1st Year MBBS Foundation Module Study Guide at Avicenna Medical College
This study guide provides a comprehensive overview of the foundation module for first-year MBBS students at Avicenna Medical College. It includes information on learning methodologies, objectives, assessment methods, rules, regulations, and curriculum frameworks. Students will experience an integrated curriculum focusing on system-based modules to link basic science knowledge with clinical problems, allowing for a deeper understanding through case-based discussions and skills acquisition.
Uploaded on Oct 08, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
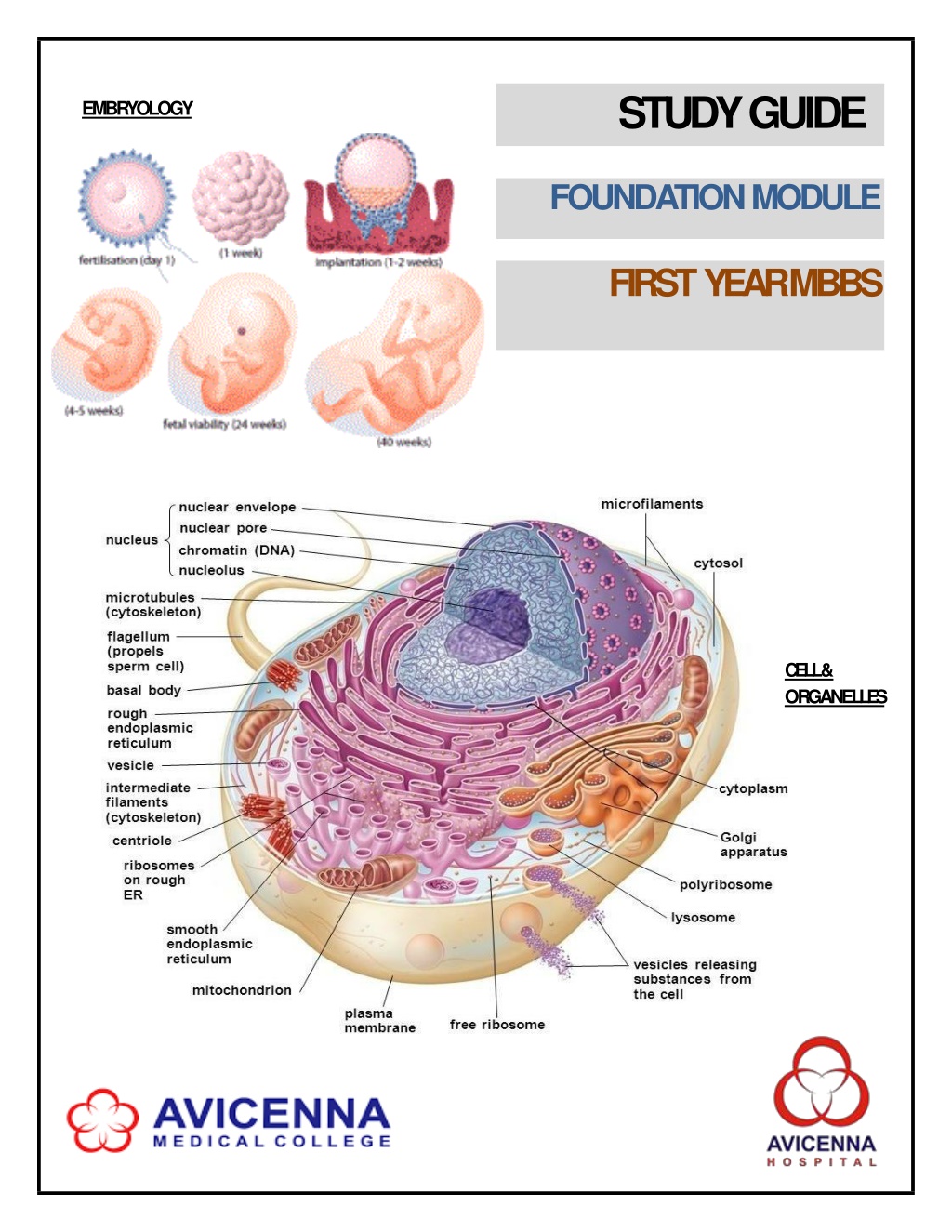
STUDYGUIDE EMBRYOLOGY FOUNDATIONMODULE FIRST YEARMBBS CELL & ORGANEL L ES
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE STUDY GUIDE FOR FOUNDATIONMODULE Page No 3 4 5 7 7 8 16 18 22 23 S.No CONTENTS 1 2 3 4 4.1 4.2 5 6 7 8 Overview Introduction to StudyGuide LearningMethodologies Module 1:FOUNDATION Introduction Objectives andstrategies LearningResources AssessmentMethods Modular Examination Rules And Regulations(AVMC) Schedule Page | 2
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Year:One Duration: 4 weeks Timetable hours: Lectures, Case-Based Learning (CBL), Team based Learning (TBL), Self-Study, Practical, Skills, Demonstrations, Field Visits, Visit to Wards& Laboratory MODULE INTEGRA TEDCOMMITTEE MODULECOORDINATOR: CO-COORDINATORS: Professor Dr. Zubair Ahmad(Biochemistry) Professor Dr. Rubina Hafeez (Pathology) Professor Dr.Rehana Shahid(Anatomy) DEPARTMENTS & RESOURCE PERSONS FACILITA TINGLEARNING BASIC HEALTHSCIENCES CLINICAL AND ANCILLARYDEPARTMENTS FAMILYMEDICINE Professor Dr. Muhammad Luqman ANATOMY Professor Dr.Rehana Shahid BIOCHEMISTRY Professor Dr. Zubair Ahmad MEDICALEDUCATION Professor Dr. Waheed Ahmad COMMUNITYMEDICINE Professor Dr. Rana Muhammad Akhtar Khan INTERNALMEDICINE Dr. Muhammad Usman Amir PATHOLOGY HEMATOOGY Dr. Syeda Ijlal Zehra Zaidi Professor Dr. Rubina Hafeez PHYSIOLOGY Professor Dr. Binyamin Ahmad PHARMACOLOGY Professor Dr. Rana Tariq Mehmood AVMCMANAGEMENT Professor Dr. Gulfreen Waheed, PrincipalAVMC Brig.Dr. Gul e Rana , Director AVMC Dr. Sadia Awan Dr. Muhammad Muzzammil Sadiq Dr. Usama Bin Ishtiaq STUDY GUIDE COMPILEDBY: Department of Health CareEducation Page | 3
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE INTRODUCTION WHAT IS A STUDYGUIDE? It is an aidto: Inform students how student learning program of the semester-wise module has been organized Helpstudentsorganize andmanagetheirstudiesthroughoutthemodule Guide students on assessment methods, rules andregulations THE STUDYGUIDE: Communicates information on organization and management of themodule. Thiswill helpthestudentto contactthe rightpersonin caseof anydifficulty. Definestheobjectiveswhich areexpectedto beachieved at theendof themodule. Identifies the learning strategies such as lectures, small group teachings, clinical skills, demonstration, tutorial and casebasedlearning that will be implemented to achieve the module objectives. Provides a list of learning resources such as books, computer assisted learning programs, web- links,journals,forstudentsto consultin orderto maximize their learning. Highlights information on the contribution of continuous and semester examinations on the student s overallperformance. Includes information on the assessment methods that will be held to determine every student s achievement ofobjectives. Focuses on information pertaining toexamination policy, rules and regulations. CURRICULUMFRAMEWORK Students will experience integrated curriculum of the 1st &2nd semesters. INTEGRATED CURRICULUM comprises system-based modules such as foundation and blood which links basic science knowledge to clinical problems. Integrated teaching means that subjects are presented as a meaningful whole. Students will be able to have better understanding of basic sciences when they repeatedlylearnin relation to clinicalexamples. Case-based discussions, computer-based assignments, early exposure to clinics, wards, and skills acquisitionin skillslabarecharacteristicsof integrated teachingprogram. Page | 4
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE A VICENNA MEDICA L COLLEGE LEARNINGMETHODOLOGIES Thefollowing teaching/ learningmethodsareusedto promotebetterunderstanding: InteractiveLectures Hospital / Clinic visits Small Group Discussion Case-BasedLearning Practicals Skillssession E-Learning Self-DirectedStudy INTERACTIVELECTURES:In large group, the lecturer introduces atopic or common clinical conditions and explainsthe underlying phenomenathrough questions, pictures, videosof patients interviews, exercises, etc.Studentsareactively involved in the learningprocess. HOSPITAL VISITS: In small groups, students observe patients with signs and symptoms in hospital or clinical settings. This helps students to relate knowledge of basic and clinical sciences of the relevant module. TEAM-BASED LEARNING: Team-Based Learning is an evidence based collaborative learning teaching strategy designed around units of instruction, known as modules, that are taught ina three-step cycle: preparation, (b) in-class readiness assurance testing, and (c) application-focusedexercise. Page | 5
1 1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Preparation before class: Students must complete preparatory materials before aclassor the start of the module. Materials may be text, visual or other, and set at a level that is appropriate to the students and thecourse. In-class Readiness Assurance Testing: Students complete an individual readiness assurance test (IRAT), consisting of 5 to 20 multiple choice questions. After submitting their individual answers, and they take the sametest, the teamRAT(TRAT),with their team.All membersof eachteamsharethe sameTRAT score, and both IRAT and TRAT scores count toward the students grades. Instructor Feedback:Theinstructor reviews material from the RATthat seemsto be difficult for students. In-class application focused exercise: The remainder of the session is taken up with exercises that help students learn how to apply and extend the knowledge that they have pre-learned and tested. Teams are given an appropriate problem or challenge, and must arrive at a consensus to choose a best solution out of options provided. Teams then display their answer choice, and the educator facilitates a classroomdiscussionbetween teamsto explorethetopicandthe possible answersto the problem. SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION (SGD): This format helps students to clarify concepts acquire skills or attitudes. Sessions are structured with the help of specific exercises such as patient case, interviews or discussion topics. Students exchange opinions and apply knowledge gained from lectures, tutorials and self study. The facilitator role is to ask probing questions, summarize, or rephrase to help clarify concepts. CASE-BASEDLEARNING: A small group discussion format where learning is focused around a series of questions based on a clinical scenario. Students discuss and answer the questions applying relevant knowledge gainedin clinical andbasichealth sciencesduring themodule. PRACTICAL: Basic science practicals related to anatomy, biochemistry, pathology, pharmacology and physiologyarescheduledfor studentlearning. SKILLSSESSION:Skillsrelevant to respectivemodule areobservedandpracticed where applicablein skills laboratory or DepartmentofPhysiotherapy. SELFDIRECTEDSTUDY:Students assume responsibilities of their own learning through individual study, sharing and discussing with peers, seeking information from Learning Resource Center, teachers and resource persons within and outside the college. Students can utilize the time within the college scheduled hoursofself-study. E-LEARNING: E-Learning is a strategy by which learning occurs through the utilization of electronic media, typically the Internet. The basic aspects of medical professionalism and ethics will be addressed throughane-learningcourse. Page | 6
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE MODULE 1 :FOUNDATION INTRODUCTION This module has been designed to introduce you to the basics of health sciences. The course covers the molecular level of cell biology including genetics and its role in embryology, microbiology and pathology. In community medicine,health issuesandpolicieson diseasecontrolat thenational level will bediscussed. You will also experience clinical skills such as learning to communicate effectively so that you can relate to patientsandtheirlovedoneswith compassionandunderstandingin comingyears.Through working within teams, your co-operative and approachable working style will be enhanced. Through group and individual work, you will develop problem solving skills to apply your medical knowledge to practical situations. This, supplemented by lectures, and practical classes, is a significant component of thecourse. Thisstudyguidehasbeendeveloped to help guideyouandkeepyoufocusedonthe objectivesforthis module. Welcometo the fieldof medicineandhopethatthe journey aheadwill beexcitingandfulfilling for youall. Page | 7
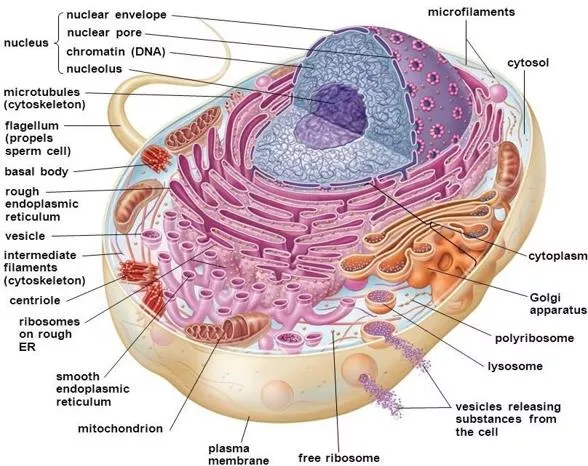
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE TOPICS, COURSE OBJECTIVES ANDSTRA TEGIES At theendof themodulethestudentswill beable to: OBJECTIVES STRATEGIES GENERALHISTOLOGY Explaintheconceptoforganizationof cellsto tissue,tissuesto organandorgansto system InteractiveLecture Describe the parts ofmicroscope Practical Describethe structuralorganizationof cellmembraneanddiscussthe function of the components Describethestructureandfunctions of thefollowing cytoplasmic organelles: i. Golgiapparatus ii. Lysosomes iii. Peroxisomes iv. Smooth endoplasmicreticulum v. Rough endoplasmicreticulum vi. Ribosomes vii. Cellular inclusions viii. Mitochondria ix. Nucleus Interactive Lecture/Skill s Describetheultra structureandfunctionof thecytoskeleton Describe cell junctioncomplex Discuss the following basic tissues of thebody i) Epithelium ii) Connective tissue iii) Muscle iv) Bones v) Cartilage vi) Neuraltissue InteractiveLecture Describethemicroscopicfeaturesof epithelialtissues,explaintheir functional importance and their surfacemodification Withuseof microscopeidentifythefollowing: i. Epithelium ii. Connective tissue Practical 2019 Page | 8
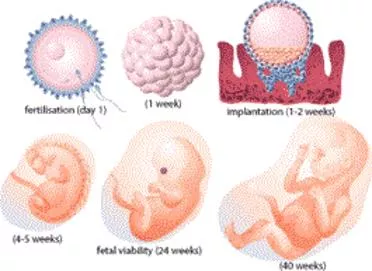
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Name the basic histologicalstains. Define the followingterms: i. Fixation ii. Embedding iii. Sectioning iv. Staining Practical Describe the microscopic features ofconnective tissues Differentiate between types of connective tissues: loose connective tissue, Adipose connective tissue, reticular connective tissue, dense connective tissue, regularand irregular InteractiveLecture GENERALEMBRYOLOGY Small Group Discussion/Interacti ve lecture Explain the basic terms related toembryology Explain cell cycle, division, abnormal cell division andmutations Discuss the significance of karyo typing and its clinical significance Differentiatebetweenthestagesof mitosisandmeiosis SmallGroup Discussion Discuss male reproductive organs and theirfunctions Discuss female reproductive organs and theirfunctions Describe the process of spermiogenesis, oogenesis andovulation InteractiveLecture Interactive Lecture/Case- Based Learning Describe the phases of female reproductive cycles and theirdisturbance leading to polymenorrhoea, oligomenorrhea andinfertility Correlatethe cyclic changesoccurringin theovarywith that of uteruswith their endocrinecontrol InteractiveLecture Describe the phases offertilization Discuss the results offertilization Discuss artificial reproductive techniques and Describe the stepsinvolved duringin vitro fertilizationandembryotransfer SmallGroup Discussion Describe cleavage and blastocyst formation InteractiveLecture Page | 9
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Discussthe resultsof implantation atabnormalsite Interactive Lecture/ Case-BasedLearning Describethe eventsof thesecond week of developmentincluding Formationof amniotic cavity, amnion, bilaminar embryonic disc, yolk sac, chorionic sac and primary chorionicvilli Describethefollowing eventsof thethirdweekof development i. Formation of primitive streak andnotochord ii. Gastrulation iii. Formation of neuraltube iv. Formation ofsomites v. Formation of intra embryoniccoelom vi. Formation of blood cells and bloodvessels vii. Formation of secondary and tertiary chorionicvilli InteractiveLecture Describe folding of embryo and itsresults Discuss the derivatives ofgerm layers and neural crest cells Small Group Discussion/Tutorial Describe the structure, development and functions ofplacenta and fetal membranes InteractiveLecture Explainthedevelopmentalprocessduring firstthreeweeksof gestation Interactive Lectures/ Small Group Discussion/Tutorial Discussthe importanteventsof embryonicperiod from4th weekto 8th week and during the organo-geneticperiod Discuss the events of fetalperiod Describe thetypesof twin / multiple pregnancies Interactive Lecture / Small Group Discussion/ Case-BasedLearning Defineteratogenesis. Classify the teratogens. Describe the basic principles ofteratogenesis Discuss the common congenitalanomalies Case-Based Learning/SmallGroup Discussion Small Group Discussion/Tutorial Calculate the expected date of delivery (EDD) and describe various methods used to assess fetalwellbeing Identifytheplacenta,fetalmembranes,umbilical cord,germlayers, stagesof fertilization on a given model, photograph orspecimen Practical Page | 10
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE GENERALANATOMY Discuss the history ofanatomy InteractiveLecture Discuss anatomy including its various branches and state theirpractical application in different fields ofmedicine Discuss the various techniques related to living anatomysuch as: i. Plain and contrastradiographs ii. Radio-opaquemedia iii. Special X-ray techniques like Barium meal and Angiographyetc iv. Ultrasonography v. CT vi. MRI vii. Endoscopy Discusstheintegrationof structuresand functionsof humanbodybyrelating with thearrangementof differentlevels organization Describethetermsof position in relation to anatomicalposition: i. Anterior / Posterior ii. Ventral / Dorsal iii. Superior / Inferior iv. Caudal / Rostral v. Medial / Lateral vi. Proximal / Distal vii. Palmar / plantar viii. Superficial/Deep SmallGroup Discussion Describe the different anatomicalplanes Describe thetermsof movementsatjoints: i. Flexion / Extension ii. Abduction / Adduction iii. Lateral rotation / Medialrotation iv. Pronation / Supination v. Plantar flexion / Dorsal flexion vi. Circumduction vii. Eversion / Inversion Page | 11
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Introduction to Skeletal system (Bones and Joints) i. Describe the parts of appendicular and axialskeleton ii. Discuss the functions ofbone iii. Classify bones on the basis of shape, development, region and structure iv. Describegeneralconceptsof developmentandossificationof bones v. List the parts of youngbone vi. Explain the blood supply oflong bones vii. Classifyjoint onthe basisof structure,regionsandfunctions. viii. Discuss the characteristics of synovialjoints ix. Classify synovial joints on the basis ofstructure and movement x. Define dislocation, sprain and inflammation ofjoints Introduction to MuscularSystem: i. Classifymuscles ii. Define spasm, paralysis, atrophy andregeneration InteractiveLecture Discuss the following terms: i. Ossification ii. Ligament iii. Aponeurosis iv. Raphe v. Fascia vi. Tendon vii. Synovialsheath viii. Bursa SmallGroup Discussion Discuss the following: i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Veins Venules Anastomosis Lymphatics Introduction to NervousSystem: Discuss the general organization ofnervous system Classify nervous system on the basis ofstructure and function Discuss the general organization of Autonomic NervousSystem InteractiveLectures Describe reflex arc and list itscomponents Describe gross anatomy of blood vascularsystem Integratethe functionof defencewith thegeneralanatomyof lymphnodes andlymphatics Appreciatethe functionofsupport andprotection by usingthe general anatomy of skin andfascias InteractiveLectures Page | 12
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE BIOCHEMISTRY OBJECTIVES STRATEGIES INTRODUCTION TOBIOCHEMISTRY DefineBiochemistry Discuss its role, importance and applications in medicalpractice Interactive Lectures CELL Explainthecell organelleswith theirbiochemical function Discussthe biochemical composition andfunctionsof the cellmembrane Interactive Lectures WATER &pH Discuss the physicochemical properties of water ( eg surface tension,viscosity, adsorption) Describethemechanismof dissociationof water andmaintenanceof normalpH Discuss Buffers and their role in acid basebalance. CHEMISTRY OFCARBOHYDRATES ClassifyCarbohydrates Explain structure, functions and biochemical importance (in health and disease) of monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides andpolysaccharides CHEMISTRY OFLIPIDS ClassifyLipids DefineLipids Explainthechemistry,structureandfunctionsof fattyacids. Describe properties and biological functions of simple lipids (TAG) andcompound lipids (PL) Explain sterols (Cholesterol), their chemistry, structure and biochemical importance in health anddisease CHEMISTRY OFPROTEINS Classify Proteins with their biochemicalimportance Classify Amino Acids on the basis of structure, properties, nutritional significance and their biologicalrole Define peptides,polypeptides Discuss the biomedical importance of peptidesand polypeptides Explain the structure ofproteins Classify protein on the basis of physiochemical properties, functionsand chemical reactions;andrecognize theirimportance in balanceddiet andhealth Explain the primary, secondary and tertiary structure ofprotein ENZYMES: Discussthe mechanismof actionandkineticsof co-enzymes,co-factorsand isoenzymes. Discuss Classificationandproperties of Enzymeactivity. Discuss Factors and inhibitors of Enzymeactivity. Discuss clinical enzymology Interactive Lectures Interactive Lectures Interactive Lectures Interactive Lectures Interactive Lectures Page | 13
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE CHEMISTRY OF NUCLEICACIDS Explain the nucleotide chemistry with theirbiomedical importance Explain DNA and RNA structure andtypes. PRACTICALS: Discuss Lab Protocols and LabHazards Demonstrate Safety measures while working in BiochemistryLab Prepare solutions with differentconcentrations Detect the Carbohydrates (Scheme and Polysaccharides), Carbohydrates (Mono and Disaccharides), Lipid (Solubility, Emulsification, Saponification), Proteins (Scheme and General Tests), Amino acid, Individual Proteins (Albumin, Globulin, Casein) in a givensolution Demonstrate flamephotometry Perform qualitative test for salivaryamylase Interactive Lectures Practical Performance/Skil ls BIOETHICS OBJECTIVES STRATEGIES Describe the desirable attitudes of a medicalprofessional Recognize the importance of respectful behaviour withteachers , staff and colleagues Applyprinciplesof integrity, honesty,truth telling andtrustworthiness in academic situations InteractiveLecture/ Small Group Discussion COMMUNICATIONSKILLS OBJECTIVES STRATEGIES InteractiveLecture/ SmallGroup Discussion Identify basic elements of communicationskills Recognize the impact of effectivecommunication COMMUNITYMEDICINE OBJECTIVES STRATEGIES InteractiveLecture Discuss the concept of health anddiseases HEALTH CA REEDUCATION OBJECTIVES STRATEGIES InteractiveLecture/ SmallGroup Discussion Identify different methods of assessment used in LNMC modularexams Relate to LNMC assessment policies PATHOLOGY OBJECTIVES STRATEGIES InteractiveLecture Discuss the types and pathogenesis ofedema Page | 14
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE PHYSIOLOGY OBJECTIVES STRATEGY INTRODUCTION TO PHYSIOLOGY & FUNCTIONAL ORGANIZATION OF HUMANBODY Recognize the importance ofphysiology in modern medicine InteractiveLecture/ SmallGroup Discussion EXTRACELLULAR FLUID & INTERNALENVIRONMENT Describe functional organization of human body and fluidcompartments InteractiveLecture/ SmallGroup Discussion HOMEOSTASIS AND CONTROL SYSTEM OFBODY Recognizethe role of physiochemicalaspectsforthemaintenanceof homeostasis InteractiveLecture/ SmallGroup Discussion FUNCTIONAL IMPORTANCE OF CELLMEMBRANE Explain composition and basic structure of cell membrane its functional importance and adaptation InteractiveLecture/ SmallGroup Discussion CELLORGANELLES Describethestructureandfunctions of variouscellorganelles InteractiveLecture/ SmallGroup Discussion TRANSPORT ACROSS CELL MEMBRANE (ACTIVE &PASSIVE) Describe membrane transport mechanism types andeffects InteractiveLecture/ SmallGroup Discussion BULK TRANSPORT, ENDOCYTOSIS, EXOCYTOSIS,TRANSCYTOSIS Describe different types oftransport mechanism through cell membrane Describe diffusion and its physicalbasis InteractiveLecture/ SmallGroup Discussion CELL SIGNALLINGMECHANISM Discussthe chemistryof signals,receptorsandimportance of lipid andproteins in membranes. Cell growth andrepair InteractiveLecture/ SmallGroup Discussion PRACTICAL Effects of osmotic variations in ECF oncell Practical RESEARCH & SKILLSLAB OBJECTIVES STRATEGY HANDWASHING Identify the indications ofhand washing Demonstratetheprotocols andstepsof handwashing in sequentialmanner SmallGroup Discussion Page | 15
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE LEARNINGRESOURCES SUBJECT RESOURCES A. GROSSANATOMY 1. K.L. Moore, Clinically OrientedAnatomy 2. Neuro Anatomy by RichardSnell B. HISTOLOGY 1. B. Young J. W. Health Wheather s FunctionalHistology C. EMBRYOLOGY 1. Keith L. Moore. The DevelopingHuman 2. Langman s Medical Embryology ANATOMY A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Harper s IllustratedBiochemistry 2. Lehninger Principle ofBiochemistry 3. Biochemistry byDevlin BIOCHEMISTRY A. TEXTBOOKS 1. Textbook Of Medical Physiology by Guyton AndHall 2. Ganong S Review of MedicalPhysiology 3. Human Physiology by LauraleeSherwood 4. Berne & LevyPhysiology 5. Best & Taylor Physiological Basis of MedicalPractice B. REFERENCEBOOKS 1. Guyton & Hall PhysiologicalReview 2. Essentials Of Medical Physiology byJaypee 3. Textbook Of Medical Physiology byInduKhurana 4. Short Textbook Of Physiology byMrthur 5. NMSPhysiology PHYSIOLOGY Page | 16
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE OTHER LEARNINGRESOURCES Hands-on Activities/PracticalStudents will be involved in Practical sessions and hands-on activitiesthat link with the foundation moduleto enhancethelearning. Utilize thelabto relatethe knowledge to thespecimensandmodels Labs available. A skills lab provides the simulators tolearn the basic skills and SkillLabs procedures. This helps build the confidence to approach thepatients. Video familiarize the student with the proceduresandprotocols to assist Videos patients. To increase the knowledge students should utilize the available internet resources and CDs/DVDs. This will be an additional advantage to increase Computer Lab/CDs/DVDs/Internet learning. Resources: Self Learning is scheduled to search for information to solve cases,read through different resources and discuss among the peers and with the SelfLearning faculty to clarify theconcepts. Page | 17
1ST YEAR MBBS, SEMESTER 1 FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE ASSESSMENTMETHODS: Theory (knowledge): Best Choice Questions (BCQs) also known as MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions) are used to asses objectives covered in eachmodule. BCQs: A BCQ has a statement or clinical scenario followed by four options (likelyanswers). After reading the statement/scenario student select ONE, the most appropriate answer/response from the given list ofoptions. Correct answer carries one mark, and incorrect zero mark . There is NO negative marking. Studentsmarktheirresponsesonspecifiedcomputer-basedsheetdesignedfor AVMC SampleBCQs: o A25yearoldpatientpresentedwith thecomplainofproductivecough,breathlessnessandwheezing. He has been diagnosed withchronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Themostcommonriskfactorforthedisease is: a) Airpollution b) Coalmining c) Infection d) Tobaccosmoke OSPE: Objective Structured Practical Examination (See the proposed plan ofOSPE) It may comprise between 12-25stations. The content may assess application of knowledge, orpractical skills. Studentwill completetaskin define timeat onegivenstation. All the studentsare assessedonthesamecontentbythesameexaminer in thesameallocated time. A structured examination will have observed, unobserved, interactive and reststations. Observed and interactivestations: Theywill beassessedbyinternal orexternalexaminersthroughthetaskorviva. Unobservedstation: It will be static station in which students will have to answer the questions related to the given pictures, models or specimens on the provided responsesheet. Rest station: It is astationwhere notaskisgiven,andduring thistimestudentcanorganizehis/her thoughts. Page | 18
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE A VICENNA MEDICA L COLLEGE Page | 19
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE InternalEvaluation Students will beassessedto determine achievement of moduleobjectivesthroughthe following: Module Examination: will be scheduled on completion of each module. The method of o examination comprises theory exam which includes BCQs and OSPE (Objective Structured PracticalExamination). Graded Assessmentof studentsbyIndividual Department: Quiz, viva, practical, assignment, o small group activities such asCBL,TBL,TOL,online assessment, ward activities, examination, andlogbook. Marksof both modular examination andgradedassessmentwill constitute20%weightage. As per UHS policy, this 20% will be added by UHS to SemesterExamination. Example : Number of Marks allocated for Semester Theory and Internal Evaluation InternalEvaluation (Class tests + Journals + Assignments + Modular Exam) 20% Semester Examination TheoryMarks Total(Theory) Semester 100% 80% FormativeAssessment Individual department may hold quiz or short answer questions to help students assess their own learning. The marks obtained are not included in the internalevaluation More than 75% attendance is needed to sit for the modularand semesterexaminations Page | 20
1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE UHSGradingSystem It will be based on GPA 4system Marks obtained in Percentagerange NumericalGrade AlphabeticalGrade 80-100 75-79 70-74 67-69 63-66 60-62 56-59 50-55 4.0 4.0 3.7 3.3 3.0 2.7 2.3 2.0 0 A+ A A- B+ B B- C+ C U <50 Un-grade-able Page | 21
1 1ST YEAR MBBS, FOUNDATIONMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE MODULAR EXAMINATION RULES & REGULATION ) AVMC Studentmustreportto examinationhall/venue, 30 minutesbeforetheexam. Exam will begin sharp at the giventime. No student will be allowed to enter the examination hall after 15 minutes of scheduled examinationtime. Studentsmustsitaccordingto theirroll numbersmentioned ontheseats. Cell phones are strictly not allowed in examinationhall. If anystudentisfoundwith cell phonein anymode(silent, switchedoff oron)he/shewill benot be allowed to continue theirexam. No students will be allowed to sit in exam without University Admit Card, LNMC College ID Card and LabCoat Student must bring the following stationary items for the exam: Pen, Pencil, Eraser, and Sharpener. Indiscipline in the exam hall/venue is not acceptable. Students must not possess any written materialorcommunicatewith theirfellowstudents. Page | 22
 undefined
undefined