Considerations on Joint Transmission in IEEE 802.11-24/0444r2
This presentation explores considerations on Joint Transmission (JT) in IEEE 802.11-24/0444r2, specifically focusing on delivering user data between Access Points (APs). It discusses the ways to increase user throughput through Joint Transmission, considerations on data delivery mechanisms, and the advantages of in-band versus backhaul data delivery methods.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
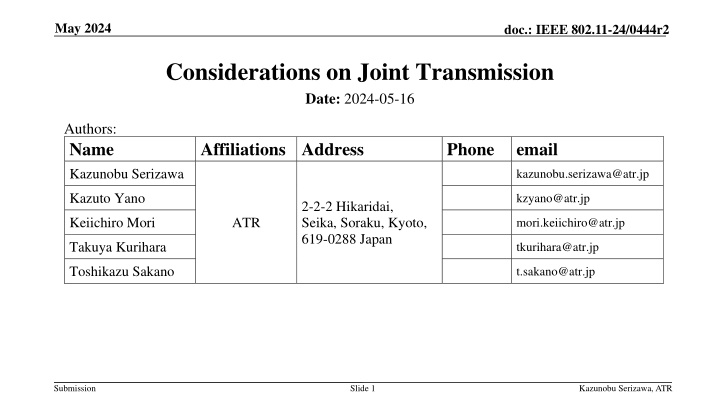
May 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0444r2 Considerations on Joint Transmission Date: 2024-05-16 Authors: Name Kazunobu Serizawa Affiliations Address Phone email kazunobu.serizawa@atr.jp Kazuto Yano kzyano@atr.jp 2-2-2 Hikaridai, Seika, Soraku, Kyoto, 619-0288 Japan Keiichiro Mori ATR mori.keiichiro@atr.jp Takuya Kurihara tkurihara@atr.jp Toshikazu Sakano t.sakano@atr.jp Submission Slide 1 Kazunobu Serizawa, ATR
May 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0444r2 Abstract This presentation intends to discuss considerations on Joint Transmission (JT), especially focused on the way to deliver user data between APs. Submission Slide 2 Kazunobu Serizawa, ATR
May 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0444r2 Introduction Joint Transmission (JT) is a way to increase the user throughput by cooperating multiple APs ([1]-[7]). It needs to deliver user data for JT from a Primary AP (P-AP) initiating JT to one or more Secondary APs (S-APs). This data delivery can be made in- band or through backhaul ([8]-[11]). This presentation discusses some considerations on data delivery. Submission Slide 3 Kazunobu Serizawa, ATR
May 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0444r2 Joint Transmission Multi-AP joint transmission (JT) is a way to increase the user throughput, especially in the situation of less-scattering (LOS) environment, by transmitting different user data to an STA from multiple APs simultaneously. DATA 2 AP1 (P-AP) AP2 (S-AP) Simultaneous transmission from multiple APs DATA 1 DATA 2 STA Submission Slide 4 Kazunobu Serizawa, ATR
May 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0444r2 Ways to deliver user data There are two ways to deliver user data from the P-AP to one or more S-APs. By in-band transmission By out-band transmission through backhaul Through in-band or backhaul. DATA 2 AP1 (P-AP) AP2 (S-AP) Simultaneous transmission from multiple APs DATA 1 DATA 2 STA Submission Slide 5 Kazunobu Serizawa, ATR
May 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0444r2 In-band data delivery It is easy to protect TXOP. If the link speed between the P-AP and S-AP(s) is low, it may consume a time in delivering the user data from the P-AP to the S-AP(s). Under this situation, there may be little advantages for using JT. DATA 2 DATA 1 AP1 (P-AP) Time DATA 2 AP2 (S-AP) Negotiation for JT BlockAck for JT Time Time STA Submission Slide 6 Kazunobu Serizawa, ATR
May 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0444r2 Data delivery through backhaul The link speed of backhaul is higher than of the in-band one. If the user data from the P-AP to the S-AP(s) delivered via backhaul, it can reduce the delivering time , and it can further increase the throughput. DATA 2 DATA 1 AP1 (P-AP) Time Via backhaul In-band DATA 2 AP2 (S-AP) Negotiation for JT BlockAck for JT Time In-band Time STA Submission Slide 7 Kazunobu Serizawa, ATR
May 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0444r2 Data delivery through backhaul (cont.) Several issues may need to be considered as follows: The P-AP will need to send a frame to the S-AP(s) to inform the time to transmit DATA frame to the STA. It may also need a way to protect TXOP during for delivering the user data from the P-AP to the S-AP(s). Time to start JT (T) Time for delivery over backhaul Notify T DATA 1 AP1 (P-AP) Time DATA 2 AP2 (S-AP) Negotiation for JT BlockAck for JT Time (It may need a way to protect TXOP here.) Time STA Submission Slide 8 Kazunobu Serizawa, ATR
May 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0444r2 Summary This contribution discusses the ways to deliver user data for joint transmission from the P-AP to the S-APs. In-band delivery will easily protect TXOP, however, it may consume time in delivering the user data from the P-AP to the S-AP(s) if the link speed between these APs is low. Data delivery through backhaul can further increase the throughput due to a higher backhaul link speed for the data delivery compared to the in- band one. It may need to be considered further several issues, such as a way to send a frame to the S-AP(s) to inform them of the time to transmit DATA frame to the STA, and a way to protect TXOP during for delivering the user data from the P-AP to the S-AP(s). Submission Slide 9 Kazunobu Serizawa, ATR
May 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0444r2 References [1] Multi-AP Joint Transmission Simulations with Impairments , IEEE 802.11-23/1843r0 [2] Multi-AP Simulations: framework and Joint Transmission results , IEEE 802.11-23/1176r1 [3] Joint Transmission for UHR Additional Results , IEEE 802.11-23/0243r0 [4] System Level Simulation of Co-BF and Joint Tx , IEEE 802.11-22/1821r1 [5] Joint Transmission for 11be ,IEEE 802.11-20/0071r1 [6] Consideration on Joint Transmission , IEEE 802.11-19x/1595r0 [7] Multi-AP for reliability with Coherent and Non-coherent transmissions , IEEE 802.11-23/2009r0 [8] Joint Transmission for UHR A Refresher and New Results , IEEE 802.11-22/2188r0 [9] Joint Transmissions: Backhaul and Gain State Issues , IEEE 802.11-19/1089r0 [10] Multi-AP backhaul analysis , IEEE 802.11-19/1588r0 [11] WLAN Backhaul Options , IEEE 802.11-23/0677r0 Submission Slide 10 Kazunobu Serizawa, ATR