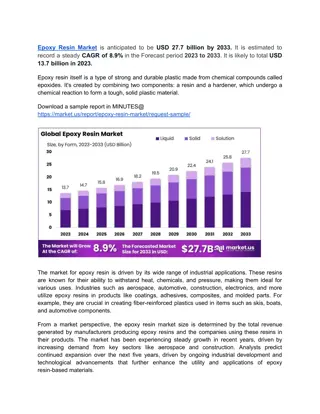
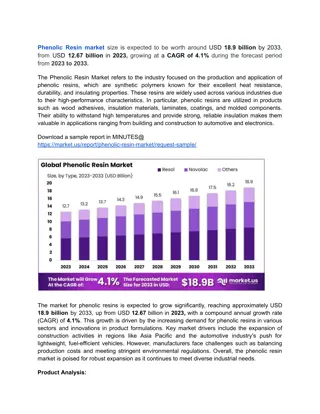
Acetylation Sulfonamide Derivatives of Phenolic Resin Study
Work conducted on modifying phenolic resin through acetylation, sulfonation, and sulfonamide formation using primary amines like ampicillin and amoxicillin. Characterization of derivatives was done using spectroscopic techniques, showing potential for antibiotic applications. Experimental processes and physical properties of the resins were investigated. Swelling studies and release studies were also conducted to further evaluate the properties of the modified resins.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Acetylation ,sulfonamide Derivatives of phenolic Resin Firyal M.A.Al-Salami, Safana S.J.Abu-Ganah Department of Chemistry, College of Science Al- Mustansirya University,* Babylon University and * Khudheyer J. Kadem Summary: In this work the OH functional group of phenol formaldehyde resin was acetelated by acetyl chloride then sulfonated by chloro sulfonic acid and the product was modified to its corresponding sulfonamide, using different primary drug amines such as ampicilline and amoxilline. The different derivatives were characterized by 1H-NMR, FT-IR and UV. spectroscopes, and physical properties were measured and the rate of hydrolysis of sulfonamide for amoxilline derivative was studied, therefore it was concluded that the amoxilline sulfonamide resin could be possibly used as antibiotic material to uses for different other applications.
EXPERIMENTAL Acetylation of novolac P1: 5gm. of supplied novolac was dissolved in 10ml of DMF ,1:1 molar ratio of acetyl chloride was added gradually in a round bottomed flask which was equipped with condenser, stirred about 30mins., the excess of acetylchloride was distilled off. The red resin was isolated with 90% conversion. Sulfonation of acetylated phenol formaldehyde resin P2 Five grams of acetylated novolac was dissolved in 10 ml of dioxane to obtain high Liquidity, then the 4ml of chlorosulfonic acid was added gradually with continuous stirring to ensure maximum homogeneity through out the resin at 0 0C the viscose resulting sample was obtained then dried the sample in vacuum oven at 50 0C.
Preparation of N-Substituted acetylated phenol formaldehyde sulfonamide resins. P3-P4 . A mixture of sulfonated novolac (5g, 0,025 mole) and 20 ml of dioxane , and (0,025 mole) of some primary amine such as ampicilline or amoxilline was added to reaction mixture , refluxed with stirring about 15 mins. by using water bath ,then evaporated the solvent, the colored polymeric precipitate was isolated, washed and dried in a vacuum oven. Table 1 shows the physical properties of prepared N-sulfonamide acetylated phenol formaldehyde resins
Table (1) :Physical properties of prepared N-Substituted sulfonamide of acetylated phenolic resins . O C CH3 O CH2 CH2 n SO2Cl Polymer. Ar- NH2 Color Conversion % Softening point 0C [ in] dl/g No. P3 P4 amoxicillin ampicillin red orange 70 75 >300 >300 0.81 0.78
Swelling studies Dynamic swelling studies of prepared resins made as follows:- Resins were swollen in different at 37 0C remove from the water bath at regular intervals were dried superficially with filter paper. Weighted and placed in the same bath. The swelling S% is calculated from the following equation: S %= (M1-M0)/M0* 100 Where M0is the mass of dry resin at time 0 . M1is the mass of swollen resin at time t . Swelling curves of amoxilline and ampicilline resin in solution water at 37 0C. Table (2) shows the swelling % of polymer P3 and P4in pH4 (acidic medium). Table(2): Swelling% of P3and P4in acidic medium pH4 Release studies [11] 50 mg of amoxilline- acetylated phenol formaldehyde sulfonamide was placed in 100 ml of buffer solution with pH 4 at 37 0C .At periodic intervals 3 ml of solution of resin with drawing and tested max= 300 nm using UV-VIS- spectrophotometer, the release studies were continued for four days . S% S% P3 S% P4 1day 4.1 5.2 2day 6.7 6.0 3day 8.1 7.8 4day 10 9
In this work the supplied phenol formaldehyde (novolac) was acetylated and sulfonated with chlorosufonic acid as described in the following scheme (1)- O CH3 C O H O 0 C n+ CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3COCl . . . . - HCl n HSO2Cl O CH3 C O CH2 CH2 . . n (P2) Scheme (1) SO2Cl
The sulfonated resin was modified with some primary drug amines such as ampicillin or amoxilline as antibiotic drug which carried amino group , the reaction was shown below:- O CH3 C O O CH3 C O CH2 CH2 . . n+ CH2 CH2 ArNH2 . . n SO2Cl SO2NH - Ar (P3 , P4 ) O O CH3 S CH3 S , ArNH2 = H2 N CH C NH H2 N CH C NH N N CH3 CH3 O O COOH COOH OH ( Amoxilline) (Ampicilline)
The mechanism[12,13]of hydrolysis is shown in the following Scheme (2,3):- H+ O OH Resin - SO2 -NH -Amoxi.+H+ S+ Resin S NH -Amoxi Resin NH -Amoxi O O H2 O H O O+ OH H + Resin S OH Resin S Amoxilline NH -Amoxi O O Scheme (2) O- O H O +OH- Resin S NH -Amoxi Resin S NH -Amoxi O O O + Resin S OH Amoxilline Scheme (3) O Scheme (2) shows the mechanism of releasing amoxilline from sulfonamide resin, in acidic media, H+is bonded to oxygen atom of sulfonamide group, and increase, the positive charge of sulfur atom, then enhanced the nucleophilic attack of water. Scheme (3) shows the mechanism of releasing amoxilline in basic medium which is stronger nueleophilic in respect to water, the rate of hydrolysis takes place faster than acidic, as shown in Fig (4), for P3,P4 resin.
Conclusions: The P-N-substituted sulfonamide acetylated phenolic resin were synthesized as antibiotic agents, the novel functional polymers as biomaterial have many application, that exhibit pharmacologic properties or that can be utilized as carriers for selective and sustained delivery agents with greater specify of action.
Fig (3): Acetylated phenol Formaldehyde resin ampicilline sulfonamide P3
a-P3&P4 in pH4. b- P3&P4 in pH 10. Fig (4): Controlled drug release of P3&P4 at 37 0C in a-pH4 and b-pH10