Introduction to Coulomb's Law in Electrostatics
Discover the principles of electrostatics through Coulomb's Law. Learn about the relationship between charges, forces, and distances in electrical interactions. Explore examples illustrating the attractive and repulsive forces between charged objects.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
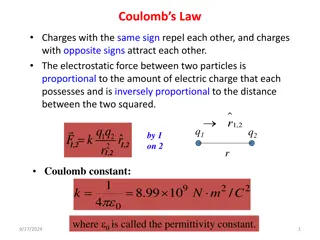
Coulombs Law Charles Coulomb discovered that the repulsive force due to similar charges or the attractive force of dissimilar charges was inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two charged bodies. _ _ _ _ _ + + F 1/r2 + _ + _ + + + + + _ _ _ _ _ + _ + r + _ _ + + _ _ + _ + + _ +
Coulombs Law Coulomb further discovered that the force was proportional to the product of the charge on each of the objects. q1 q2 _ _ _ _ _ + + + _ + _ + _ _ + + + + _ F q1q2 _ _ _ + + + _ _ + + _ _ _ + + _ + + Sphere 1 Sphere 2
Coulombs Law kq q Fe= 1 2 2 r Where: k = 8.99 x 109N m2/C2 q1, q2 = the charge of each sphere in Coulombs. r = the distance between the two charged bodies. Does this formula appear similar to anything else you have seen before?
What does the electrostatic force look like as distance varies? ??= ??1?2 + ?2 + Electrostatic Force 0 Distance of Separation As the distance between the two charged objects increases, the electrostatic force between them will decrease. Just like in gravity, ??and ? form an inverse-square relationship.
Example #1 Two identically sized conductive spheres carry charges of 1.5 C and -6.0 C, respectively. They are separated by a distance of 9.0 cm. What is the electrostatic force between the two spheres? Is it attractive or repulsive?
Example #1(cont.) ??= ??1?2 ?2 ?2)(1.5 10 6?)(6.0 10 6?) (0.090?)2 ??= (9.0 109??2 ??= 10.? -6.0 C 1.5 C ??(2 ?? 1) ??(1 ?? 2) Sphere 1 Sphere 2 Since the charges are opposite in charge, the two spheres will be attracted to each other.
Key Ideas Like charges repel. Opposite charges attract. The electrostatic force is proportional to the charge on the two objects and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.