Implementing Heaps: Node Operations and Runtime Analysis
Understanding the implementation of heaps involves knowing various node operations like finding the minimum node, last node, next open space, children, and parent. The runtime analysis of heap operations such as peekMin, removeMin, and insert are crucial for optimizing performance. This recap covers building a Min Binary Heap, maintaining Min Heap invariants, and visualizing heap implementation through arrays. Key concepts include level order filling, percolating up, and the computational cost associated with heap functionalities.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Lecture 16: Midterm recap + Heaps ii CSE 373 Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 373 19 SP - KASEY CHAMPION 1
3 Minutes Practice: Building a minHeap Construct a Min Binary Heap by inserting the following values in this order: 5, 10, 15, 20, 7, 2 Min Binary Heap Invariants Min Binary Heap Invariants 1. 1. Binary Tree Binary Tree each node has at most 2 children 2. 2. Min Heap Min Heap each node s children are larger than itself 3. 3. Level Complete Level Complete - new nodes are added from left to right completely filling each level before creating a new one Min Priority Queue ADT state state Set of comparable values - Ordered based on priority 5 2 behavior behavior removeMin removeMin() () returns the element with the smallest priority, removes it from the collection peekMin peekMin() () find, but do not remove the element with the smallest priority 15 2 5 10 7 percolateUp percolateUp! ! insert(value) insert(value) add a new element to the collection 2 15 20 7 10 percolateUp percolateUp! ! percolateUp percolateUp! ! CSE 373 SP 18 - KASEY CHAMPION 2
Administrivia HW 4 due Wednesday night HW 5 out Wednesday (partner project) - Partner form due tonight How to get get a tech job with Kim Nguyen - Today 4-5pm PAA CSE 373 19 SP - KASEY CHAMPION 3
Midterm Grades Course Grade Breakdown Midterm: 20% Final Exam: 25% Individual Assignments: 15% Partner Projects: 40% Big OCode Modeling Trees Tree Method Hashing Design Decisions CSE 373 19 SP - KASEY CHAMPION 4
Midterm Performance CSE 373 SP 18 - KASEY CHAMPION 5
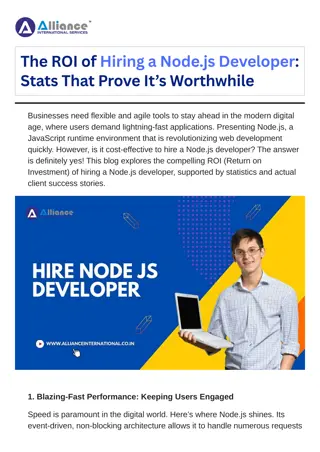
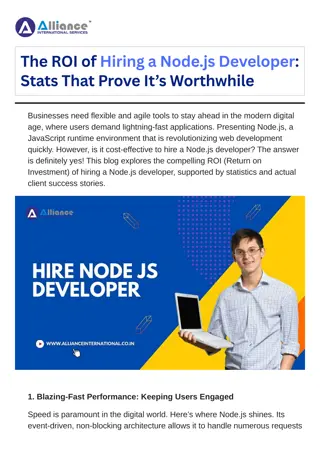
Implementing Heaps How do we find the minimum node? ???????() = ???[0] A How do we find the last node? ????????() = ???[???? 1] B C How do we find the next open space? ?????????() = ???[????] How do we find a node s left child? E F G D ????? ??? ? = 2? + 1 How do we find a node s right child? J K L H I ??? ?? ??? ? = 2? + 2 How do we find a node s parent? Fill array in level level- -order order from left to right ? 1 2 ?????? ? = 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 9 10 10 11 11 12 12 13 13 A A B B C C D D E E F F G G H H I I J J K K L L CSE 373 19 SP - KASEY CHAMPION 6
Heap Implementation Runtimes char peekMin() timeToFindMin A Tree Tree Array Array (1) (1) C B char removeMin() findLastNodeTime + removeRootTime + numSwaps * swapTime (n) Tree Tree n + 1 + log(n) * 1 F D E Array Array (log(n)) 1 + 1 + log(n) * 1 void insert(char) findNextSpace + addValue + numSwaps * swapTime 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 A A B B C C D D E E F F (n) n + 1 + log(n) * 1 Tree Tree (log(n)) Array Array 1 + 1 + log(n) * 1 CSE 373 SP 18 - KASEY CHAMPION 7
Building a Heap Insert has a runtime of (log(n)) If we want to insert a n items Building a tree takes O(nlog(n)) - Add a node, fix the heap, add a node, fix the heap Can we do better? - Add all nodes, fix heap all at once! CSE 373 SP 18 - KASEY CHAMPION 8
Cleaver building a heap Floyds Method Facts of binary trees - Increasing the height by one level doubles the number of possible nodes - A complete binary tree has half of its nodes in the leaves - A new piece of data is much more likely to have to percolate down to the bottom than be the smallest element in heap 1. Dump all the new values into the bottom of the tree - Back of the array 2. Traverse the tree from bottom to top - Reverse order in the array 3. Percolate Down each level moving towards overall root see lecture 16 slides for example / animations CSE 373 SP 18 - KASEY CHAMPION 9