Intussusception
Intussusception is a medical condition where one part of the intestine slides into another section, causing serious issues if not treated promptly. This comprehensive guide covers diagnosing ileocolic intussusception, the essential pre-procedure steps, and details of the air reduction procedure. It emphasizes the importance of timely intervention and highlights key considerations for healthcare providers managing this condition.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Intussusception Intussusception
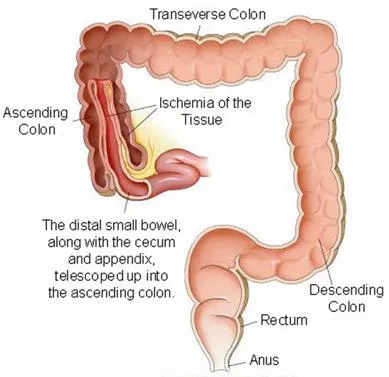
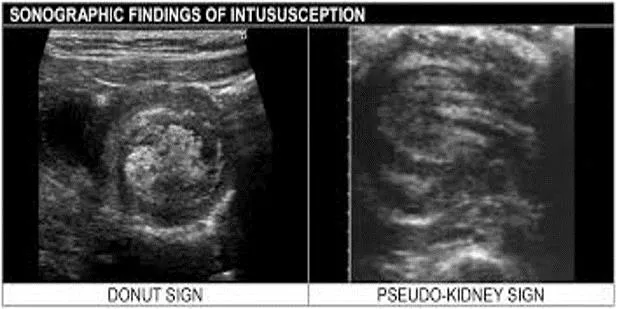
Diagnosing Ileocolic Intussusception Diagnosing Ileocolic Intussusception Emergent air reduction under FL will be needed if ileocolic intussusception is confirmed by US Goal is to less than 60 minutes from fluoro order placement to starting case Wait for attending MD to start the procedure Ileocolic intussusceptions are most commonly seen along the ascending colon or at the level of the transverse colon. These are larger (>3 cm on transverse dimension) than the transient small bowel to small bowel intussusceptions (<2cm) that do not need or can be reduced by radiology. Sometimes it is difficult to differentiate them (if between 2-3cm). In such cases, the attending may repeat the US at the FL bedside prior to attempt the air reduction Know prior to start reduction: How long symptoms have started (clinical HX) Presence of trapped fluid (US) Presence of trapped lymph-nodes (US) https://coreem.net/core/intussusception/ Vascular flow along the bowel wall (US) https://healthjade.net/intussusception/ Free air (radiographs / scout for the air enema reduction
Pre Pre- -procedure procedure Intussusception Air Reduction Intussusception Air Reduction Prior to procedure ask referring team for: Prior to procedure ask referring team for: IV IV Monitoring Monitoring Nurse presence Nurse presence Surgery team to be aware the procedure will be performed Surgery team to be aware the procedure will be performed On your FL procedure table have ready: On your FL procedure table have ready: 18G needle (for pneumoperitoneal decompression if perforation) 18G needle (for pneumoperitoneal decompression if perforation) Air reduction tubing and Sphygmomanometer (Shiels air enema kit) Air reduction tubing and Sphygmomanometer (Shiels air enema kit) Additional rectal tip (blue tip if younger than 6 month of age) Additional rectal tip (blue tip if younger than 6 month of age) Lubricant Lubricant Plenty of tape to secure rectal seal and avoid air leakage during procedure Plenty of tape to secure rectal seal and avoid air leakage during procedure
Procedure Procedure Intussusception Air Reduction Intussusception Air Reduction Get Inform Consent Explain procedure to the patient and/or guardian Explain potential risks: Failure to reduce and need for surgery Bowel perforation Recurrence, higher rate during first 24 hrs Hemorrhage Infection If patient ill If patient ill- -appearing (lethargic, septic, not fighting rectal tube) appearing (lethargic, septic, not fighting rectal tube) consider requesting additional back up in consider requesting additional back up in room during procedure (ED faculty/fellow, Surgical faculty/fellow, or equivalent) because of high risk of room during procedure (ED faculty/fellow, Surgical faculty/fellow, or equivalent) because of high risk of arrest arrest
Procedure Technique Procedure Technique Scout view to look for free air. Add a lateral decubitus scout if there is any question of pneumoperitoneum. If pneumoperitoneum, abort the case and call ED. No free air on scout, proceeded to air reduction With help of attending, tape rectal catheter to create a tight seal Test the sphygmomanometer and connect to rectal tubing Start pumping air under continues fluoroscopic monitoring Maintain mean pressure of 120mmHg, not above Try to reflux air into the small bowel Take breaks as needed If no reduction, may try again in a few minutes If question residual, may look with US Residual intussusception at the cecum https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/930708-overview?form=fpf