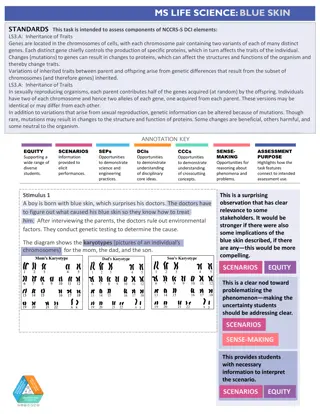
Genetic Inheritance Patterns and Ratios
Genetics involves the study of inherited characteristics, such as monohybrid inheritance and the observed versus theoretical ratios. Explore how genetic traits are passed down from parents to offspring through Punnett squares and backcrossing techniques.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Genetics The study of inherited characteristics
Monohybrid inheritance Let the allele for round seeds be: Let the allele for wrinkled seeds be: R (dominant allele) r (recessive allele) Parentsphenotype genotype round seeds x wrinkled seeds RR rr Gametes R R r r F1 generation gametes gametes R r r R Rr Rr Rr Rr F1 phenotypes 100% plants producing round seeds F1 genotypes 100% heterozygotes Rr
F1 intercross Parents phenotype round seeds x round seeds genotype RrRr R r R r Gametes F2 generation gametes R RR Rr gametes R r r Rr rr Phenotype 75% plants producing round seeds 25% plants producing wrinkled seeds Genotype 25% RR 50% Rr 25% rr Ratio 3:1 Round seeds: wrinkled seeds
Does the observed ratio match the theoretical ratio? The theoretical or expected ratio of plants producing round or wrinkled seeds is 3 round :1 wrinkled Mendel s observed ratio was 2.96:1 The discrepancy is due to statistical error The observed ratio is very rarely the same as the expected ratio The larger the sample the more nearly the results approximate to the theoretical ratio Statistical tests such as the chi-squared test can be used to test the closeness of fit of the observed and theoretical ratios
What if the parents are not homozygous? The use of the term F1 generation is limited to the offspring of two homozygous parents The use of the term F2 is limited to the offspring of intercrossing the F1 generation In all other cases the terms offspring (1) and offspring (2) should be used The complete set of headings will be: Parents phenotypes Parents genotypes Gametes Offspring (1) genotypes Offspring (1) phenotypes Gametes Offspring (2) phenotypes Offspring (2) genotypes
Backcross To test whether a plant producing round seeds is homozygous RR or heterozygous Rr it can be crossed with a homozygous rr plant If plant is homozygous dominant RR If plant is heterozygous Rr Parents phenotype round x wrinkled genotype Rr rr gametes R Parents phenotype round x wrinkled genotype RR rr gametes R r r r R r r Offspring Offspring gametes R Rr Rr gametes R Rr Rr gametes r r gametes r r R Rr Rr r rr rr Offspring Offspring phenotype 100% round phenotype 50% round 50% wrinkled Genotype 100% Rr genotype 50% Rr 50% rr
This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.