parallel component of weight FgII
STATE VARIABLE Change in equilibrium length of a spring x
STATE VARIABLE Spring Force Fs
STATE VARIABLE Centripetal Force Fc
STATE VARIABLE Centripetal acceleration ac
STATE VARIABLE Distance between two objects r
STATE VARIABLE Radius of circle r
STATE VARIABLE Gravitational field strength g
STATE VARIABLE Universal Gravitational constant G