Exploring Evolutionary Mechanisms: Genetic Drift, Gene Flow, Mutation, and Recombination
Delve into the effects of evolutionary mechanisms such as genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination in populations. Understand how changes in allele frequencies occur due to various factors like natural disasters and the bottleneck effect, impacting the gene pool and future generations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Unit 11 7F Analyze and evaluate the effects of other evolutionary mechanisms, including genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination.
Lets remember An allele is an alternative form of one gene B stands for black b stands for brown The allele would be
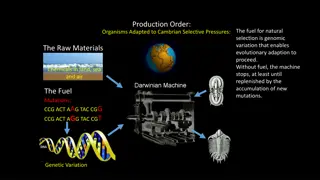
Genetic Drift An evolutionary mechanism in which allele frequencies change in a population
Allele frequency changes due to Natural disaster like flood, fire, or earthquake A random change of the population (some are eliminated) Different from natural selection b/c its by chance or randomly
Original Pop Pop after change R = red star r = green heart 5r 6R, 5r
http://legacy.hopkinsville.kctcs.edu/sitecore/instructors/Jason-Arnold/VLI/Module%203/Module3Evolution/f15-07_genetic_drift-_c.jpghttp://legacy.hopkinsville.kctcs.edu/sitecore/instructors/Jason-Arnold/VLI/Module%203/Module3Evolution/f15-07_genetic_drift-_c.jpg
https://worldofbiology.wikispaces.com/file/view/genetic_drift.pnghttps://worldofbiology.wikispaces.com/file/view/genetic_drift.png
Bottleneck Effect The change in allele frequency where only genes of the surviving population members can be passed to future generations
http://4.bp.blogspot.com/-OMOTL9KKgWw/UOyBMa8yD-I/AAAAAAAAAs4/pCXfKtkGvl4/s1600/bottleneckeffect.gifhttp://4.bp.blogspot.com/-OMOTL9KKgWw/UOyBMa8yD-I/AAAAAAAAAs4/pCXfKtkGvl4/s1600/bottleneckeffect.gif
Gene Pool the sum of all the genes in an interbreeding population
Gene Pool http://faculty.uca.edu/johnc/gene_pool_lg.gif 2 blue alleles 1 red allele 12 green alleles
http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab8/images/lgpop.gifhttp://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab8/images/lgpop.gif
Founder Effect The change in allele frequency in a gene pool that changes from a large population to a small population Ex: small number of individuals get separated from a larger population the change in the allele frequency is the founder effect
http://www.umbc.edu/bioclass/biol100/powerpoints/lecture10/img032.jpghttp://www.umbc.edu/bioclass/biol100/powerpoints/lecture10/img032.jpg
Founder Effect http://beacon-center.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/Fig1.jpg
Gene Flow Occurs when the genes of 1 population flow into a different population This change causes a shift in allele frequency
Immigration Alleles move INTO a population http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evosite/evo101/images/micro_mech_2.gif
Emigration Alleles move OUT OF a population
Lots of gene flow Slows down evolution Lots of new alleles coming into and out of a population More genetic variation within a population Makes 2 populations more similar
Lack of gene flow Less variation within a population Makes 2 populations more different and separates them
Mutation Any change in the genetic material of a cell Can occur within individual genes OR Can involve changes in piece of chromosomes
If the mutation is beneficial to the organism, the mutation will be passed on to offspring Slowly over time the mutation will become more common in a population
Recombination A source of heritable variation Occurs for 2 reasons: a.Independent assortment b.Crossing over
Independent Assortment http://bio3400.nicerweb.com/Locked/media/ch05/05_01-linkageA.jpg
Crossing Over http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab3/images/crossovr.gif
Hardy-Weinberg Principle States that allele frequencies in a population will remain constant unless one ore more factors cause those frequencies to change
Hardy-Weinberg Equation Homozygous dominant Homozygous recessive Heterozygous P2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 p = dominant allele frequency q = recessive allele frequency
Genetic Equilibrium The situation in which allele frequencies remain constant (don t change) If frequencies don t change, the population doesn't evolve
Conditions required to maintain genetic equilibrium: 1. Random mating 2. Population must be large 3. No immigration or emigration 4. No mutations 5. No natural selection