Fascinating Facts about Basking Sharks
The basking shark, second largest fish globally, is a filter feeder known for feeding near the surface. They prefer habitats with high zooplankton concentrations and are active year-round. Satellite tagging revealed their migratory patterns and social behaviors. Despite few predators, they are fascinating creatures that attract curiosity and awe.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Basking Shark By: Tanner Allison and Ben Sobey
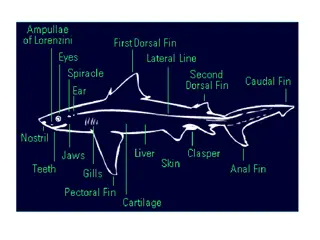
Description The basking shark is the second largest fish in the world, with a maximum recorded size of 12.2m. This filter feeder is named after its strange behaviour of feeding at the surface. The basking shark is typically blackish to grey-brown. It has an extremely large mouth with a pointed snout, and a crescent-shaped caudal fin. Gill openings have prominent gill rakers. The earliest fossil basking shark is 29 to 35 million years old
Habitat Basking sharks are planktivores, and areas with high concentrations of zooplankton appear to be their favoured habitat, typically including fronts where water masses meet, headlands, and around islands and bays with strong tidal flow. They spend much of their time near the surface, although there is recent evidence that basking sharks may also use deepwater habitats greater than 1000 m.
Yearly Life Basking sharks do not hibernate, and are active year-round. In winter, basking sharks move to depths of 900 m to feed on deep-water plankton https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kDKjTiSk maM
Migration Satellite tagging confirmed basking sharks move thousands of kilometres during the winter. They shed and renew their gill rakers in an ongoing process They are slow-moving sharks, and do not evade approaching boats (unlike great white sharks). They are not attracted to humans. Though the basking shark is large and slow, it can breach, jumping entirely out of the water
Interactions Basking sharks are social animals and make schools, usually in small numbers (three or four), but reportedly up to 100 individuals. Although the basking shark's eyes are small, they are fully developed. They may visually inspect boats, possibly mistaking them for other basking sharks. Females seek shallow water to give birth.
Predators Basking sharks have few predators. White sharks have been reported to scavenge on the remains of these sharks. Killer whales have been seen feeding on basking sharks off California and New Zealand. Lampreys are often seen attached to them, although they are unlikely to be able to cut through the shark's thick skin.
Diet The basking shark is a passive feeder, filtering zooplankton, small fish, and invertebrates from up to 2,000 short tons or 1,800 t of water per hour. They feed at or close to the surface with their mouths wide open and gill rakers erect. Unlike the mega mouth shark and whale shark, the basking shark does not appear to actively seek quarry, but it does possess large olfactory bulbs that may guide it. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k3_7ZzNu sDU
Importance to Humans Historically, the basking shark has been a staple of fisheries because of its slow swimming speed, placid nature, and previously abundant numbers. Commercially, it was put to many uses: the flesh for food and fishmeal, the hide for leather, and its large liver for oil. It is currently fished mainly for its fins for shark fin soup. Parts such as cartilage are also used in traditional Chinese medicine and as an aphrodisiac in Japan, further adding to demand.
If extinction occurred Over the past two centuries, people have killing for sport, food, and oil from there half- tonne livers, and to get them out of the way of commercial fishing operations. Many were also killed accidentally by fishing gear unless not on purpose. If basking sharks did become extinct we wouldn't be able to have food oil and some other products that the basking sharks give us.
Check Your Knowledge 1. What is the biggest basking shark recorded? 2. Where do they typically eat? 3. How many sharks are in a basking shark school? 4. Why do fishermen hunt basking sharks? 5. What is the main predator of the basking shark?
Answers 1. 12.2 meters long. 2. close to the surface. 3. 3 or 4 4. they hunt them for food, leather and medicine 5. killer whale