Monte Carlo Simulations and Probabilistic Techniques
Dive into the world of Monte Carlo simulations and probabilistic methods, understanding the basic principles, the Law of Large Numbers, Pseudo-Random Number Generators, and practical Monte Carlo steps. Explore topics like conditional probability, basic geometry, and calculus through engaging exercises. Uncover the convergence of averages, the concept of randomness, and more in this comprehensive exploration.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Other Monte Carlo Simulations by Gio 0
Basic Principle: Monte Carlo Method The Monte Carlo Method is the approach (methodology) of using randomness to describe problems that may have a deterministic solution The Law of Large Numbers (LLN) states that with an increase in the number of measurements the expected value grows to equal the average value A Pseudo-Random Number Generator is an algorithm for generating numbers that appear reasonably random in sequence 1
Law of Large Numbers 1 die VS. 30 dice VS. 103 dice Convergence of Average and Expected Value 2
Pseudo Random Number Generator Approximate randomness Probability distributions [0, 1] 3
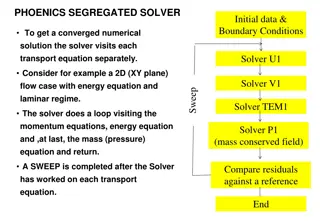
Monte Carlo Steps Step 1: Define the probability space and the points within that space; use a large number of points to define the space Step 2: Define the conditions of the problem that constrains the space Step 3: Discriminate between the points that reside within the constraints of the problem and those that do not Step 4: Use the points that reside within the constraints to define the space of the solution Important: The greater the number of points, the greater the accuracy of the simulation 4
Colab Exercises Conditional Probability Basic Geometry Calculus 5
Conditional Probability Which combination of numbers, on average, give a larger value; three numbers between 1-4 or two number between 1-6? Always double the lowest number in each combination. 6
Basic Geometry Determine the area of basic geometric shapes without using the area formulas for those shapes Relative areas 7
Calculus Determine the area under the curve without integrating Random sampling 8