Glaucoma: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
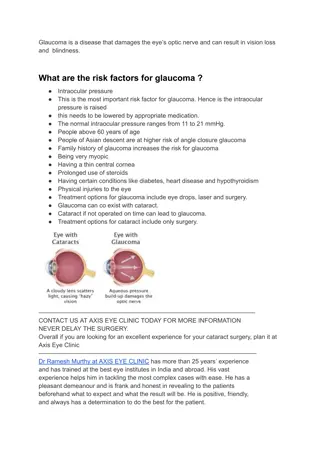
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that can lead to irreversible vision loss. There are different types such as open-angle, closed-angle, secondary, and normal-tension glaucoma, each with unique characteristics and causes. Symptoms vary from rapid damage in closed-angle glaucoma to gradual peripheral vision loss in open-angle glaucoma. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent vision impairment.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Eye: Overview of Glaucoma By D. J. ILES
What is Glaucoma? (6000 6091) Closed-angle glaucoma Open-angle glaucoma Secondary glaucoma Normal-tension glaucoma
Closed Closed- -angle Glaucoma angle Glaucoma Frontal/Central field of vision Happens quickly and can cause damage to the optical nerve quickly Symptoms would be loss of vision and eye pain Head trauma
Open Open- -angle Glaucoma angle Glaucoma Lateral field of vision Happens slowly over time Loss of peripheral vision Changes to shape of eye over time
Secondary Glaucoma Can be caused by secondary like diabetes or cataracts Can be either of the angled glaucomas Normal-tension glaucoma can happen even if the eye pressure is normal
Incapacitating Episode For purposes of evaluation, it is an eye condition severe enough to require a clinic visit to a provider specifically for treatment purposes.
General Rating Formula for Diseases of the Eye Episodes needing 7 or more tx over 12 months ------- 60 Episodes needing at least 5 but < 7 or more tx over 12 months ------- 40 Episodes needing at least 3 but < 5 or more tx over 12 months ------- 20 Episodes needing at least 1 but < 3 or more tx over 12 months ------- 10
Visual Acuity Ratings Condition can be Unilateral or Bilateral Dependent upon eye score and field of vision As visual field shrinks, rating goes up (Bilateral)
Do any of the conditions rate 100%? Tuberculosis of the eye (active) Malignant neoplasms of the eye, orbit, and adnexa (excluding skin)
Cataracts If replacement lens present, evaluate under the general rating formula for diseases of the eye. If no replacement lens, evaluate based on aphakia Minimum rating (Unilateral or Bilateral) ------- 30
What about SMC? Blindness in both eyes ------- L Blind in one eye and total blindness in the other eye with only the ability to perceive light --- L 1/2