Insights on Key Concepts in Computer Science
Explore the average scores and reviews by reviewers in EECS 582, along with stats on reviewed papers. Dive into classic principles like simplicity and iterative design, and learn about storage systems, kernels, and more. Uncover the significance of UNIX, relational databases, and file systems in the evolution of computing.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
EECS 582 Midterm Review Mosharaf Chowdhury EECS 582 W16 1
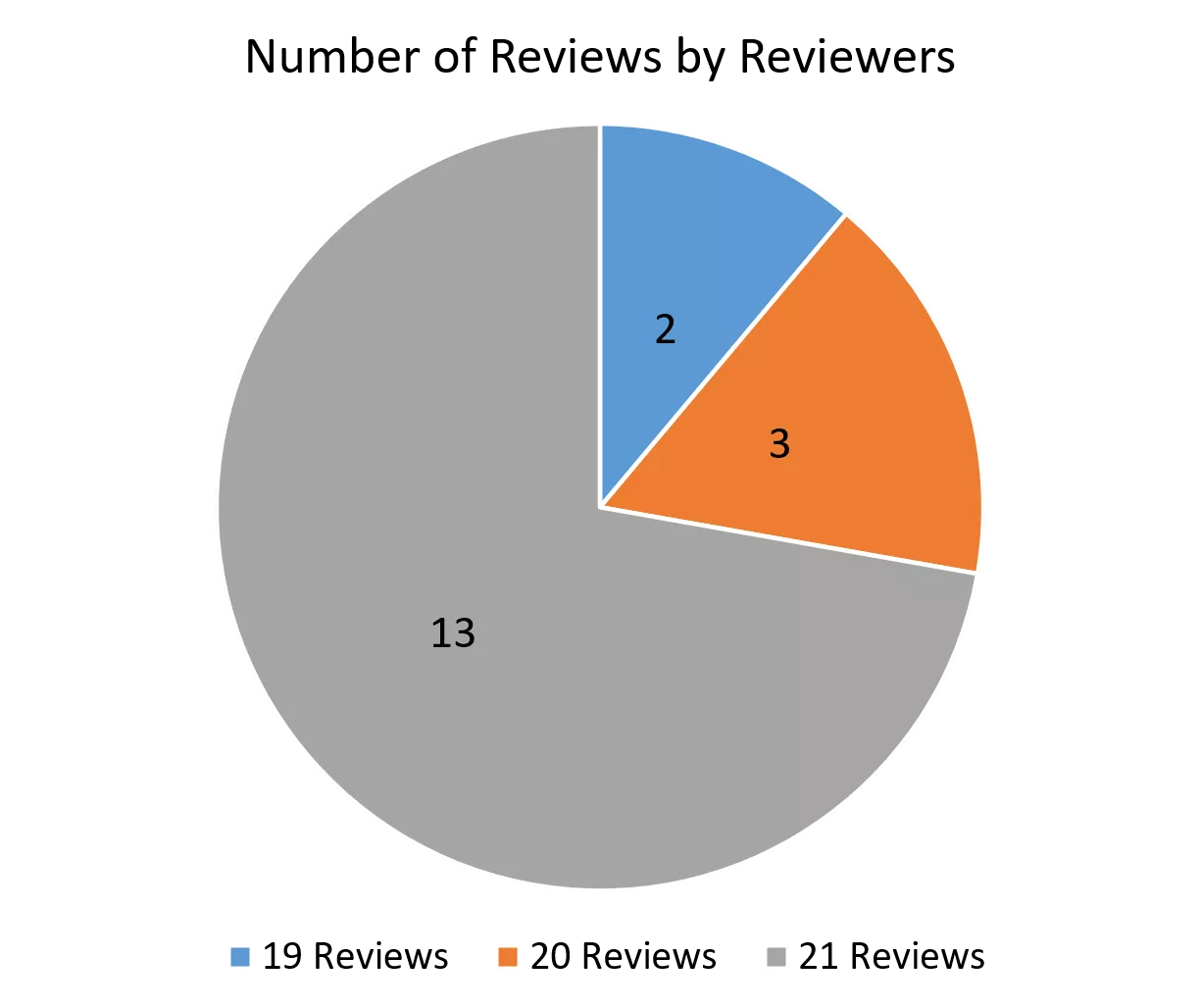
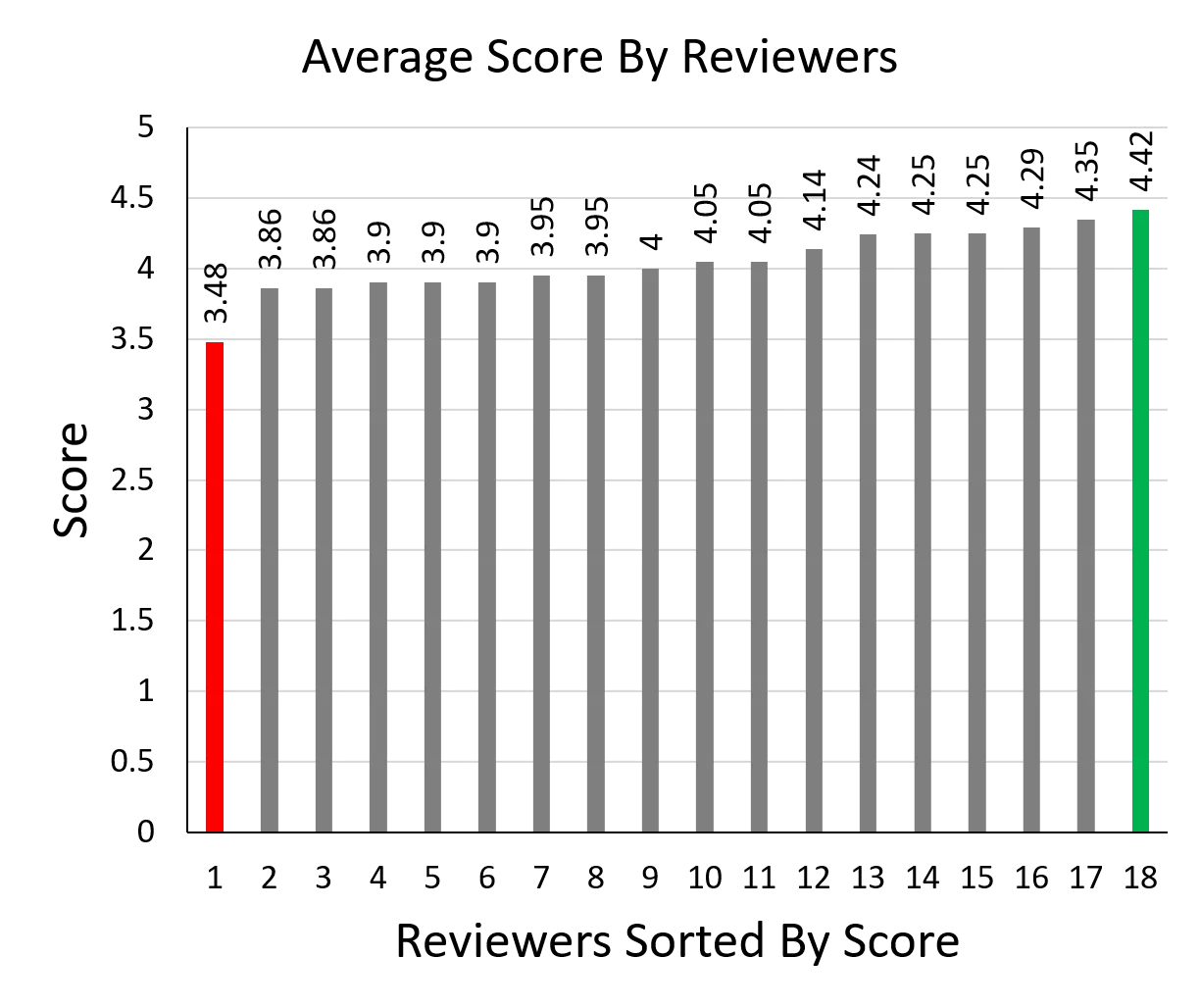
Stats on the 18 Reviewers Number of Reviews by Reviewers Average Score By Reviewers 5 4.42 4.35 4.29 4.25 4.25 4.24 4.14 4.05 4.05 4.5 3.95 3.95 3.86 3.86 3.9 3.9 3.9 4 4 3.48 2 3.5 3 Score 3 2.5 2 1.5 13 1 0.5 0 1 2 3 4 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Reviewers Sorted By Score 5 6 7 8 19 Reviews 20 Reviews 21 Reviews EECS 582 W16 2
Stats on the 21 Papers Weve Reviewed Average Score of Papers 5 4.5 4 3.5 3 Score 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Papers Sorted by Score EECS 582 W16 3
Stats on the 21 Papers Weve Reviewed Average Score of Papers 5 4.5 4 3.5 3 Score 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 EECS 582 W16 4
Classics Average Score of Papers 5 4.5 4 3.5 3 Score 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 EECS 582 W16 5
Classics UNIX (Arguably) the first commodity OS Simplicity is king when you must support diverse applications Everything is a file! System R The first relational database implementation Design iteratively and be ready to throw away Find the right metric and do everything when you must deliver performance (i.e., specialization instead of generalization) EECS 582 W16 6
Storage and File Systems Average Score of Papers 5 4.5 4 3.5 3 Score 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 EECS 582 W16 7
Storage and File Systems RAID Industry standard for durable, high-performance storage Parallelize for performance and fault-tolerance FFS Improved UNIX s default file systems Be aware of and exploit hardware characteristics JFS Provides crash recovery to file systems Log what you ll do before you do it! EECS 582 W16 8
Kernels Average Score of Papers 5 4.5 4 3.5 3 Score 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 EECS 582 W16 9
Kernels Exokernel Minimal kernel instead of a full-fledged one End-to-end argument: only provide services that everyone needs to balance between specialization (performance) and generalization (applicability) Multikernel Make communication explicit when you must communicate Shared-nothing design EECS 582 W16 10
Kernels IX Separate control and data planes to provide I/O performance Kernels aren t inherently slow; it s about how we do things Commuter Interfaces dictate scalable design EECS 582 W16 11
Virtual Memory and RPC Average Score of Papers 5 4.5 4 3.5 3 Score 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 EECS 582 W16 12
Virtual Memory and RPC Memory Coherence Shared-everything design requires frequent updates Keeping things coherent is expensive but provides simple programming models RPC Makes distributed nature more explicit while keeping the same programming model as a non-distributed system No shared memory EECS 582 W16 13
Concurrency and Scheduling Average Score of Papers 5 4.5 4 3.5 3 Score 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 EECS 582 W16 14
Concurrency and Scheduling SEDA and Fibers Thread- and event-based programming models both have their advantages and drawbacks (ease of programming vs. scalability and performance) It is possible to find a balance between the two Lottery and Stride Scheduling Randomized and deterministic proportional scheduling The key challenge is in determining the proportions (weights) EECS 582 W16 15
Reliability and Fault Tolerance Average Score of Papers 5 4.5 4 3.5 3 Score 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 EECS 582 W16 16
Reliability and Fault Tolerance Eraser Detecting bugs, specially the non-deterministic ones, is hard Provide a tight coverage to allow manual inspection Nooks Failure is inevitable Isolate it and start again EECS 582 W16 17
Virtual Machines Average Score of Papers 5 4.5 4 3.5 3 Score 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 EECS 582 W16 18
Virtual Machines Xen and ESX Virtualization comes in many shapes and forms (e.g., full virtualization vs paravirtualization) Choose the one that fits your requirements (e.g., performance, consolidation, deployability) Fit for your workload Live Migration Keep things running until you must stop ReVirt Quis custodiet ipsos custodes? (Roman poet Juvenal in Satires) It s turtles all the way down! EECS 582 W16 19