Decentralization and Local Governance in Nepal: A Comprehensive Overview
Explore the essence of decentralization and local governance in Nepal, highlighting the process, benefits, and global significance. Understand how these initiatives promote democratization, equity, and effective service delivery while fostering good governance and citizen participation. Discover the arguments in favor of decentralization and its pursuit in developing countries.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Decentralization, and Local Governance in Nepal Reshmi Raj Pandey Ministry of Federal Affairs and Local Development 1
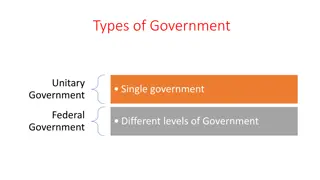
Decentralization Part of the overall governance system Process by which authority, responsibility, power, resources and accountability are transferred from the central level of government to the sub-national level Based on the principle of subsidiarity Decentralization not an alternative to centralization, both are needed 2
Local Governance Promotes democratization, equity, inclusion, people s participation, local ownership and effective service delivery. Its goal : to promote good governance, build partnership with civil society, private sector and governments units at the local level. A cross-cutting sector which addresses local accountability, transparency and participation of citizen. 3
Decentralization and Local Governance The decentralization now a world- wide phenomenon. Both developed and developing countries are pursuing it. Developed countries use it as an effective tool for the reorganization of the government to provide the public goods and services efficiently. Developing countries use it to free from ineffective and inefficient governance. 4
Four Arguments in favour of Decentralization (Prud homme) 1 Variance factor: Demand varies for local services from place to place Efficiency factor: It is possible to produce locally financed and provided services at lower cost because of time saving, local resources use and exercising of responsibility and oversight 5
Four Arguments in favour of Decentralization (Prud homme) 2 Political factor: (a). It provides a training ground for democracy. (b). It makes possible to bar the central government to become all powerful. Institutional factor: Co-ordination at the local level is easier. 6
Why decentralization is pursued in developing countries? 1 Promotion of national unity (Africa) People s pressure to strengthen democratization process (Latin America) Smooth transition from socialist/command economy to market economy (Central and Eastern Europe) 7
Why decentralization is pursued in developing countries? 2 Improvement of service delivery to the large population in the centralized countries (East Asia) Address ethnic, linguistic, religious and geographic diversities (South Asia, Russia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Ethiopia, etc.) 8
Decentralization and Local Governance in Nepal 1 1963 Power Decentralization Commission 1969 Decentralization Committee 1982 Decentralization Act 1991 Administrative Reform Commission 1996 High Level Decentralization Committee 1999 Local Self-Governance Act (LSGA) 9
Decentralization and Local Governance in Nepal 2 2000 2001 Local Body Fiscal Commission Decentralization Implementation Plan Budget Speech (2001/02): Sectoral Devolution Local Body Strengthening Recommendation Committee Interim Constitution 2006/7 Minimum Conditions and Performance Measures (MCPM) 2015 Performance Contract with LDOs/EOs 2003 2007 10
g]kfndf @)%( kl5 lgjf{lrt hg k|ltlglw gx'Fbf -;+qmd0fsfndf_ :yfgLo lgsfosf] ;~rfng
:yfgLo lgsfox?sf] sfo{ ;~rfng -lj=;+=@)%( b]lv xfn;Dd_ k|hftGqsf] axfnL -lj=;+=@)$&_ kl5 ufpF ljsf; ;ldlt, gu/kflnsf / lhNnf ljsf; ;ldlt P]]g, @)$* cg';f/ @)$* b]lv @)%# ;Dd klxnf] sfo{sfn ;dfKt . lj=;+= @)%$ >fj0f b]lv @)%( c;f/ d;fGt;Dd :yfgLo lgsfox?sf] bf]>f] sfo{sfn ;dfKt, o; jLr :YffgLo lgsfosf] ;'b[9Ls/0f ug{ s]xL kxnx? ePsf, :yfgLo :jfoQ zf;g P]g, @)%% pRr:tl/o ljs]Gb|Ls/0f k|ltj]bg, @)%#, @)^! :yfgLo lgsfo ljQLo cfof]usf] :yfkgf @)%& lgIf]k0f sfo{of]hgf, @)%* lgjf{lrt hgk|ltlglwx?sf l/Sttf -@)%(.$.! b]lv xfn @)&!.#.#! ;Dd !@ aif{ _ hgk|ltlglw jxfnLsf j}slNks Joj:yfx?, dgf]gog, lgjf{rg k|of;, lghfdtL sd{rf/L / sd{rf/L ;+oGq4f/f ;+rfngsf] k|of; . 12
;+qmd0fsfndf :yfgLo lgsfosf] ;+rfng :yfgLo :jfoQ zf;g P]g, @)%% sf] bkmf @#( df ;+zf]wg u/L ;/sfn] a9Ldf Ps aif{sf] nflu-bf]>f] pkbkmfn] k'gM Ps aif{ yKg ;lsg] u/L_ Dofb yk ug]{{ jf cGo tj/jf6 :yfgLo lgsfosf] sfo{ ;+rfng ug{ / ;f] lgsfosf] ;b:osf] sfd, st{Ao / clwsf/sf] k|of]u ug{ u/fpg cfjZos Joj:yf ug{ ;Sg], u/L :yfgLo :jfoQ zf;g -klxnf] ;+zf]wg_ cWofb]z, @)^) dfkm{t ;+zf]wg ul/of] . @)%(.$.#) / &.!# sf] /fhkqsf] ;"rgf cg';f/ uflj;sf] xsdf uflj; ;lrj cWoIf, O{nfsf s[lif. kz' sfof{no k|ltlglw / O{nfsf :jf:Yo sfof{no k|ltlglw ;d]t # ;b:oLo sfo{;+rfng ;ldlt dfkm{t ;+rfng ug{ ;lsg] , gu/kflnsfsf xsdf sfo{sf/L clws[t cWoIf, k"jf{wf/, hg:jf:Yo,cfGtl/s /fhZj,lhNnf k|zf;g, dfnkf]t sfof{no / lhlj; of]hgf clws[t ;d]t & ;b:oLo sfo{;+rfng ;ldlt dfkm{t / lhlj;sf xsdf :yfljc cWoIf, lhNnf s[lif, lzIff, hg:jf:Yo, dlxnf ljsf;, k"jf{wf/, k|fzf;g, dfnkf]t / kz' sfof{nosf clws[t k|ltlglw ;d]t ( ;b:oLo sfo{;+rfng ;ldlt dfkm{t sfdsfh ug]{ u/L tf]lsPsf] . 13
;+qmd0fsfndf :yfgLo lgsfosf] ;+rfng === g]kfn ;/sf/ dlGqkl/ifbsf] ldlt @)^).^.!@sf] lg0f{on] pk/f]Qm cg';f/ ul7t :yfgLo lgsfo sfo{;+rfng ;ldltnfO{ :yfgLo :jfoQ zf;g P]g @)%% cg';f/sf sfd st{Ao / lhDd]jf/L lbPsf] k'li6 ub}{ sfo{;+rfng ;ldltsf] x]/km]/ ljefuLo dGqL:t/af6 x'g ;Sg] u/L clwsf/ k|Tofof]hg u/]sf] . g]kfn ;/sf/ dlGqkl/ifbsf] ldlt @)^!.$.!$sf] lg0f{on] ;fljssf] :yfgLo lgsfo sfo{;+rfng ;ldltdf ;fdfGo ;+zf]wg ;d]t u/L sfo{ ;+rfng ;ldltsf] Joj:yf :yfgLo :jfoQ zf;g-klxnf] ;+zf]wg_ cWofb]z,@)^! dfkm{t x'g] u/L :jLs[lt k|bfg . ;f] Joxf]/f g]kfn /fhkqsf] ;'rgf dfkm{t ;fj{hlgs ul/Psf] o; ;+zf]wgdf vf; u/L sf]n]lgsfsf] k|ltlglwnfO{ lhlj; / gkfsf] sfo{;+rfng ;ldltdf /fvLPsf] / lhNnf k|zf;g, dfnkf]t, k"jf{wf/ sfof{nosf k|ltlglwnfO{ x6fO{ -cfdGq0f ug{ ;Sg] u/L_ lhlj; sfo{;+rfng ;ldlt & ;b:oLo agfOPsf] . cWofb]zx? @)^),@)^!,@)^@ af6 cGo tj/af6 :yfgLo lgsfosf] sfo{ ;+rfng ug]{ sfo{nfO{ lg/Gt/tf lbO{Psf] . 14
;+qmd0fsfndf :yfgLo lgsfosf] ;+rfng === @)^@.@.#) b]lv @)^@.!@.# ;Dd lhlj;sf ljleGg kbdf g]kfn ;/sf/ - :yfljd+qL:t/_ af6 ;efklt, pk;efklt, lhlj; ;b:o dgf]gog u/L ;+rfng ug]{ k|of; ePsf] . @)^#.!.@)sf] g]kfn ;/sf/sf] lg0f{oaf6, @)%( c;f]h !* kl5 ;/sf/n] u/]sf lhlj; ;efklt, pk;efklt, ;b:o nufotsf ;a} lgo'lQm. dgf]gog vf/]h u/L ;efkltsf] sfd :yfljcn] ug]{ / @)^@ df3 @^ ut] dxfgu/, pkdxfgu/ / gu/kflnsfx?sf] ePsf] lgjf{rg vf/]h u/L k|d'vsf] sfd sfo{sf/L clws[t / j8fWoIfsf] sfd j8f ;lrjn] ug]{ u/L Joj:yf ePsf] . @)^#.!.@! sf] g]kfn ;/sf/ dlGqkl/ifbsf] lg0f{ofg';f/ rfn" cf=j=sf nflu lhNnf / gu/ kl/ifbsf] clwsf/ qmdzM :yfljc / sfo{sf/L clws[t n] ug]{ / cfGbf]ng/t bx?sf] ;j{blno ;+oGq;+u ;dGjo u/L sfd ug]{ . lj;+= @)^# df3 ! ut] b]lv g]kfnsf] cGtl/d ;+ljwfg @)^#sf] sfof{Gjog ePsf] . ;+ljwfgsf] wf/f !#( df :yfgLo :jfoQ zf;g ;DaGwL lgsfox?sf] lgjf{rg ul/g], lgjf{rg geP;Ddsf nflu :yfgLo txdf lqmofzLn /fhg}lts bnx?sf] ;xdlt / ;eflutfdf lhNnf, gu/ / ufpF :t/df cGtl/d :yfgLo lgsfo u7g ul/g] s'/f pNn]v 5 . 15
jt{dfg ;dodf :yfgLo lgsfosf] ;+rfng === @)^%.@.!(sf] :yfgLo ljsf; dGqL:t/Lo lg0f{ofg';f/, @)^# b]lv g} ;j{blno ;+oGqdfkm{t :yfgLo lgsfox? ;+rfng e} /x]sf]df @)^$ ;fnsf] ;+ljwfg ;ef lgjf{rgdf :yfgLo ?kdf !) k|ltzt eGbf a9L dt k|fKt ug]{ /fhg}lts bnaf6 Ps Ps hgf k|ltlglw ;dfj]z ePsf] :yfgLo lgsfo u7g ug]{ s'/f pNn]v . pk/f]Qm k|lqmofnfO{ :ki6 kfb}{ @)^^.#.@%sf] :yfgLo ljsf; dGqL:tl/o lg0f{ofg';f/ k|ToIf lgjf{rgdf efu lnPsf / ;+ljwfg ;efdf k|ltlglwTj ePsf bnaf6 Ps Ps hgf k|ltlglw ;dfj]z ug]{ lg0f{o ePsf] . clVtof/ b'?kof]u cg';Gwfg cfof]usf] )^*.(.* kqcg';f/ k|fKt sf] lgb]]{zg cg';f/ :yfgLo ljsf; dGqL:t/sf] @)^*.(.!(sf] lg0f{oaf6 sfg"gL Joj:yf k'/f gu/L agfO{Psf ;Dk"0f{ ;j{blno ;+oGq vf/]h u/L lhlj; / gkfsf xsdf qmdzM :yfljc / sfo{sf/L clws[t / uflj;sf xsdf ulj; ;lrj cWoIf / :jf:Yo, s[lif jf kz' sfof{nosf] :yfgLo k|lglglw ;b:o /x]sf # ;b:oLo ;ldltn] :yfgLo lgsfosf] sfdsfh ug]{ Joj:yf ePsf] . 16
Principles of LSGA 1 Devolution of powers, responsibilities, means and resources Building and Development of Institutional Mechanism and Functional Structure Devolution of power to collect and mobiliza resources to discharge duties and responsibilities 17
Principles of LSGA 2 Orientation towards establishing civil society based on democratic process, transparent practice, public accountability and people s participation Development of local leadership Encouragement of the private sector to participate in local self-governance 18
Major Provisions of LSGA and Regulations 1 Participatory planning process (periodic/annual plans) Outline of tasks, functions, responsibilities, structures and composition of local bodies Right to Formulate By-laws 19
Major Provisions of LSGA and Regulations 2 Decentralization Implementation and Monitoring Committee (DIMC) and its Working Committee Financial management and auditing system 20
Major Provisions of LSGA and Regulations 3 Local resource autonomy/mobilization Revenue sharing mechanism broadened (on royalties of electricity, forestry, tourism, land registration) Formula-based DDC grant allocation system implemented Provision of Sub-national borrowing Local Body Fiscal Commission established Recognition of Local Bodies Associations 21
Local Development in Nepal LSGA has given local development roles to local bodies including primary health, basic education, local infrastructures and other socio-economic activities The central government provides the conditional and Unconditional, Minimum Conditions and Performance based grants as well as mobilizes donor support for local delopment 22
Major Achievements and Initiatives-1 Formula based Block Grants introduced Minimum Conditions and Performance Measures (MCPM) adopted Performance Contract with LDOs and Executive Officers Local Governance and Community Development Program (LGCDP) towards local governance sector wide approach Local Infrastructure Development Policy Establishment of Department of Local Infrastructure Development and Agricultural Roads (DoLIDAR) under agriculture perspective plan (APP) District Technical Office established within DDC as its technical hand and one district one major local infrastructure development project 23
Major Achievements and Initiatives -2 District and Municipal Periodic Planning District Transport Master Plan implemented 52000 km local road network constructed Nepal is famous for suspension bridge construction and everyday one such bridge is constructed Social Mobilization, ward citizen forums and citizen awareness centres for empowerment and enhanced downward accountability Gender Equality and Social Inclusion Policy and at least 35 percent budget for GESI Mobilization of NGOs, civil society, private sector and donors at the local level People s contribution and users committee 24
Major Achievements and Initiatives-3 Introduction of Municipal and District Development Funds as non-operating municipal and district treasuries National Foundation for the Development of the Indigenous Nationalities, National Dalit Commission and other inclusion related institutions formed Territorial reform (131 new municipalities formed and VDCs reduced to 3276) Social mobilization, Ward Citizen Forums, Citizen Awareness Centres and Child Clubs Social transformation campaigns (CFLG, EFLG, ODF, Full literacy, Child marriage eradication, Child labor free, full immunization, etc.) Web-based reporting started 25
Problems, Issues and Challenges @)^*.(.!( b]lv ;a{blno ;+oGq vf/]h ePkl5 klg dxTjk"0f{ lg0f{ox?, of]hgf th'{df k|s[of, ah]6 afF8kmfF8, cg'udg nufotsf k|s[of / r/0fdf /fhgLlts bnx? ;+usf] consultation ug]{ cEof; ul/Psf] . /fhgLlts bnx?sf] sfg"gL(Legal) e"ldsf st} gb]lvPtf klg hgtf;+usf] ;DaGw, Legitimacy / hjfkmb]lxtf sfod} /xgfn] l4ljwf / hl6ntf b]lvPsf] . /fhgLlts bnx? :yfgLo lgsfosf sfdsfhsf ;DaGwdf st} klg hjfkmb]lx x'g' kg]{ ;+oGq 5}g . /fhgLlts bnx?sf ljrdf cGt/ bnLo ;xdlt, ;dGjo / ;xsfo{ u/L :yfgLo ljsf;sf ;jfnx?df P]Soj4tf h'6fpg sl7g ePsf] .
Problems, Issues and Challenges -1 Absence of elected people s representative for last 12 years creating generation gap in new political leadership formation Diverse understanding among different agencies/actors on decentralization and inadequate commitment of central level government institutions Safeguarding interest of local governance vis- -vis federal restructuring Low frequency of DIMC (only 4 meetings in 15 years) Ambiguous and overlapping tasks and expenditure assignments 23 Contradictory Acts not amended 27
Problems, Issues and Challenges -2 Revenue assignment, grants and revenue sharing not clearly linked with Expenditure Assignments Weak linkage between District Periodic Plan (DPP) and annual District Development Plan (DDP) High cost of local infrastructures due to dispersed settlements More than 2/3 local roads are not all weather roads as we need about 2800 motorable bridges in those roads Still 800 VDCs are not covered by road connectivity Distortion in users committee mobilization Weak compliance of EIAs/IEEs 28
Problems, Issues and Challenges -3 Issue of over exploitation and mismanagement of natural resources of stones, boulders and sand Poor accountability of local staff deployed from the central government agencies Weak discipline among the LB staffs in absence of elected officials and transfer provision Structure and number of Local Bodies specially VDCs not viable Politicization of Users Committees and less contribution of users Weak coordination of regulation of NGOs at local level 29
Problems, Issues and Challenges -4 Weak capacities of the centre to regulate, facilitate and monitor the decentralized governance Weak market decentralization by the Local bodies Expansion of citizen awareness centres and community mediation centres Quality standards not defined More budget allocation by LBs on smaller projects Promise of non-publication of Party Two failed Building code implementation Disaster resilient houses reconstruction in earthquake affected areas Need of VDC restructuring to strengthen the local service 30
Problems, Issues and Challenges -5 Poor vertical and horizontal coordination Many of small local infrastructure projects still implemented by line ministries Weak Management Information and Reporting System Non-implementation of judicial power Ensuring downward accountability at local level Ensuring Local Bodies interest vis-a-viz federal restructuring Formation of metro cities 31
Thank you! 32