Origin and History of Life in AP Biology
Explore the fascinating journey of life from the Big Bang theory to the formation of monomers, polymers, protocells, and self-replicating systems. Delve into the Miller-Urey Experiment, RNA World Hypothesis, LUCA, and the impact of extinctions on the evolution of species.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 18: Origin and History of Life Mr. Freidhoff AP Biology
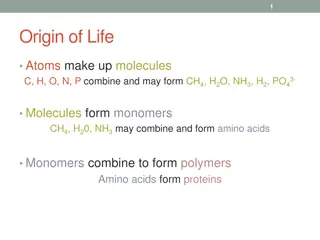
18.1: Life History Big Bang Theory: All matter existed in a small area until there was a massive expansion of space and time. Atoms started to condense and form, then molecules. Universe is 13.8 BYO
18.1: Life History Miller-Urey Experiment (1953) Mixture of methane, ammonia, hydrogen, and water were placed in closed system. Atmosphere of early Earth Mixture was heated and an electrical current was placed through it. Mimicked temperature and lighting strikes. After a week, a variety of amino acids and other organic aids were produced. Experiment was reproduced and all 20 amino acids were found.
Stages of Life Stage 1: Monomers Stage 2: Polymers Stage 3: Protocells Stage 4: Self-Replicating System
18.1: Life History Monomers: Mixture of inorganic molecules and reactions created monomer molecules. Polymers: Monomers connect and assemble into larger structures.
18.1: Life History Protocells: Fluid-filled vesicles with a membrane-like structure. Lipids form spheres naturally in water. Self-Replication System: RNA provided the template for DNA. DNA more stable, more resistant to mutations.
18.1: Life History RNA world hypothesis All life uses RNA, suggests that RNA was first polymer. RNA can be an enzyme or a heritable factor.
18.1: Life History LUCA: Last Universal Common Ancestor Must share all of the characteristics of life.
18.2: Extinctions Extinction: When a species completely dies off due to environmental factors.
18.2: Extinctions Mass extinction: Widespread and rapid decrease of biodiversity on Earth. 5 major mass extinctions, humans are causing next great mass extinction.