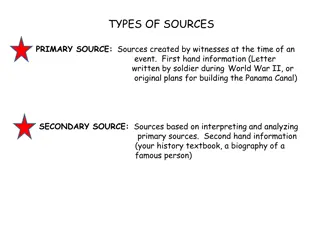
Key Events and Impacts of Periods 5 and 6 in US History
The content covers key events and impacts of Periods 5 (1844-1877) and 6 (1865-1898) in US history. It includes the settlement of the West, the 2nd Industrial Revolution, the Gilded Age, urbanization, populism, Jim Crow laws, Western expansion, the Mexican-American War, Civil War, and Reconstruction. Important topics like Native American settlement, industrial developments, societal changes, and urbanization are explored.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
APUSH Final Exam Review Periods 6 (1865-1898) & 5 (1844-1877) Key Events: 1) Period 6 Final settlement of the West, 2nd Industrial Revolution, Gilded Age, Urbanization, Populism, Jim Crow 2) Period 5 Continued Western Expansion, Mexican-American War, Immediate build-up to the Civil War, Civil War, Reconstruction
Two Great Online Study Resources: Gilder-Lehrman.org (excellent thematic breakdown videos, documents, etc.) Crash Course US History (10-15 min. YouTube videos on important content/thematic info from all 9 time periods)
Period 6: Final Native American Settlement 1) RRs are being built through NA land on Great Plains; buffalo are being slaughtered (US Army directive) 2) Constant fighting for diminishing land/hunting grounds among Plains tribes disrupting, RR construction travel and white settlement 3) Solution: reservation system and final assimilation (Dawes Severalty Act 1887)
Period 6: 2ndIndustrial Revolution 1) Begins in East with Vanderbilt s RR empire pre-post Civil War 2) Continues as TC RR is completed in 1869 3) Leads to extensive speculation, corruption, protection of business by fed. gov t (Wabash v. Illinois corporations are equally protected as individuals by 14thamendment)
Period 6 2ndIndustrial Rev (cont d) 3) Focus on heavy manufacturing (oil, steel, machinery) and agribusiness 4) Consolidation of smaller industries into empires by Carnegie, Rockefeller, etc. 5) Sherman Anti-Trust Act (1890) fails to provide any real regulation of large-scale companies
Period 6: Impact of 2ndIndustrial Rev on US Society 1) 90% wealth held by 10% of population 2) Social Darwinist beliefs become popular ( explains success and failure) 3) Growth of middle class (factory managers, execs) and working class (former farmers, immigrants, etc.) 4) Rise of organized labor (with minimal success) and NO federal support 5) Boom and Bust economic cycles
Period 6: Impact of 2ndIndustrial Rev. on US Cities 1) Continued dominance of political machines (i.e. Tammany Hall/ Boss Tweed in NYC) 2) Arrival of southern/eastern European and Asian immigrants; opening of Ellis Island processing depot; Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 3) New buildings for business and residence (skyscrapers, tenements , row-homes in ethnic neighborhoods)
Period 6: Impact of 2ndIndustrial Rev. on the South 1) Tobacco makes a comeback/industry and RR arrives/cheap labor 2) Large war debt from Civil War; Northerners owns great deal of industry located South 3) Overproduction/competition in cotton leads to crop lien (buy goods now, pay back next harvest) 4) Culturally: Jim Crow laws/segregation dominate South should African Americans assimilate or fight back for their civil rights?
Period 6: Impact of 2ndIndustrial Revolution on Agriculture 1) RRs are given first cut of land; any land near RR stops is valuable 2) RR and other private companies buy land from fed. gov t and can sell it to private buyers/investors for resale 3) Leads to agribusiness ; small farmers cannot compete
Period 6: Backlash Against Industry and Agribiz: the Populists 1) Born from Farmers Alliances/Grangers in West/Mid-West in 1892 2) Platform: unlimited coinage of silver, graduated income tax, public ownership of RRs, gov t subsidies for farmers, 8-hour workday, direct election of US Senators 3) Action: Coxey s Army marches on DC in 1894 4) Champion: William J. Bryan (1896 election loses to McKinley)
Sample MC Questions 1stStimulus: Be it enacted by Congress that in all cases where any tribe or band of Indians has been located upon any reservation created by Congress Congress may allot the lands: To each head of a family, one quarter of a section To each single person over 18 years of age, one- eight of a section Every Indian who has adopted the habits of a civilized live is declared a citizen of the US -Dawes Act (1887)
1stStimulus - Question 1: Which of the following situations most directly resulted from the passage of this act? A) An increase in Native American tribal lands west of the Mississippi River B) A decrease in federal control over Native American affairs C) An increase in immigration from southern and eastern Europe after 1890 D) A reduction in tribal autonomy
Answer: D) A reduction in tribal autonomy Why? Purpose of the Dawes Act was to break Native Americans of tribal bonds on reservations and force them to finally assimilate through individual land plots and promises of citizenship
1stStimulus - Question 2 The process described in the Dawes Act most directly reflects which of the following continuities in US history? A) Debates about expansion of voting rights B) Debates about the role of assimilation in national identity C) Debates about the growth of executive power D) Debates about economic globalization
Answer: B) Debates about the role of assimilation in national identity Why? Throughout US history we have seen questions and concerns raised about what makes someone an American . Is American someone who follows European-Christian values/beliefs? Are those who do not fit this mold expected to conform to this identity or does their unique culture/tradition also fit the identity of American ?
Sample MC Questions 2ndStimulus -Source: The Bosses of the Senate, Joseph Keppler, Puck Magazine, 1889
2nd Stimulus Question 1 The main point of this political cartoon most directly reflects which of the following ideas? A) The Social Gospel, a Protestant intellectual movement to help the plight of the poor in the late 19th century B) Progressivism, from 1900-1924 C) Populism, a pro-agricultural political movement, from 1890-1896 D) Social Darwinism, a belief that only the fittest would survive in business, from 1870s-1880s
Answer: D) Social Darwinism Why? During the 2nd Industrial Rev., it commonly believed that business tycoons who controlled the industries were the strongest of society.
2nd Stimulus Question 2 The ideas expressed by the artist illustrates which of the following issues of the Industrial Revolution? A) Labor unions had too much influence in government B) The US Senate was able to pass legislation to promote fair business practices C) The belief that monopolies controlled the Senate D) The economy was producing an equitable society
Answer: C) The belief that monopolies controlled the US Senate Why? Most labor unions were attacked by the US gov t in the 1880s, US society was FAR from equitable, and the gov t often passed legislation that helped business owners grow their industries at the expense of their workers
Period 5 (1848-1877): Westward Expansion Continues: 1) Mexico opens up Tejas Province for US settlement; US-settlers lead independence movement in 1820s 2) Oregon Fever at its height (as industry begins in N. and cotton-based plantation farming continues to proliferate in S.) 3) Leads to increased tension with Britain (over Oregon) and Mexico (over Texas)
Period 5 (1848-1877): Conflict and Capitulation Under Polk 1) Polk settles border dispute over Oregon Terr. with Britain (49th parallel) 2) Goads Mexico into a fight over Texas (now an independent Republic); Mexican-American war fought between 1846-1848 3) Wilmot s Proviso attempts to make land ceded by Mexico off limits to expansion of slavery; result is wildly increased sectional tension 4) Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo cedes California, Texas, and most of SW America US
Period 5 (1848-1877): Onset of War (1848-1850s) 1) Free Soil Party formed in 1848 (opposed expansion of slavery into territories, not practice itself) 2) Popular Sovereignty is another method for deciding slavery s expansion ( Bleeding Kansas ) 3) Gold Rush of 1848-1849 makes CA eligible for statehood by 1850; its admission as a free state would throw off sectional balance in Senate
Period 5 (1858-1877) Onset of War (cont d) 4) Compromises of 1850: CA is admitted free, harsher Fugitive Slave Law is imposed 5) Harriet Beecher Stowe writes Uncle Tom s Cabin (1852) 6) Kansas-Nebraska Act (1852) introduced by Stephen Douglas does away with Missouri Compromise; former Whigs and Free Soilers from Republican Party in opposition 7) Dred Scott decision (1857) declares slaves property , not and never were citizens, and could be brought by masters ANYWHERE in US 8) John Brown s raid/execution beginning of southern militias
Period 5 (1848-1877): Onset of War (cont d) 9) Lincoln wins election of 1860 (promises to halt slavery s expansion); South secedes 10) Fort Sumter fired upon in April 1861 by Confederate Army
Period 5 (1848-1877): Northern Advantages/Challenges During War: 1) Advantages: Larger population/larger industrial base/larger transportation network 2) Challenges: keeping border states loyal; keeping Europe from recognizing/allying with Confederacy
Period 5 (1848-1877): Southern Advantages/Challenges 1) Cause (defense of home/way of life) 2) Cotton (belief that Europe depended on it) 3) Little/no industry or RRs 4) Little/no tax base or ability to tax 5) Hyperinflation, food shortages, demoralization after 1863
Period 5 (1848-1877): End of Slavery: 1) Emancipation Proclamation done to give North their own cause to fight; done to keep Europe out 2) 13th Amendment: eliminates chattel slavery forever (1865)
Period 5 (1848-1877): Presidential vs. Radical Reconstruction 1) Questions: What to do with 4 million freedmen ? What to do with defeated Confederacy? 2) Lincoln: 10% population swears oath of loyalty to US state may re-establish its own government (cannot include slavery); pardons would be issued to Confederates who swore loyalty and renounced slavery 3) Freedman s Bureau established in 1865 to assist former slaves in education, jobs, tracking down family, legal issues, etc. (folds in 1872)
Period 5 (1848-1877): Presidential vs. Radical Reconstruction (cont d) 1) Johnson: keeps Lincoln s 10% plan and pardon plan (freely uses both) 2) Result: old Confederates leaders/wealthy plantation owners are back in power by 1866 3) Result: black codes/sharecropping begins in South 4) Result: Republicans attack Johnson s leniency ( waving the bloody shirt ); win majorities in mid-term elections
Period 5 (1848-1877): Presidential vs. Radical Reconstruction 5) Radicals Plans: Civil Rights Bill (1866) invalidates black codes; Johnson vetoes and Congress overrides 6) Radicals Plans: 14th Amendment (grants citizenship to freedmen; grants equal protection of law) 7) Radicals Plans: Military Reconstruction Act divides South into 5 districts governed by US military; begins martial law in districts; requires states to adopt 14th Amendment and voting rights as conditions for readmission 8) Radicals Plans: 15th Amendment (right to vote cannot be denied based on race) 9) Radicals Plans: Civil Rights Act (1875) forbade racial discrimination (would seldom be enforced)
Period 5 (1848-1877): Results of Reconstruction 1) Black voters overwhelmingly side with Republicans; win seats in state legislatures 2) Southern whites side with Democrats; KKK is formed to intimidate black voters and their white supporters (suppressed by Force Acts of 1870, 1871) 3) Redemption of South begins as Radicals are voted out/die out and more moderate , business-minded Republicans take office 4) Redemption is complete in 1877 when Military Reconstruction/martial law ends in South in exchange for election of Hayes (Republican) 5) Jim Crow era begins as US military evacuates South
Sample MC Questions Stimulus 1 With malice toward none, with charity for all, with firmness in the right as God gives us to see the right, let us strive on to finish the work we are in, to bind up the nation s wounds, to care for him who shall have borne the battle and for his widow and his orphan, to do all which may achieve and cherish a just and lasting peace among ourselves and with all nations. -Source: Abraham Lincoln, 2nd Inaugural, 3/4/1865
1st Stimulus Question 1 The ideas expressed in the passage most directly led to the political controversies of the 1860s and 1870s over the A) Role of the federal gov t in the settlement of the West B) Process of reconstructing the United States in the aftermath of the Civil War C) Authority of the states to promote economic development D) Extension of American democratic values abroad
Answer: B) Process of reconstructing the United States in the aftermath of the Civil War Why? The United States was presented with several ideas on how to reconstruct itself after the war, most notably Presidential vs. Radical Reconstruction
1st Stimulus Question 2 The previous beliefs most clearly reflect which of the following continuities in US history? A) Tensions between the executive and judicial branches B) Changing relationships between state and local governments C) Social change more difficult to achieve than political change D) American military actions impact on the world
Answer: C) Social change more difficult to achieve than political change Why? Despite Lincoln s plea for moderation, the aftermath of the war led to increased controversy. The political and constitutional changes of the Civil War/Reconstruction Era failed to alter many of the social beliefs and attitudes of the 19th century
Sample MC Stimulus 2 In one view the slaveholders have a decided advantage over all opposition the advantage of complete organization. They are organized; and yet were not at the pains of creating their organizations. The state governments, where slavery exists, are complete slavery organizations. The church organizations in those states are equally at the service of slavery; while the Federal government with its army and navy to the Supreme Court is pledged to support, defend, and propagate the crying curse of human bondage. The pen, the purse, and the sword, are united against the simple truth, preached by humble men in obscure places. Source: Frederick Douglass, 1857
Stimulus 2 Question 1 In his opinion in the case Dred Scott v. Sandford, Chief Justice Taney upheld the sentiment above by stating that A) separate but equal facilities for people of different races was constitutional B) Corporations were entitled to the same protections guaranteed to individuals under the 14th Amendment C) School prayer violated the principle of separation of Church and State D) Congress had no right to regulate slavery in the US
Answer: D) Congress had no right to regulate slavery in the US Why? Taney used to occasion of the Scott trial to state once and for all that slaves were property, not people, and could be brought to any part of the US by their owners just as property could.
Stimulus 2 Question 2 In what way did the actions of Lincoln in 1860 contradict Douglass s sentiments in the quote above? A) Lincoln promoted the freedom of settlers within territories to determine the slave status of their new state B) Lincoln passed the Homestead Act to give free land to all western settlers C) Lincoln favored the exclusion of slavery from any of the new territories D) Lincoln enacted the policy of giving newly freed slaves forty acres and a mule.
Answer: C) Lincoln favored the exclusion of slavery from any of the new territories Why? As a Republican, Lincoln supported the Free-Soil belief that the territories should be off-limits to the spread of slavery thereby allowing small farmers a fair chance to compete for economic success