Non-Mendelian and Sex-Linked Genetics
Today we explore non-Mendelian genetics focusing on plant stem length inheritance, discuss sex-linked traits inherited through X and Y chromosomes, including examples of X-linked dominant and recessive disorders affecting men and women differently.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
In a plant, long stems are dominant (L) to short stems (l). If a homozygous dominant flower and a homozygous recessive plant are crossed, what would be the phenotypic ratio of their offspring?
CO: LO:
REMEMBER: Mendel s principles form the basis of the modern science of genetics. The inheritance of biological characteristics is determined by specific segments of DNA called genes. Genes are passed from parents to their offspring.
Today were going to talk about a special case: sex-linked traits Remember: Each person inherits an X chromosome from mom and either an X or a Y from dad We use the letters X and Y to represent chromosomes (not alleles)
What do you think a sex-linked trait is? Examples?
Sex-linked traits Are traits that are determined by either the Y or X chromosome If they are determined by the Y chromosome they are referred to as Y-linked Y-linked disorders are very rare and often cause infertility in men If they are determined by the X-chromosome they are referred to as X-linked
X-linked dominant These conditions (such as vitamin D resistant rickets) are rare and can affect both men and women Men are more affected than women Both men and women can pass on the affected chromosome to their children
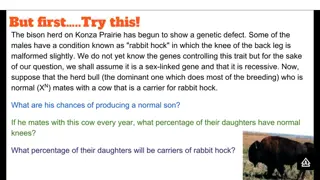
X-linked recessive These disorders (such as hemophilia and color blindness) more frequently affect men than women Both men and women can pass these traits on to their children (at different rates) An affected man/unaffected woman will have sons who are unaffected and daughters who are carriers An affected woman/unaffected man will have a 50% chance of passing the trait. If she passes on her affected X chromosome, then her daughters will be carriers and her sons will be affected This is why men are more likely to be color blind than women
How could you find out the chances that you have hemophilia running in your family?
Pedigree chart: a chart that shows relationships within a family.
Lets practice 1. Pedigree Worksheet together 2. Flip knob create your own pedigree chart
Bellwork: January 7 Complete the Flipnob activity you started yesterday. Copy the pedigree below. You must show who has freckles by shading and label each person with their genotype. Grandpa Grandma David Fred Mickey Elizabeth Wilma Michelle Monica Barney John Sonny Krista Janet
CO: I will predict genetic outcome using non-Mendelian inheritance. LO: I will draw a pedigree chart. I will write notes and answer questions.
Types of Inheritance 1. Mendelian: genetic traits are controlled by a single gene ----- dominant or recessive; flower color 2. Sex-linked: genetic traits are controlled by the X or Y chromosome -----X-linked recessive; colorblindness 3. Co-dominance: both alleles contribute to the phenotype equally(ex. Blood type) 4. Incomplete dominance: when the presence of both alleles leads to a blending of traits (ex. Red flower + white flower = pink flower) 5. Polygenic: when a trait is controlled by multiple alleles
Co-dominance When the genotype is heterozygous, then both traits will show up equally Note: when writing we show this with two different capital letters
Incomplete Dominance When the genotype is heterozygous, then the trait will be a blend of the two alleles Note: Sometimes, we write this by using an abbreviation of the trait in a capital letter (C =color) and the alleles as a superscript (CR = red flower) or subscript (CR). Sometimes, we just say the heterozygous trait is a blend.
Polygenic Inheritance Multiple genes control the inheritance of traits
Both genes and the environment determine how traits are expressed in a population
Rest of the Day 1. Vocab Strips: Read and sort the vocabulary words and definitions (use the pictures to help!) 2. Questions on the next slide. 3. Homework: What is Evolution? by Stated Clearly Watch video and write 3 facts you learned and 3 questions to share tomorrow in class.
Non-Mendelian Inheritance In rabbits, white coat color (CW) and black coat color (CB) are codominant, and both of these alleles are dominant over albino (c); heterozygotes (CWCB) are spotted. 1. Draw a Punnett Square that shows the genotypes of the offspring from a heterozygous black-coated rabbit and a homozygous white-coated rabbit? Mrs. PigglyWiggly is a carrier of the sex-linked hemophilia allele, and Mr. PigglyWiggly is normal (as far as blood chemistry goes). 2. Draw a Punnet square that shows the theoretical genotypes among their children.
Non-Mendelian Inheritance Spongebob loves growing flowers for his gal pal, Sandy. She loves the Poofkin flowers red, purple, and blue! Interestingly enough, the Poofkin flowers display incomplete dominance in their genes for color. 1. Using R for red and B for blue, what would be the genotypes for the following phenotypes? red: ______ purple: _____ blue: _____ 2. Complete a Punnett square for a red Poofkin and a purple Poofkin.