Forces in Motion: A Comprehensive Overview
Forces play a crucial role in our daily activities, influencing motion and direction. This chapter delves into the concept of forces as pushes or pulls, exploring balanced and unbalanced forces and their impact on velocity. By examining real-life scenarios like kicking a soccer ball or opening a door, readers gain valuable insights into the fundamental principles of motion and forces.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 3 3.3 Motion and Forces Forces
Forces Think about your daily activities Pushing open a door, kicking a soccer ball, pulling open a drawer All of these actions result in a force being applied to some object
Forces A force is a push or a pull that one objects exerts (or applies) on another Force is a vector It has a size (strength) AND a direction Ex: when you lift your backpack, you apply an upward force Force is measured in newtons (N)
Forces Changing Motion When you apply force to a moving object, it can cause the motion to change (but not always!) What happens to the motion and direction of the ball when the tennis player hits it?
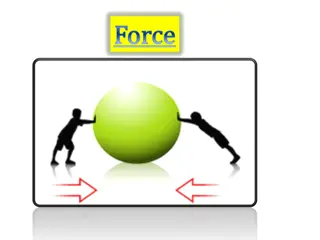
Forces Balanced Forces Force does not always cause a change in velocity When 2 or more forces act on an object at the same time, they combine to form a net force (net = total) In the picture below, the net force is zero because the two forces acting on the opposite sides of the refrigerator are equal, so they cancel out When forces on an object are equal in size and opposite in direction, they are called balanced forces
Forces Unbalanced Forces When unequal forces are applied to an object, the net force occurs in the direction of the larger force If the net force is NOT zero, we call this an unbalanced force Which side will win the tug of war? Why/how do you know?
Forces Unbalanced forces change velocity If forces acting on an object are balanced (net force is zero), velocity doesn t change BUT if the forces are unbalanced, then you will see a change in velocity Think about what would happen if you and a friend were on opposite sides of the door pushing With the same force? ____________________________________________________ With different amounts of force? ____________________________________________
Forces Recap What is the difference between a balanced force and unbalanced force?
Forces 5 N 4 N 8 N 15 N 15 N 7 N Net force: Net force: Net force: Change in motion: Change in motion: Change in motion: 10 N 20 N 4 N Net force: Change in motion: