Cargo Handling and Storage Essentials
Learn key considerations for cargo handling, calculate space for commodities, understand documentation flow, and protect stocks in this comprehensive lesson plan. Explore equipment, stacking methods, and best practices for efficient storage operations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Storage WFP Logistics, We Deliver
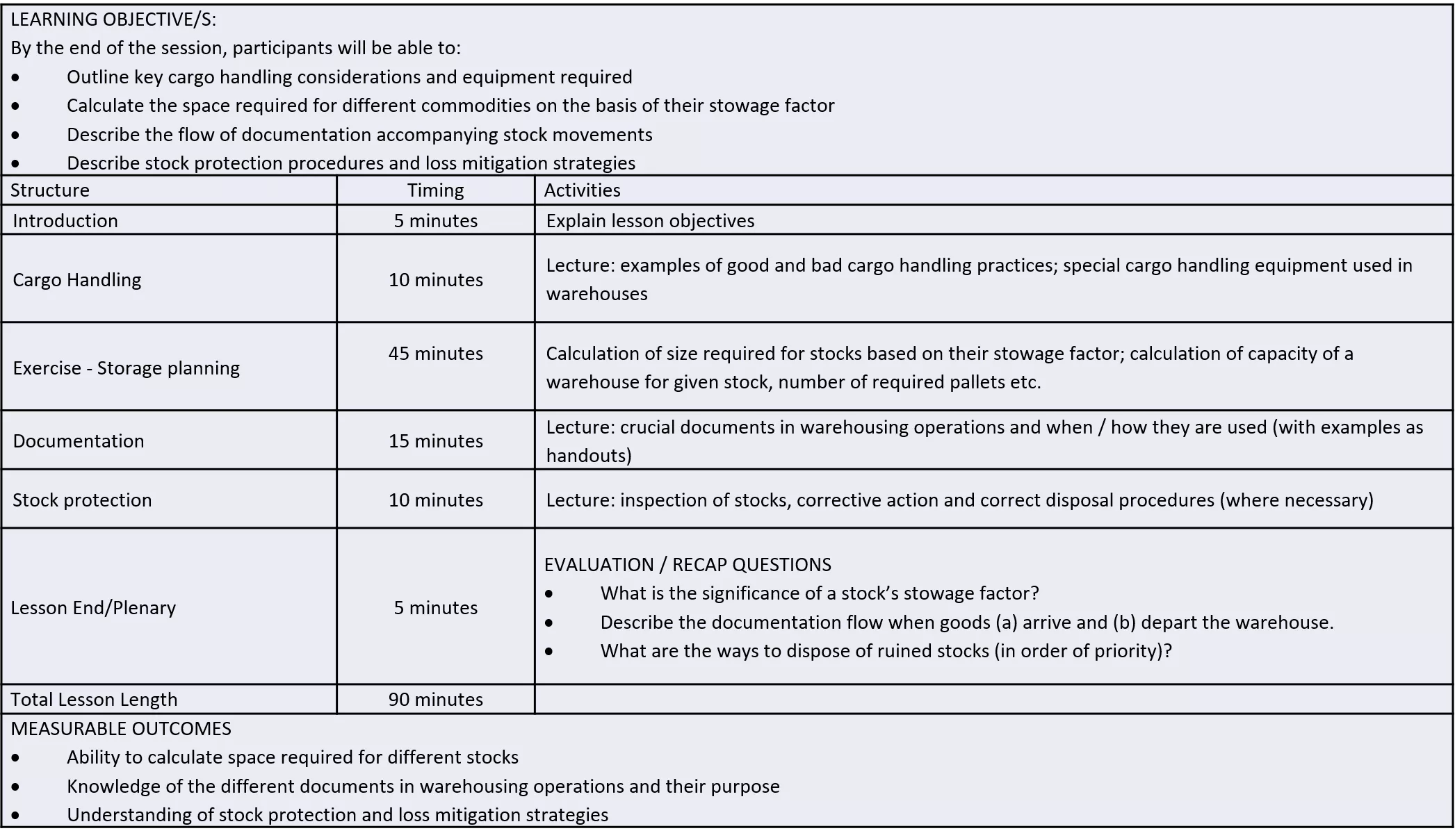
Lesson Plan: Storage LEARNING OBJECTIVE/S: By the end of the session, participants will be able to: Outline key cargo handling considerations and equipment required Calculate the space required for different commodities on the basis of their stowage factor Describe the flow of documentation accompanying stock movements Describe stock protection procedures and loss mitigation strategies Structure Timing Introduction 5 minutes Activities Explain lesson objectives Lecture: examples of good and bad cargo handling practices; special cargo handling equipment used in warehouses Cargo Handling 10 minutes 45 minutes Calculation of size required for stocks based on their stowage factor; calculation of capacity of a warehouse for given stock, number of required pallets etc. Exercise - Storage planning Lecture: crucial documents in warehousing operations and when / how they are used (with examples as handouts) Documentation 15 minutes Stock protection 10 minutes Lecture: inspection of stocks, corrective action and correct disposal procedures (where necessary) EVALUATION / RECAP QUESTIONS What is the significance of a stock s stowage factor? Describe the documentation flow when goods (a) arrive and (b) depart the warehouse. What are the ways to dispose of ruined stocks (in order of priority)? Lesson End/Plenary 5 minutes Total Lesson Length MEASURABLE OUTCOMES Ability to calculate space required for different stocks Knowledge of the different documents in warehousing operations and their purpose Understanding of stock protection and loss mitigation strategies 90 minutes
Stacking Methods Unbonded Stacking Bonded Stacking
Stacking Methods Clean area before creating stack Use good and clean pallets Select stacking method Identify space for spoiled and empty packaging Identify space for reconditioning & repackaging damaged cargo Use stack card
Bad Practices The stack should be built to give a firm bonded or interlocked stack Do not stack so high that packages at the bottom are crushed or split Do not throw or drop X Remove projecting nails and splinters or the bottom bags may be torn and food spilt Do not stack close up to, or on top of, the roof beams so as to risk damaging the structure Do not stack too close to the roof reducing ventilation and access
Handling of Hazardous Material Hazardous materials include (but not limited to): Pesticides Corrosive Material Fuel & Lubricants Considerations National Legislation and Regulations Gas Cylinders Environmental Concerns Staff Safety Additional Security Measures
Warehouse Activities Storage Planning Goods receipt Goods Dispatch ? Storage
Measurements Commodities and Warehouse KG Weight (1000 KG) MT SQM (M2) Length X Width Area CBM (M3) Volume Length X Width X Height
Stowage factor What is stowage factor? How do you calculate it? Volume (cbm) / Weight (mt) You have received a commodity in boxes with the following characteristics: Height Width Length Weight 15cm 45cm 60cm 0.025mtn What is the stowage factor of this commodity?
Exercise (A) : Capacity of a Warehouse In groups, list on flip charts what elements of one of the categories below would constrain the supply chain 1 a) What is the floor space in a warehouse that is 32 m long and 10 m wide? 1 b) What is the volume / "theoretical storage capacity" of a warehouse that is 32m long and 10m wide and 4m high? 2) Calculate the total "usable volume" of the warehouse when it has four (4) stacks as pictured below of the same size. Maximum storage height: 4m 3) Calculate the total occupied space (in MT) of the warehouse filled with the commodities indicated. 1m KITCHEN KITS RICE 3.5m (Stowage Factor = 2.3 cbm/mtn) (Stowage Factor = 1.4 cbm/mtn) 14.5m 14.5m 1m 1m 10m 1m BLANKETS WHEAT 3.5m 1m 1m 1m (Stowage Factor = 4.5 cbm/mtn) (Stowage Factor = 1.7 cbm/mtn) 14.5m 14.5m 1m 32m
Exercise (B) : Capacity of a Warehouse If time permitted 4) Calculate the stack capacity for the following: Rice in 50 kg bags with a stowage factor of 1.4cbm/mt You have 70 pallets (size 0.9m x 1.2m) Maximum storage height: 3m 5) What is the minimal number of pallets (0.9m x 1.2m) required to store 200mtn of a commodity that has a stowage factor of 2? Maximum storage height: 2.5m a) How many pallets will you need to square off the surface of the pallets? b) What are the surface dimensions of the stack? 1m+ 1m+ X m 1m 10m (Stowage Factor = 2 cbm/mtn) Ym 1m+ 24m 35 minutes to prepare / 10 minutes to debrief
Answers (A): Capacity of a Warehouse 1 a) Ground surface: 32 x 10 = 320 sqm 1 b) Theoretical storage capacity: 32 x 10 x 4 = 1280 cbm 2 Usable volume: Working space = (32 x 1 x 3) + (10 x 1 x 3) = 126 Usable volume = (320 126) x 4 = 194 x 4 = 776 cbm 3) Occupied space (All stacks have the same dimension) Stacks volume = 3.5 x 14.5 x 4 = 203 cbm Rice occupied space = 203 / 1.4 = 145 MT Kitchen Kits occupied space = 203 / 2.3 = 88.3 MT Wheat occupied space = 203 /1.7 = 119.5 MT Blankets occupied space = 203 / 4.5 = 45.2 MT Total occupied space: 145 + 88.3 + 119.5 + 45.2 = 398 MT
Answers (B): Capacity of a Warehouse If time permitted 4) Stack capacity calculation: Surface on the ground = 0.9 x 1.2 x 70 = 75.6 sqm Maximum capacity (cbm) = 75.6 x 3 = 226.8 sqm Maximum capacity (MT) = 226.8 / 1.4 = 162 MT (of rice)
Answers (B): Capacity of a Warehouse If time permitted 5) a) How many pallets will you need to square off the surface of the pallets? Required Volume: 200mt * 2 = 400cbm (stack capacity*stowage factor) Required Surface: 400cbm / 2.5m = 160sqm (required volume/ maximum storage height) Surface of a pallet: 0.9m * 1.2 m = 1.08sqm Minimal number of pallets: 160sqm / 1.08sqm = 148 (required surface/ surface of pallets) Actual pallets to be used: 150 (in order to form a rectangular stack, 12X12 pallets =144, 12X13 pallets=156, 11X14=154 etc) a) What are the surface dimensions of the stack? Surface Dimension of Stack: 12m x 13.5m (10 pallets X 1.2m and 15 pallets x 0.9m) There might be other options as well depending on how the warehouse is organized, but in the drawing above the 13.5m wide and 12m long would probably be the best. Other examples: 9m x 18m (10 pallets x 0.9m and 15 pallets x 1.2m) but not optimal with the given warehouse dimensions.
Inventory Management Receipt Storage Dispatch Waybill Stack Card Release Note Loading Authorisation Tally Sheet Stock Card* Daily Receipts Report Daily Stock Position Tally sheet Daily Stock Position Waybill Daily Dispatch Report Daily Stock Position
Inventory Management GOLDEN RULE: "IF IT MOVES - RECORD IT"
Daily Consolidated Movements & Stock Report I. WAREHOUSE DETAILS 1. Warehouse Name 2. Location 3. Reporting Date II. STOCK MOVEMENTS/STOCK DETAILS 4. Commodity 5. S.I. Number 6. Project # 7. 8. Opening Stock 13. Receipts 16. Dis patc hes 17. Losse s 18. Closing Balance Unit- Wgt KG 9. Good 10 Damaged 11. 12. 14. Good 15. 19. Go od 20. Dam aged 21. 22. Spoiled Unavailable Damaged Spoiled Unavailabl e III. CERTIFICATION 23. Prepared by 26. Certified by: 24. Title 27. Title 25. Signature 28. Signature
Stock Checks Purpose? When and where? Procedure and technics? Crosschecks, analysis & reporting
Inspection Techniques What to Look For How to Look Contamination Where to inspect Infestation Use your senses Damaged Packaging Equipment Expiry Dates Other considerations
Corrective Action Fumigation Safety & Security Measures Fumigation Procedures Fumigation in Silos Poisoning & Traps Raticides Insecticides
Disposal Mandatory Requirements Priority Disposal Methods Salvage Sale Donation Destruction Burning Burial
Questions WFP Logistics, We Deliver