Evolution of Animal Classification
Unveil the fascinating world of animal classification with a new system, delving into the definition of animals, informal groups, key events in animal evolution like symmetry and germ layers, embryological development of protostomes and deuterostomes, tissues formation, body cavity types, and cephalization importance. Discover the intricacies of animal evolution and diversity through engaging visuals and informative content.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Definition of Animal? Eukaryotic Heterotroph Multicellular No rigid cell wall Gametic (sexual) reproduction Kingdom Animalia 35-40 phyla Monophyletic What % invert? Most ectotherms Dramatically different body form/function
Anus Mouth
Key Events in Animal Evolution: Symmetry Why is Bilateral symmetry so prolific?
Key Events in Animal Evolution: Germ Layers https://www.youtu be.com/watch?v= dXpAbezdOho
Embryological Development Protostome
Embryological Development Deuterostome
Key Events in Animal Evolution: Tissues Two germ layers in primitive animals Three germ layers in complex animals Give rise to all tissue types Ectoderm skin and nervous Mesoderm skeletal and muscle Endoderm digestive Zebrafish embryo
Key Events in Animal Evolution: Body Cavity Organisms larger and more complex Need complex organs and systems Led to evolution of body cavity Three body cavity types
Body Cavity Types
Key Events in Animal Evolution: Cephalization Concentration of body functions at anterior Only in bilateral symmetry Why Important?
Key Events in Animal Evolution: Segmentation 3 major lineages 3 benefits of segmentation Protection Mobility Complexity
Other Key Features of the Animal Body Plan How do protists, bacteria, etc., get O2 to parts of body? What happens as animals get larger? How do animals solve this problem? 2 types:
Subkingdom Parazoa Phyla Porifera Most basal animal phyla 7000 marine, 150 freshwater Adults sessile Larvae planktonic Synapomorphies? Basic structure Yellow sliver
Filter Feeders https://www.youtu be.com/watch?v=p TZ211cIjX8
Size limited - why? OBSERVE: Preserved sponges (pg 398)
Reproduction Asexual Fragmentation Budding Sexual Hermaphroditic (monoecious) Few oviparous Most viviparous
Eumetazoa: The Radiata Distinct tissues (which?) called? True body symmetry - ? No coelom No real organs Two phyla:
Phylum Cnidaria 9,000 species Almost all marine All carnivorous Two body plans General life cycle 4 classes DRAW one, OBSERVE others: Aurelia medusa (pg 405) Aurelia planula Aurelia polyp
Are cnidarians smart? Are cnidarians fast? How are they carnivorous?
Cnidocytes Types of organelles Stinging (most) Adhesive Grasping Lassos Springs Hydra nematocyst http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PPYiC 1HDu-M http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6zJiBc _N1Zk
Class Hydrozoa (hydras) 2700 sp. Mostly marine Named after 9- headed hydra Which stage is dominant? DRAW: Live Hydra (36.2) OBSERVE: Physalia or Gonionemus (pg 404)
Class Scyphozoa 200 species Marine only? Coastal (most) Which stage dominant? Most small Most not deadly what should you do if stung? All dioecious http://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=bcmLxsJ5SAg OBSERVE: Aurelia or Live Jellyfish
Class Cubozoa Box jellyfish 50 species Recently split Umbrella is square-shaped Tropical and subtropical global Cluster of tentacles at corners of umbrella Active predators How do they actively hunt? https://www.youtube.com/watch ?v=TSyvV6F1VzA
Chironex fleckeri Sea Wasp Tropical Australia
Class Anthozoa (corals, sea anemones) 6200 sp. All marine All regions of ocean Polyp stage only Basic anatomy DRAW: Anemone dissection (pg 405)
Corals Miniature anemones Colonial Two types: Hard secrete calcium carbonate Soft no rigid skeleton Broadcast reproducers Symbiosis with? DRAW: Hard or Soft coral (pg 407)
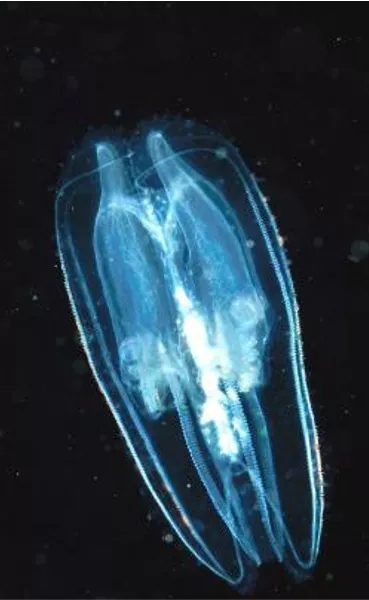
Phylum Ctenophora 100 sp. Marine tropics Eight rows of comb-like cilia Two long tentacles Formerly Cnidaria http://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=icKB9E fURhQ