Derivative Markets and Investment Options
Explore the world of derivative markets through stock options on Apple, futures contracts, and the impact of exercise price, time to expiration, volume, and open interest on option values. Gain insights into listed call and put options, different option prices, and the dynamics of futures contracts in the financial market.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
2.5 Derivative Markets Derivative Asset/Contingent Claim Security with payoff that depends on the price of other securities Listed Call Option Right to buy an asset at a specified price on or before a specified expiration date Listed Put Option Right to sell an asset at a specified exercise price on or before a specified expiration date 2-1
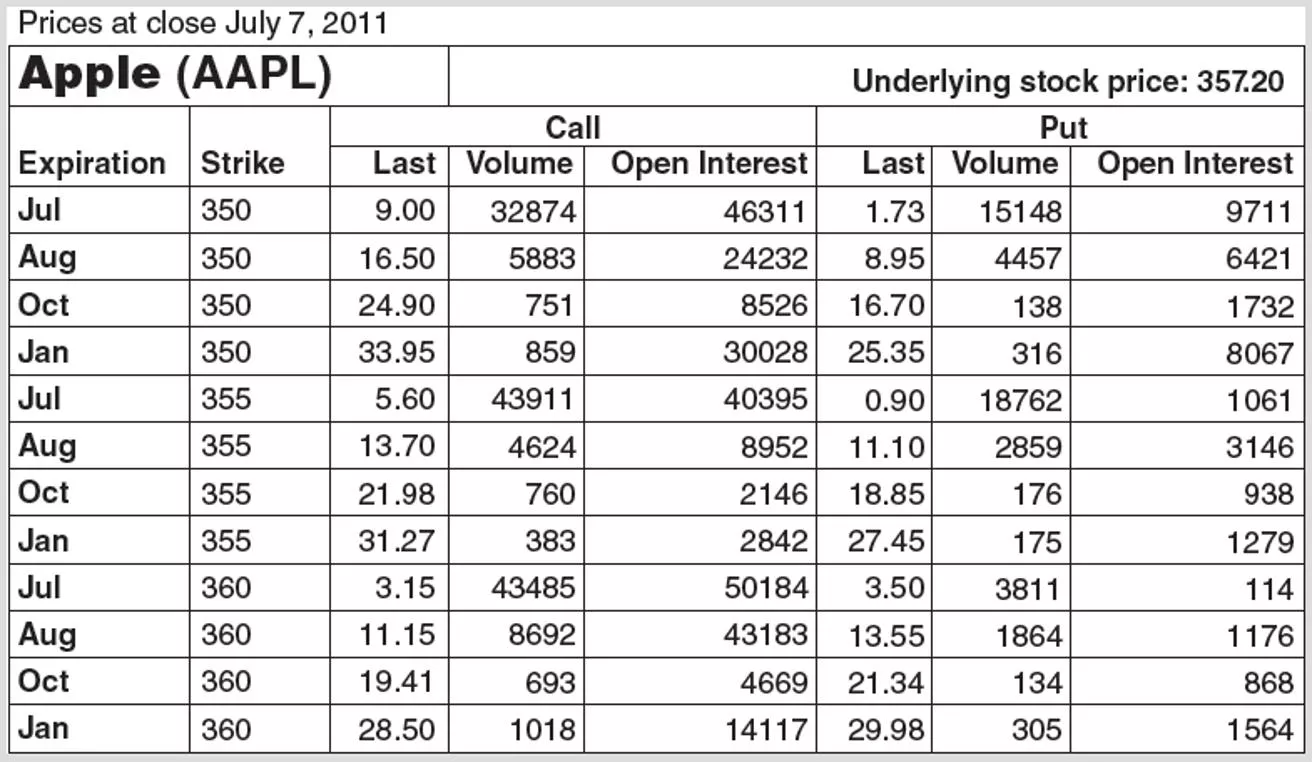
2.5 Derivative Markets Using the Stock Options on Apple The right to buy 100 shares of stock at a stock price of $355 using the July contract would cost $560 (ignoring commissions) Is this contract in the money ? When should you buy this contract? Stock price was equal to $357.20; you will make money if stock price increases above $357.20 + $5.60 = $362.80 by contract expiration 2-3
2.5 Derivative Markets Using the Stock Options on Apple The right to buy 100 shares of stock at a stock price of $355 using the July contract would cost $90 (ignoring commissions) Is this contract in the money ? Why do the two option prices differ? 2-4
2.5 Derivative Markets Using the Stock Options on Apple Look at Figure 2.9 to answer the following questions How does the exercise or strike price affect the value of a call option? A put option? Why? How does a greater time to contract expiration affect the value of a call option? A put option? Why? How is volume different from open interest ? 2-5
2.5 Derivative Markets Futures Contracts Purchaser (long) buys specified quantity at contract expiration for set price Contract seller (short) delivers underlying commodity at contract expiration for agreed- upon price Futures: Future commitment to buy/sell at preset price Options: Holder has future right to buy/sell 2-6
Figure 2.10 Futures Contracts Corn futures prices in the Chicago Board of Trade, July 8, 2011 2-7
2.5 Derivative Markets Corn futures prices in the Chicago Board of Trade, July 8, 2011 Contract size: 5,000 bushels of corn Price quote for Dec. 12 contract: 614 0 translates to a price of $6.14 + 0/8 cent per bushel, or $6.14 If you bought the Dec. 12 contract, what are you agreeing to do? Purchase 5,000 bushels of corn in December for 5,000 $6.14 = $30,700 What is your obligation if you sell the Dec. 12 contract? How does this contract differ from an option? 2-8
2.5 Derivative Markets Derivatives Securities Options Basic Positions Call (Buy/Sell?) Put (Buy/Sell?) Terms Exercise price Expiration date Futures Basic Positions Long (Buy/Sell?) Short (Buy/Sell?) Terms Delivery date Deliverable item 2-9