Antenatal Assessment for Fetal Health Monitoring
There is a growing focus on antenatal assessment to prevent fetal deaths, with a decline in maternal mortality rates worldwide. The primary goal is to ensure fetal well-being, screen high-risk factors, and detect congenital abnormalities early on. Various tests like Maternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (MSAFP) and combined biochemical tests are utilized for assessing fetal health and detecting conditions like Down syndrome. Understanding these assessments is crucial for monitoring and ensuring the health of the fetus throughout pregnancy.
Uploaded on Sep 21, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Majority of fetal deaths occur in the antepartum period. There is progressive decline in maternal deaths all over the world. Currently more interest is focused to evaluate the fetal health. The primary objective of antenatal assessment is to avoid fetal death.
To ensure satisfactory growth and well being of the fetus throughout pregnancy. To screen out the high risk factors that affect the growth of the fetus. To detect those congenital abnormalities or inborn metabolic disorders during early pregnancy
Pregnancy with obstetric complications. Pregnancy with medical complications. Others Routine antenatal testing
Maternal serum alpha fetoprotein (MSAFP) AFP is a oncofetal protein. It is produced by yolk sac and fetal liver. Highest level of AFP in fetal serum and amniotic fluid is reached around 13 weeks and thereafter it decreases. Maternal serum level reaches a peak around 32 weeks
Maternal serum alpha fetoprotein (MSAFP) MSAFP level is elevated in a number of conditions: Wrong gestational age Open neural tube defects (NTDs) Multiple pregnancy IUFD Anterior abdominal wall defects Renal anomalies Low levels are found in trisomies (Down s syndrome) and gestational trophoblastic disease
It is a combined biochemical test which includes MSAFP, HCG and UE3(unconjugated oestriol). It is used for detection of Down s syndrome. In an affected pregnancy level of MSAFP and UE3 tend to be low while that of hCG is high. It is performed at 15-18 weeks.
Amniotic fluid Ache level is elevated in most cases of open neural tube defects. It has got better diagnostic value than AFP. Inhibin A is a dimeric glycoprotein. It is produced by the corpus luteum and the placenta. Serum level of inhibin A is raised in women carrying a fetus with Down syndrome.
Amniocentesis Chorion villous sampling (CVS) Cordocentesis.
Aspiration of amniotic fluid from the pregnant uterus for examination. Typically scheduled between the 14th and 16th weeks of pregnancy. An ultrasound is done to determine the position of the fetus and the location of a pocket of amniotic fluid and the placenta.
Alpha-fetoprotein: Increased levels of AFP: open body defect, such as anencephaly, myelomeningocele, or omphalocele. Decreased level of AFP: chromosomal defects such as Down syndrome Bilirubin Determination: if a blood incompatibility is suspected.
Chromosome analysis: few fetal skin cells are always present in amniotic fluid. These cells may be cultured and stained for karyotyping for genetic analysis. Color: . A strong yellow color suggests a blood incompatibility. A green color suggests meconium staining, a phenomenon associated with fetal distress. Fetal fibronectin Fibronectin is a glycoprotein that plays a part in helping the placenta attach to the uterine decidua. Detection of fibronectin in either the amniotic fluid or in the mother s vagina can serve as an announcement that preterm labor may be beginning.
Inborn errors of metabolism: can be detected by amniocentesis, for example: cystinosis and maple syrup urine disease (amino acid disorders). Lecithin/Sphingomyelin Ratio: Lecithin and sphingomyelin are the protein components of the lung enzyme surfactant that the alveoli begin to form at the 22nd to 24th weeks of pregnancy .After amniocentesis, the L/S ratio may be determined quickly by a shake test. An L/S ratio of 2:1 is traditionally accepted as lung maturity.
CVS is performed for prenatal diagnosis of genetic disorders. It is carried out transcervically between 10- 12 weeks and transabdominally from 10 weeks to term. A few villi are collected from the chorion frondosum under ultrasonic guidance. While it provides earlier diagnosis than amniotic fluid studies, complications like fetal loss(1-2%), oromandibular limb deformities or vaginal bleeding are higher
This technique is used to take a sample of fetal blood during pregnancy in order to screen for chromosomal abnormalities, hemoglobinopathies and other disorders affecting blood or cells. It is performed under local anaesthestic usually after 18 weeks gestation. Risks: the invasive procedure may lead to abortion, preterm labour and intrauterine fetal death. These may be due to bleeding, cord haematoma formation, infection or preterm rupture of membranes.
All the information as obtained in amniocentesis or chorion villus sampling, could be gathered. Additional values are mentioned below: Hematological- for fetal anaemia, bleeding disorders (autoimmine thrombocytopenia), rhesus disease. Fetal infections- toxoplasmosis, viral infections Fetal blood gas and acid base status- in fetal growth restricition Fetal therapy- blood transfusion
Ultrasonographic examination of the fetus in the early (10-14 weeks) pregnancy can detect fetal anomalies. Crown-rump length (CRL) smaller than the gestational age is associated with the risk of chromosomal anomalies (trisomy or triploidy). Increased nuchal translucency (soft tissue marker) at 10-14 weeks is associated with many chromosomal abnormalities (trisomy, monosomy, triploidy
The clinical assessment of fetal growth can be evaluated by the following parameters: Maternal weight gain Blood pressure Assessment of the size of the uterus and height of the fundus Clinical assessment of excess liquor
Biophysical profile is a screening test for uteroplacental insufficieny. The following biophysical tests are used: 1. Fetal movement count 2. Cardiotocography 3. Non stress test (NST) 4. Fetal biophysical profile (BPP) 5. Doppler ultrasound 6. Vibroacoustic stimulation test 7. Contraction stress test (CST)
A healthy fetus moves with a degree of consistency, or at least 10 times a day. In contrast, a fetus not receiving enough nutrients because of placental insufficiency has greatly decreased movements. Based on this, asking a woman to observe and record the number of movements the fetus is making offers a gross assessment of fetal well-being
Cardif count 10 formula Daily fetal movement count (DFMC) Mothers perceive 88% of the fetal movements detected by Doppler imaging. Loss of fetal movements is commonly followed by disappearance of FHR within next 24 hours. In either of the above methods, if the results is ominous, the candidate is subjected to NST
In non-stress test, a continuous electronic monitoring of the fetal heart rate along with the recording of fetal movements (cardiac tocography) is undertaken. There is an observed association of FHR acceleration with fetal movements, which when present, indicates a healthy fetus. Non stress test Reactive (Reassuring)- when two or more accelerations of more than 15 beats per minute above the baseline and longer than 15 seconds in duration are present in a 20 minutes observation in association with movement of fetus Non-reactive (Nonreassuring)- Absence of any fetal reactivity.
Important features to note while interpreting a CTG Accelerations and normal base line variability (5- 25 bpm) denote a healthy fetus. Absence of accelerations is the first feature to denote onset of gradual hypoxia. Absence of accelerations, reduced base line variability may be due to fetal sleep, infection, hypoxia or due to maternal medications. Interpretation of the CTG should always be made in the context of clinical situation.
Baseline FHR is the mean level of FHR between the peaks and the depressions in beats per minute (bpm). Accelerations are increase in FHR by 15 bpm or more lasting for at least 15 seconds. Deceleration is decrease in FHR below the baseline by 15 bpm or more. Baseline variability is the oscillation of baseline FHR excluding the accelerations and decelerations. A baseline variability of 5-25 bpm is a sign of fetal wellbeing
With contraction stress testing, the fetal heart rate is analyzed in conjunction with contractions. A source of oxytocin for contraction stress testing currently is achieved by nipple stimulation. Gentle stimulation of the nipples releases oxytocin in the same way as happens with breastfeeding. With external uterine contraction and fetal heart rate monitors in place, the baseline fetal heart rate is obtained.
Next, the woman rolls a nipple between her finger and thumb until uterine contractions begin, which are recorded by a uterine monitor. Three contractions with a duration of 40 seconds or longer must be present in a 10- minute window before the test can be interpreted. The test is negative (normal) if no fetal heart rate decelerations are present with contractions. It is positive (abnormal) if 50% or more of contractions cause a late deceleration
To elicit an abnormal FHR response Performed by iv infusion of dilute oxytocin until three contractions occur in 10 minutes Positive test: Late deceleration after each of the three contractions; FHR baseline variability; no FHR increase after FM Indicates decreased fetal reserve Negative test: No decelerations Fetus is safe within one week Suspicious: Repetitive variable decelerations Associated with abnormal FHR in labor, particularly in post-term gestation
A specially designed acoustic stimulator is applied to the mother s abdomen to produce a sharp sound of approximately 80 decibels at a frequency of 80 Hz, startling and waking the fetus. During a standard nonstress test, if a spontaneous acceleration has not occurred within 5 minutes, apply a single 1- to 2-second sound stimulation to the lower abdomen. This can be repeated again at the end of 10 minutes if no further spontaneous movement occurs, so that two movements within the 20- minute window can be evaluated
A biophysical profile combines five parameters 1. fetal reactivity 2. fetal breathing movements 3. fetal body movement 4. fetal tone 5. amniotic fluid volume
With use of this system, each item has the potential for scoring a 2, so 10 would be the highest score possible. It is popularly called a fetal Apgar. Biophysical profiles may be done as often as daily during a high-risk pregnancy. If the fetus score on a complete profile is 8 10, the fetus is considered to be doing well. A score of 6 is considered suspicious; a score of 4 denotes a fetus probably in jeopardy.
Biophysical profile Parameters Minimal normal criteria Score 1. Non stress test (NST) Reactive pattern 2 2. Fetal breathing movement 1 episode lasting >30 sec 2 3. Gross body movement 3 discrete body/ limb movements 2 4. Fetal muscle tone 1 episode of extension (limb or trunk) with return of flexion 2 5. Amniotic fluid 1 pocket measuring 2cm in two perpendicular planes
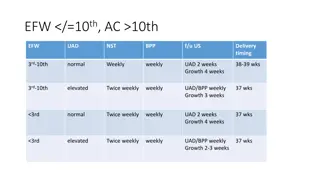
BPP score Interpretation Management 8-10 No fetal asphyxia Repeat testing at weekly interval 6 Chronic asphyxia If >36weeks- deliver 4 Chronic asphyxia If 36 weeks deliver, if ,32 weeks repeat testing in 4-6 hours. 0-2 Certain asphyxia Test for 120 min Persistent score 4---deliver regardless of gestational age. Modified biophysical profile Use only two assessments (amniotic fluid index and a nonstress test). A healthy fetus should show a reactive nonstress test and an AFI range between 5 and 25 cm. Modified BPP is considered abnormal (nonreassuring) when the NST is non-reactive and/or the AFI is <5.
The production of high frequency sound waves which are reflected or echoed when beamed into the body and an interface is encountered between different types of tissues or structures with different densities. These echoes can be translated into visible images of the tissues or structures encountered. Uses of ultrasonography Diagnose pregnancy as early as 6 weeks gestation. Confirm the presence, size, and location of the placenta and amniotic fluid Establish that a fetus is growing and has no gross anomalies, such as hydrocephalus, anencephaly, or spinal cord, heart, kidney, and bladder defects Establish sex if a penis is revealed Establish the presentation and position of the fetus Predict maturity by measurement of the biparietal diameter of the head To discover complications of pregnancy. Fetal anomalies Fetal death After birth, an ultrasound may be used to detect a retained placenta or poor uterine involution in the new mother.
At 5-10 weeks: gestational sac. At 8-14 weeks: the crown-rump length. At 14-20 weeks: length of the femur. At 18-26 weeks: the biparietal diameter. The fetal head is demonstrable by ultrasound by the 12th week of gestation. Biparietal diameter Ultrasonography may be used to predict fetal maturity by measuring the biparietal diameter (side-to- side measurement) of the fetal head. BPD is 8.5 cm or greater, it can be predicted that the infant will weigh more than 2500 g (5.5 lb) or is at a fetal age of 40 weeks. Two other measurements commonly made by ultrasound to predict maturity are head circumference (34.5 cm indicates a 40-week fetus) and femoral length.
Doppler ultrasonography measures the velocity at which red blood cells in the uterine and fetal vessels travel. Assessment of the blood flow through uterine blood vessels is helpful to determine the vascular resistance present in women with diabetes or hypertension of pregnancy and whether resultant placental insufficiency is occurring
Placental grading Based particularly on the amount of calcium deposits in the base of the placenta. Placentas can be graded by ultrasound as 1. 0 (a placenta 12 24 weeks) 2. 1 (30 32 weeks) 3. 2 (36 weeks) 4. 3 (38 weeks). 11/13/2014 7:44 AM 55 56. Determination of fetal maturity by the rapid surfactant test 1. Shake test or bubble test (clement s) 2. Foam stabililty index( FSI) 3. Phosphatidyl Glycerol and Desaturated Phosphatidylcholine 4. Others Creatinine (Cr) assess fetal renal maturity OD450 assess fetal liver maturity Lipocyte assess fetal skin maturity